#include <Task.h>
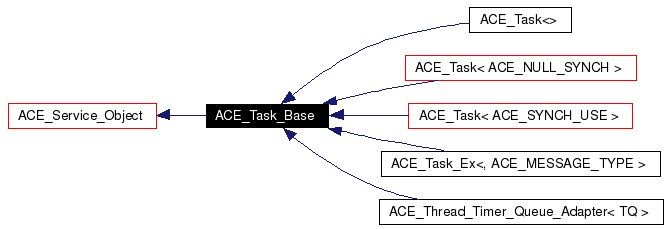
Inheritance diagram for ACE_Task_Base:

Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_Task_Base (ACE_Thread_Manager *=0) | |
| Constructor. | |
| virtual | ~ACE_Task_Base (void) |
| Destructor. | |
| virtual int | open (void *args=0) |
| virtual int | close (u_long flags=0) |
| virtual int | module_closed (void) |
| virtual int | put (ACE_Message_Block *, ACE_Time_Value *=0) |
| virtual int | svc (void) |
| Run by a daemon thread to handle deferred processing. | |
| virtual int | activate (long flags=THR_NEW_LWP|THR_JOINABLE|THR_INHERIT_SCHED, int n_threads=1, int force_active=0, long priority=ACE_DEFAULT_THREAD_PRIORITY, int grp_id=-1, ACE_Task_Base *task=0, ACE_hthread_t thread_handles[]=0, void *stack[]=0, size_t stack_size[]=0, ACE_thread_t thread_ids[]=0) |
| virtual int | wait (void) |
| virtual int | suspend (void) |
| Suspend a task. | |
| virtual int | resume (void) |
| Resume a suspended task. | |
| int | grp_id (void) const |
| Get the current group id. | |
| void | grp_id (int) |
| Set the current group id. | |
| ACE_Thread_Manager * | thr_mgr (void) const |
| Get the thread manager associated with this Task. | |
| void | thr_mgr (ACE_Thread_Manager *) |
| Set the thread manager associated with this Task. | |
| int | is_reader (void) const |
| True if queue is a reader, else false. | |
| int | is_writer (void) const |
| True if queue is a writer, else false. | |
| size_t | thr_count (void) const |
| ACE_thread_t | last_thread (void) const |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_THR_FUNC_RETURN | svc_run (void *) |
| Routine that runs the service routine as a daemon thread. | |
| void | cleanup (void *object, void *params) |
Protected Attributes | |
| size_t | thr_count_ |
| ACE_Thread_Manager * | thr_mgr_ |
| Multi-threading manager. | |
| u_long | flags_ |
| ACE_Task flags. | |
| int | grp_id_ |
| This maintains the group id of the Task. | |
| ACE_thread_t | last_thread_id_ |
| Holds the thread ID of the last thread to exit svc() in this object. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| ACE_Task_Base & | operator= (const ACE_Task_Base &) |
| ACE_Task_Base (const ACE_Task_Base &) | |
This class factors out the non-template code in order to reduce template bloat, as well as to make it possible for the ACE_Thread_Manager to store ACE_Task_Base *'s polymorphically.
Definition at line 66 of file Task.h.
|
|
Constructor.
Definition at line 17 of file Task.cpp. References ACE_OS::memset().
00018 : thr_count_ (0), 00019 thr_mgr_ (thr_man), 00020 flags_ (0), 00021 grp_id_ (-1) 00022 #if !defined (ACE_MVS) 00023 ,last_thread_id_ (0) 00024 #endif /* !defined (ACE_MVS) */ 00025 { 00026 #if defined (ACE_MVS) 00027 ACE_OS::memset( &this->last_thread_id_, '\0', sizeof( this->last_thread_id_ )); 00028 #endif /* defined (ACE_MVS) */ 00029 } |
|
|
Destructor.
Definition at line 31 of file Task.cpp.
