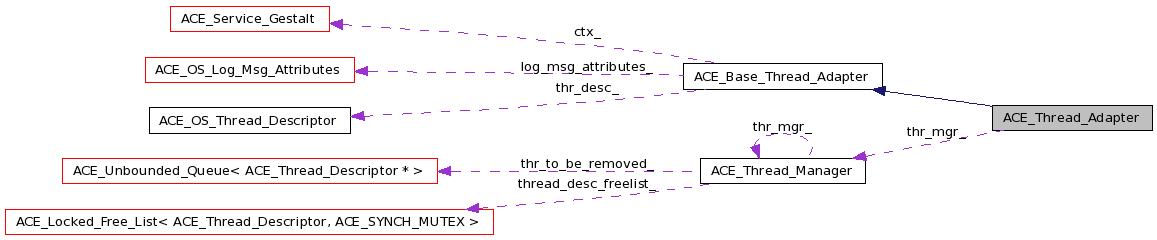
Converts a C++ function into a function that can be called from a thread creation routine (e.g., pthread_create() or _beginthreadex()) that expects an extern "C" entry point. This class also makes it possible to transparently provide hooks to register a thread with an ACE_Thread_Manager. More...
#include <Thread_Adapter.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_Thread_Adapter (ACE_THR_FUNC user_func, void *arg, ACE_THR_C_FUNC entry_point=(ACE_THR_C_FUNC) ACE_THREAD_ADAPTER_NAME, ACE_Thread_Manager *thr_mgr=0, ACE_Thread_Descriptor *td=0) | |
| Constructor. | |
| virtual ACE_THR_FUNC_RETURN | invoke (void) |
| ACE_Thread_Manager * | thr_mgr (void) |
| Accessor for the optional ACE_Thread_Manager. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| ~ACE_Thread_Adapter (void) | |
| Ensure that this object must be allocated on the heap. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| virtual ACE_THR_FUNC_RETURN | invoke_i (void) |
Private Attributes | |
| ACE_Thread_Manager * | thr_mgr_ |
| Optional thread manager. | |
Converts a C++ function into a function that can be called from a thread creation routine (e.g., pthread_create() or _beginthreadex()) that expects an extern "C" entry point. This class also makes it possible to transparently provide hooks to register a thread with an ACE_Thread_Manager.
This class is used in ACE_OS::thr_create(). In general, the thread that creates an object of this class is different from the thread that calls invoke() on this object. Therefore, the invoke() method is responsible for deleting itself.
Definition at line 46 of file Thread_Adapter.h.
| ACE_Thread_Adapter::ACE_Thread_Adapter | ( | ACE_THR_FUNC | user_func, | |
| void * | arg, | |||
| ACE_THR_C_FUNC | entry_point = (ACE_THR_C_FUNC) ACE_THREAD_ADAPTER_NAME, |
|||
| ACE_Thread_Manager * | thr_mgr = 0, |
|||
| ACE_Thread_Descriptor * | td = 0 | |||
| ) |
Constructor.
| ACE_Thread_Adapter::~ACE_Thread_Adapter | ( | void | ) | [protected] |
Ensure that this object must be allocated on the heap.
Definition at line 45 of file Thread_Adapter.cpp.
{
}
| ACE_THR_FUNC_RETURN ACE_Thread_Adapter::invoke | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Execute the <user_func_> with the <arg>. This function deletes this, thereby rendering the object useless after the call returns.
Implements ACE_Base_Thread_Adapter.
Definition at line 50 of file Thread_Adapter.cpp.
{
// Inherit the logging features if the parent thread has an
// ACE_Log_Msg instance in thread-specific storage.
this->inherit_log_msg ();
ACE_Service_Config::current (ACE_Service_Config::global());
#if !defined(ACE_USE_THREAD_MANAGER_ADAPTER)
// NOTE: this preprocessor directive should match the one in above
// ACE_Thread_Exit::instance (). With the Xavier Pthreads package,
// the exit_hook in TSS causes a seg fault. So, this works around
// that by creating exit_hook on the stack.
# if defined (ACE_HAS_THREAD_SPECIFIC_STORAGE) || defined (ACE_HAS_TSS_EMULATION)
// Obtain our thread-specific exit hook and make sure that it knows
// how to clean us up! Note that we never use this pointer directly
// (it's stored in thread-specific storage), so it's ok to
// dereference it here and only store it as a reference.
// Except if it is null, then the thr_mgr() method crashes.
// -jxh
ACE_Thread_Exit *exit_hook_instance = ACE_Thread_Exit::instance ();
ACE_Thread_Exit_Maybe exit_hook_maybe (exit_hook_instance == 0);
ACE_Thread_Exit *exit_hook_ptr = exit_hook_instance
? exit_hook_instance
: exit_hook_maybe.instance ();
ACE_Thread_Exit &exit_hook = *exit_hook_ptr;
if (this->thr_mgr () != 0)
{
// Keep track of the <Thread_Manager> that's associated with this
// <exit_hook>.
exit_hook.thr_mgr (this->thr_mgr ());
}
# else
// Without TSS, create an <ACE_Thread_Exit> instance. When this
// function returns, its destructor will be called because the
// object goes out of scope. The drawback with this appraoch is
// that the destructor _won't_ get called if <thr_exit> is called.
// So, threads shouldn't exit that way. Instead, they should return
// from <svc>.