00032 {
00033 }
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Turn the task into an active object, i.e., having of control, all running at the level (see below) with the same , all of which invoke <Task::svc>. Returns -1 if failure occurs, returns 1 if Task is already an active object and is false (i.e., do *not* create a new thread in this case), and returns 0 if Task was not already an active object and a thread is created successfully or thread is an active object and is true. Note that if is true and there are already threads spawned in this , the parameter is ignored and the of any newly activated thread(s) will inherit the existing of the existing thread(s) in the . The <{flags}> are a bitwise-OR of the following: = BEGIN<INDENT> THR_CANCEL_DISABLE, THR_CANCEL_ENABLE, THR_CANCEL_DEFERRED, THR_CANCEL_ASYNCHRONOUS, THR_BOUND, THR_NEW_LWP, THR_DETACHED, THR_SUSPENDED, THR_DAEMON, THR_JOINABLE, THR_SCHED_FIFO, THR_SCHED_RR, THR_SCHED_DEFAULT, THR_EXPLICIT_SCHED, THR_SCOPE_SYSTEM, THR_SCOPE_PROCESS = END<INDENT> If THR_SCHED_INHERIT is not desirable, applications should specifically pass in THR_EXPLICIT_SCHED. By default, or if <{priority}> is set to ACE_DEFAULT_THREAD_PRIORITY, an "appropriate" priority value for the given scheduling policy (specified in <{flags}>, e.g., ) is used. This value is calculated dynamically, and is the median value between the minimum and maximum priority values for the given policy. If an explicit value is given, it is used. Note that actual priority values are EXTREMEMLY implementation-dependent, and are probably best avoided.
If != 0 it is assumed to be an array of n thread_handles that will be assigned the values of the thread handles being spawned. Returns -1 on failure (
Assigning allows you to associate the newly spawned threads with an instance of ACE_Task_Base. If == 0, then the new threads are associated automatically with If != 0 it is assumed to be an array of n pointers to the base of the stacks to use for the threads being spawned. Likewise, if != 0 it is assumed to be an array of n values indicating how big each of the corresponding s are. Reimplemented in ACE_Thread_Timer_Queue_Adapter< TQ >. Definition at line 120 of file Task.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_hthread_t, ACE_NOTSUP_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, grp_id_, ACE_Thread_Manager::instance(), last_thread_id_, ACE_OS::memcpy(), ACE_Thread_Manager::spawn_n(), svc_run(), and thr_count_. Referenced by ACE_Thread_Timer_Queue_Adapter< TQ >::activate(), and ACE_Asynch_Pseudo_Task::start().
00130 {
00131 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::activate");
00132
00133 #if defined (ACE_MT_SAFE) && (ACE_MT_SAFE != 0)
00134 ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, this->lock_, -1);
00135
00136 // If the task passed in is zero, we will use <this>
00137 if (task == 0)
00138 task = this;
00139
00140 if (this->thr_count_ > 0 && force_active == 0)
00141 return 1; // Already active.
00142 else
00143 {
00144 if (this->thr_count_ > 0 && this->grp_id_ != -1)
00145 // If we're joining an existing group of threads then make
00146 // sure to use its group id.
00147 grp_id = this->grp_id_;
00148 this->thr_count_ += n_threads;
00149 }
00150
00151 // Use the ACE_Thread_Manager singleton if we're running as an
00152 // active object and the caller didn't supply us with a
00153 // Thread_Manager.
00154 if (this->thr_mgr_ == 0)
00155 # if defined (ACE_THREAD_MANAGER_LACKS_STATICS)
00156 this->thr_mgr_ = ACE_THREAD_MANAGER_SINGLETON::instance ();
00157 # else /* ! ACE_THREAD_MANAGER_LACKS_STATICS */
00158 this->thr_mgr_ = ACE_Thread_Manager::instance ();
00159 # endif /* ACE_THREAD_MANAGER_LACKS_STATICS */
00160
00161 int grp_spawned = -1;
00162 if (thread_ids == 0)
00163 // Thread Ids were not specified
00164 grp_spawned =
00165 this->thr_mgr_->spawn_n (n_threads,
00166 &ACE_Task_Base::svc_run,
00167 (void *) this,
00168 flags,
00169 priority,
00170 grp_id,
00171 task,
00172 thread_handles,
00173 stack,
00174 stack_size);
00175 else
00176 // thread names were specified
00177 grp_spawned =
00178 this->thr_mgr_->spawn_n (thread_ids,
00179 n_threads,
00180 &ACE_Task_Base::svc_run,
00181 (void *) this,
00182 flags,
00183 priority,
00184 grp_id,
00185 stack,
00186 stack_size,
00187 thread_handles,
00188 task);
00189 if (grp_spawned == -1)
00190 {
00191 // If spawn_n fails, restore original thread count.
00192 this->thr_count_ -= n_threads;
00193 return -1;
00194 }
00195
00196 if (this->grp_id_ == -1)
00197 this->grp_id_ = grp_spawned;
00198
00199 #if defined (ACE_MVS)
00200 ACE_OS::memcpy( &this->last_thread_id_, '\0', sizeof(this->last_thread_id_));
00201 #else
00202 this->last_thread_id_ = 0; // Reset to prevent inadvertant match on ID
00203 #endif /* defined (ACE_MVS) */
00204
00205 return 0;
00206
00207 #else
00208 {
00209 // Keep the compiler from complaining.
00210 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (flags);
00211 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (n_threads);
00212 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (force_active);
00213 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (priority);
00214 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (grp_id);
00215 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (task);
00216 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (thread_handles);
00217 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (stack);
00218 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (stack_size);
00219 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (thread_ids);
00220 ACE_NOTSUP_RETURN (-1);
00221 }
00222 #endif /* ACE_MT_SAFE */
00223 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Cleanup hook that is called when a thread exits to gracefully shutdown an ACE_Task. Definition at line 226 of file Task.cpp. References ACE_GUARD, close(), last_thread_id_, ACE_Thread::self(), and thr_count_. Referenced by ACE_OS_Thread_Adapter::invoke(), ACE_Thread_Adapter::invoke_i(), and svc_run().
00227 {
00228 ACE_Task_Base *t = (ACE_Task_Base *) object;
00229
00230 // The thread count must be decremented first in case the <close>
00231 // hook does something crazy like "delete this".
00232 {
00233 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD (ACE_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, t->lock_));
00234 t->thr_count_--;
00235 if (0 == t->thr_count_)
00236 t->last_thread_id_ = ACE_Thread::self ();
00237 }
00238
00239 // @@ Is it possible to pass in the exit status somehow?
00240 t->close ();
00241 // t is undefined here. close() could have deleted it.
00242 }
|
|
|
Hook called from ACE_Thread_Exit when during thread exit and from the default implementation of . In general, this method shouldn't be called directly by an application, particularly if the is running as an Active Object. Instead, a special message should be passed into the via the method defined below, and the method should interpret this as a flag to shut down the . Reimplemented in ACE_Stream_Head<>, ACE_Stream_Tail<>, ACE_Thru_Task<>, ACE_Svc_Handler<, >, and ACE_Svc_Handler< ACE_PEER_STREAM_2, ACE_SYNCH_USE >. Definition at line 56 of file Task.cpp. References ACE_TRACE. Referenced by cleanup(), and module_closed().
00057 {
00058 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::close");
00059 return 0;
00060 }
|
|
|
Set the current group id.
Definition at line 19 of file Task.inl. References ACE_GUARD, ACE_TRACE, grp_id_, ACE_Thread_Manager::set_grp(), and thr_mgr().
00020 {
00021 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::grp_id");
00022 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD (ACE_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, this->lock_));
00023
00024 // Cache the group id in the task and then set it in the
00025 // Thread_Manager, if there is one.
00026 this->grp_id_ = identifier;
00027 if (this->thr_mgr ())
00028 this->thr_mgr ()->set_grp (this, identifier);
00029 }
|
|
|
Get the current group id.
Definition at line 9 of file Task.inl. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, and grp_id_.
|
|
|
True if queue is a reader, else false.
Definition at line 46 of file Task.inl. References ACE_BIT_ENABLED, and ACE_TRACE.