ACE_Thread_Exit exit_hook;
exit_hook.thr_mgr (this->thr_mgr ());
# endif /* ACE_HAS_THREAD_SPECIFIC_STORAGE || ACE_HAS_TSS_EMULATION */
#endif /* ! ACE_USE_THREAD_MANAGER_ADAPTER */
return this->invoke_i ();
}
| ACE_THR_FUNC_RETURN ACE_Thread_Adapter::invoke_i | ( | void | ) | [private, virtual] |
Called by invoke, mainly here to separate the SEH stuff because SEH on Win32 doesn't compile with local vars with destructors.
Definition at line 102 of file Thread_Adapter.cpp.
{
// Extract the arguments.
ACE_THR_FUNC func = reinterpret_cast<ACE_THR_FUNC> (this->user_func_);
void *arg = this->arg_;
#if defined (ACE_WIN32) && defined (ACE_HAS_MFC) && (ACE_HAS_MFC != 0)
ACE_OS_Thread_Descriptor *thr_desc = this->thr_desc_;
#endif /* ACE_WIN32 && ACE_HAS_MFC && (ACE_HAS_MFC != 0) */
// Delete ourselves since we don't need <this> anymore. Make sure
// not to access <this> anywhere below this point.
delete this;
#if defined (ACE_NEEDS_LWP_PRIO_SET)
// On SunOS, the LWP priority needs to be set in order to get
// preemption when running in the RT class. This is the ACE way to
// do that . . .
ACE_hthread_t thr_handle;
ACE_OS::thr_self (thr_handle);
int prio;
// thr_getprio () on the current thread should never fail.
ACE_OS::thr_getprio (thr_handle, prio);
// ACE_OS::thr_setprio () has the special logic to set the LWP priority,
// if running in the RT class.
ACE_OS::thr_setprio (prio);
#endif /* ACE_NEEDS_LWP_PRIO_SET */
ACE_THR_FUNC_RETURN status = 0;
ACE_SEH_TRY
{
ACE_SEH_TRY
{
ACE_Thread_Hook *hook =
ACE_OS_Object_Manager::thread_hook ();
if (hook)
// Invoke the start hook to give the user a chance to
// perform some initialization processing before the
// <func> is invoked.
status = hook->start (func, arg);
else
// Call thread entry point.
status = (*func) (arg);
}
#if defined (ACE_HAS_WIN32_STRUCTURAL_EXCEPTIONS)
ACE_SEH_EXCEPT (ACE_OS_Object_Manager::seh_except_selector ()(
(void *) GetExceptionInformation ()))
{
ACE_OS_Object_Manager::seh_except_handler ()(0);
}
#endif /* ACE_HAS_WIN32_STRUCTURAL_EXCEPTIONS */
}
ACE_SEH_FINALLY
{
// If we changed this to 1, change the respective if in
// Task::svc_run to 0.
#if 0
// Call the <Task->close> hook.
if (func == reinterpret_cast<ACE_THR_FUNC_INTERNAL> (
ACE_Task_Base::svc_run))
{
ACE_Task_Base *task_ptr = (ACE_Task_Base *) arg;
ACE_Thread_Manager *thr_mgr_ptr = task_ptr->thr_mgr ();
// This calls the Task->close () hook.
task_ptr->cleanup (task_ptr, 0);
// This prevents a second invocation of the cleanup code
// (called later by <ACE_Thread_Manager::exit>.
thr_mgr_ptr->at_exit (task_ptr, 0, 0);
}
#endif /* 0 */
#if defined (ACE_WIN32) || defined (ACE_HAS_TSS_EMULATION)
# if defined (ACE_WIN32) && defined (ACE_HAS_MFC) && (ACE_HAS_MFC != 0)
int using_afx = -1;
if (thr_desc)
using_afx = ACE_BIT_ENABLED (thr_desc->flags (), THR_USE_AFX);
# endif /* ACE_WIN32 && ACE_HAS_MFC && (ACE_HAS_MFC != 0) */
// Call TSS destructors.
ACE_OS::cleanup_tss (0 /* not main thread */);
# if defined (ACE_WIN32)
// Exit the thread. Allow CWinThread-destructor to be invoked
// from AfxEndThread. _endthreadex will be called from
// AfxEndThread so don't exit the thread now if we are running
// an MFC thread.
# if defined (ACE_HAS_MFC) && (ACE_HAS_MFC != 0)
if (using_afx != -1)
{
if (using_afx)
::AfxEndThread ((DWORD) status);
else
ACE_ENDTHREADEX (status);
}
else
{
// Not spawned by ACE_Thread_Manager, use the old buggy
// version. You should seriously consider using
// ACE_Thread_Manager to spawn threads. The following code
// is know to cause some problem.
CWinThread *pThread = ::AfxGetThread ();
if (!pThread || pThread->m_nThreadID != ACE_OS::thr_self ())
ACE_ENDTHREADEX (status);
else
::AfxEndThread ((DWORD)status);
}
# else
ACE_ENDTHREADEX (status);
# endif /* ACE_HAS_MFC && ACE_HAS_MFS != 0*/
# endif /* ACE_WIN32 */
#endif /* ACE_WIN32 || ACE_HAS_TSS_EMULATION */
}
return status;
}
| ACE_Thread_Manager * ACE_Thread_Adapter::thr_mgr | ( | void | ) |
Accessor for the optional ACE_Thread_Manager.
Definition at line 8 of file Thread_Adapter.inl.
{
return this->thr_mgr_;
}
ACE_Thread_Manager* ACE_Thread_Adapter::thr_mgr_ [private] |
Optional thread manager.
Definition at line 85 of file Thread_Adapter.h.
 1.7.0
1.7.0