00047 {
00048 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::is_reader");
00049 return (ACE_BIT_ENABLED (this->flags_, ACE_Task_Flags::ACE_READER));
00050 }
|
|
|
True if queue is a writer, else false.
Definition at line 53 of file Task.inl. References ACE_BIT_DISABLED, and ACE_TRACE. Referenced by ACE_Stream_Tail<>::put(), and ACE_Stream_Head<>::put().
00054 {
00055 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::is_writer");
00056 return (ACE_BIT_DISABLED (this->flags_, ACE_Task_Flags::ACE_READER));
00057 }
|
|
|
Returns the thread ID of the thread whose exit caused this object's thread count to be decremented to 0. When a thread spawned in the context of this object (using activate()) returns from its svc() method ACE calls the close() hook. Before it does so, it decrements the number of active threads. If the number of threads is decremented to 0, the thread ID of the current thread is stored for access by this method. If the returned thread ID matches the calling thread's ID, the calling thread knows that there are no other threads still active in the ACE_Task.
Definition at line 71 of file Task.inl. References ACE_TRACE, and last_thread_id_.
00072 {
00073 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::last_thread");
00074 return this->last_thread_id_;
00075 }
|
|
|
Hook called during <ACE_Module::close>. The default implementation calls forwards the call to close(1). Please notice the changed value of the default argument of . This allows tasks to differ between the call has been originated from or from . Be aware that close(0) will be also called when a thread associated with the ACE_Task instance exits. Definition at line 66 of file Task.cpp. References close().
00067 {
00068 return this->close (1);
00069 }
|
|
|
Hook called to initialize a task and prepare it for execution. args can be used to pass arbitrary information into . Reimplemented in ACE_Stream_Head<>, ACE_Stream_Tail<>, ACE_Thru_Task<>, ACE_Svc_Handler<, >, and ACE_Svc_Handler< ACE_PEER_STREAM_2, ACE_SYNCH_USE >. Definition at line 47 of file Task.cpp. References ACE_TRACE. Referenced by ACE_Stream<>::insert(), ACE_Stream<>::push_module(), and ACE_Stream<>::replace().
00048 {
00049 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::open");
00050 return 0;
00051 }
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
A hook method that can be used to pass a message to a task, where it can be processed immediately or queued for subsequent processing in the hook method. Reimplemented in ACE_Stream_Head<>, ACE_Stream_Tail<>, ACE_Thru_Task<>, and ACE_Buffered_Svc_Handler<, >. Definition at line 74 of file Task.cpp. References ACE_TRACE. Referenced by ACE_Task< ACE_SYNCH_USE >::put_next().
00075 {
00076 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::put");
00077 return 0;
00078 }
|
|
|
Resume a suspended task.
Reimplemented from ACE_Service_Object. Definition at line 109 of file Task.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Thread_Manager::resume_task(), and thr_count_. Referenced by ACE_Module_Type::resume().
00110 {
00111 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::resume");
00112 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, this->lock_, -1));
00113 if (this->thr_count_ > 0)
00114 return this->thr_mgr_->resume_task (this);
00115
00116 return 0;
00117 }
|
|
|
Suspend a task.
Reimplemented from ACE_Service_Object. Definition at line 97 of file Task.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Thread_Manager::suspend_task(), and thr_count_. Referenced by ACE_Module_Type::suspend().
00098 {
00099 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::suspend");
00100 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, this->lock_, -1));
00101 if (this->thr_count_ > 0)
00102 return this->thr_mgr_->suspend_task (this);
00103
00104 return 0;
00105 }
|
|
|
Run by a daemon thread to handle deferred processing.
Reimplemented in ACE_Asynch_Pseudo_Task, ACE_Proactor_Timer_Handler, ACE_Stream_Head<>, ACE_Stream_Tail<>, ACE_Thru_Task<>, and ACE_Thread_Timer_Queue_Adapter< TQ >. Definition at line 38 of file Task.cpp. References ACE_TRACE. Referenced by svc_run().
00039 {
00040 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::svc");
00041 return 0;
00042 }
|
|
|
Routine that runs the service routine as a daemon thread.
Definition at line 254 of file Task.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, ACE_Thread_Manager::at_exit(), cleanup(), svc(), and thr_mgr(). Referenced by activate().
00255 {
00256 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::svc_run");
00257
00258 ACE_Task_Base *t = (ACE_Task_Base *) args;
00259
00260 // Register ourself with our <Thread_Manager>'s thread exit hook
00261 // mechanism so that our close() hook will be sure to get invoked
00262 // when this thread exits.
00263
00264 #if defined ACE_HAS_SIG_C_FUNC
00265 t->thr_mgr ()->at_exit (t, ACE_Task_Base_cleanup, 0);
00266 #else
00267 t->thr_mgr ()->at_exit (t, ACE_Task_Base::cleanup, 0);
00268 #endif /* ACE_HAS_SIG_C_FUNC */
00269
00270 // Call the Task's svc() hook method.
00271 int svc_status = t->svc ();
00272 ACE_THR_FUNC_RETURN status;
00273 #if (defined (__BORLANDC__) && (__BORLANDC__ < 0x600)) || defined (__MINGW32__) || (defined (_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER <= 1500)) || (defined (ACE_WIN32) && defined (__DCC__))
00274 // Some compilers complain about reinterpret_cast from int to unsigned long...
00275 status = static_cast<ACE_THR_FUNC_RETURN> (svc_status);
00276 #else
00277 status = reinterpret_cast<ACE_THR_FUNC_RETURN> (svc_status);
00278 #endif /* (__BORLANDC__ < 0x600) || __MINGW32__ || _MSC_VER <= 1400 */
00279
00280 // If we changed this zero change the other if in OS.cpp Thread_Adapter::invoke
00281 #if 1
00282 // Call the <Task->close> hook.
00283 ACE_Thread_Manager *thr_mgr_ptr = t->thr_mgr ();
00284
00285 // This calls the Task->close () hook.
00286 t->cleanup (t, 0);
00287
00288 // This prevents a second invocation of the cleanup code
00289 // (called later by <ACE_Thread_Manager::exit>.
00290 thr_mgr_ptr->at_exit (t, 0, 0);
00291 #endif
00292 return status;
00293 }
|
|
|
Returns the number of threads currently running within a task. If we're a passive object this value is 0, else it's greater than 0. Definition at line 61 of file Task.inl. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, and thr_count_. Referenced by ACE_Asynch_Pseudo_Task::stop().
00062 {
00063 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Base::thr_count");
00064 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, const_cast <ACE_Thread_Mutex&>(this->lock_), 0));
00065
00066 return this->thr_count_;
00067 }
|
|
|
Set the thread manager associated with this Task.
Definition at line 39 of file Task.inl. References ACE_TRACE.
|
|
|
Get the thread manager associated with this Task.
Definition at line 32 of file Task.inl. References ACE_TRACE. Referenced by grp_id(), ACE_OS_Thread_Adapter::invoke(), ACE_Thread_Adapter::invoke_i(), svc_run(), wait(), and ACE_Proactor_Timer_Handler::~ACE_Proactor_Timer_Handler().
|
|
|
Block until there are no more threads running in this task. This method will not wait for either detached or daemon threads; the threads must have been spawned with the
Definition at line 83 of file Task.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, thr_mgr(), and ACE_Thread_Manager::wait_task(). Referenced by ACE_Asynch_Pseudo_Task::stop().
|
|
|
ACE_Task flags.
|
|
|
This maintains the group id of the Task.
Definition at line 278 of file Task.h. Referenced by activate(), and grp_id(). |
|
|
Holds the thread ID of the last thread to exit svc() in this object.
Definition at line 287 of file Task.h. Referenced by activate(), cleanup(), and last_thread(). |
|
|
Count of the number of threads running within the task. If this value is greater than 0 then we're an active object and the value of is the number of active threads at this instant. If the value == 0, then we're a passive object. Definition at line 269 of file Task.h. Referenced by activate(), cleanup(), resume(), suspend(), and thr_count(). |
|
|
Multi-threading manager.
|
 1.3.6
1.3.6