Information for controlling threads that run under the control of the <Thread_Manager>. More...
#include <Thread_Manager.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_Thread_Descriptor (void) | |
| ACE_thread_t | self (void) const |
| Unique thread id. | |
| void | self (ACE_hthread_t &) |
| Unique handle to thread (used by Win32 and AIX). | |
| void | dump (void) const |
| Dump the state of an object. | |
| void | log_msg_cleanup (ACE_Log_Msg *log_msg) |
| int | at_exit (ACE_At_Thread_Exit *cleanup) |
| int | at_exit (ACE_At_Thread_Exit &cleanup) |
| int | at_exit (void *object, ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC cleanup_hook, void *param) |
| ~ACE_Thread_Descriptor (void) | |
| Do nothing destructor to keep some compilers happy. | |
| void | acquire_release (void) |
| void | acquire (void) |
| void | release (void) |
| void | set_next (ACE_Thread_Descriptor *td) |
| ACE_Thread_Descriptor * | get_next (void) const |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | reset (ACE_Thread_Manager *tm) |
| Reset this thread descriptor. | |
| void | at_pop (int apply=1) |
| void | at_push (ACE_At_Thread_Exit *cleanup, bool is_owner=false) |
| void | do_at_exit (void) |
| Run the AT_Thread_Exit hooks. | |
| void | terminate (void) |
| Terminate realize the cleanup process to thread termination. | |
Private Attributes | |
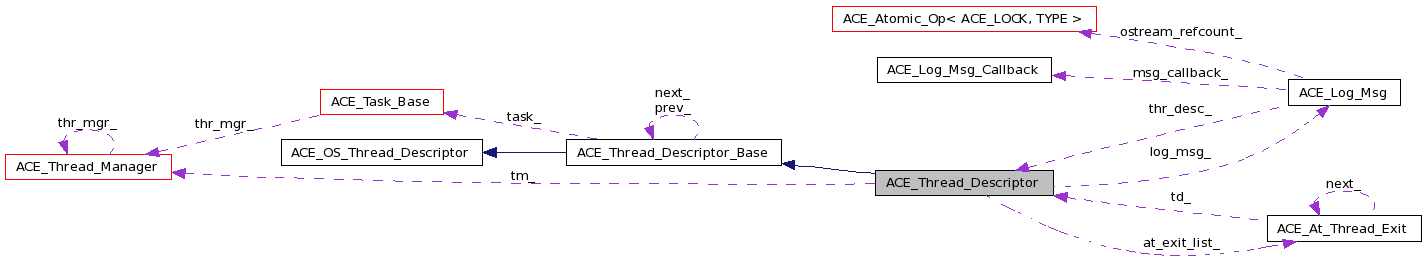
| ACE_Log_Msg * | log_msg_ |
| ACE_At_Thread_Exit * | at_exit_list_ |
| The AT_Thread_Exit list. | |
| ACE_Thread_Manager * | tm_ |
| ACE_DEFAULT_THREAD_MANAGER_LOCK * | sync_ |
| Registration lock to prevent premature removal of thread descriptor. | |
| bool | terminated_ |
| Keep track of termination status. | |
Friends | |
| class | ACE_At_Thread_Exit |
| class | ACE_Thread_Manager |
| class | ACE_Double_Linked_List< ACE_Thread_Descriptor > |
| class | ACE_Double_Linked_List_Iterator< ACE_Thread_Descriptor > |
Information for controlling threads that run under the control of the <Thread_Manager>.
Definition at line 229 of file Thread_Manager.h.
| ACE_Thread_Descriptor::ACE_Thread_Descriptor | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 261 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
: log_msg_ (0), at_exit_list_ (0), terminated_ (false) { ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Thread_Descriptor::ACE_Thread_Descriptor"); ACE_NEW (this->sync_, ACE_DEFAULT_THREAD_MANAGER_LOCK); }
| ACE_Thread_Descriptor::~ACE_Thread_Descriptor | ( | void | ) |
Do nothing destructor to keep some compilers happy.
Definition at line 89 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
{
delete this->sync_;
}
| void ACE_Thread_Descriptor::acquire | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 293 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
{
// Just try to acquire the lock then release it.
#if defined (ACE_THREAD_MANAGER_USES_SAFE_SPAWN)
if (ACE_BIT_DISABLED (this->thr_state_, ACE_Thread_Manager::ACE_THR_SPAWNED))
#endif /* ACE_THREAD_MANAGER_USES_SAFE_SPAWN */
{
this->sync_->acquire ();
}
}
| void ACE_Thread_Descriptor::acquire_release | ( | void | ) |
Do nothing but to acquire the thread descriptor's lock and release. This will first check if the thread is registered or not. If it is already registered, there's no need to reacquire the lock again. This is used mainly to get newly spawned thread in synch with thread manager and prevent it from accessing its thread descriptor before it gets fully built. This function is only called from ACE_Log_Msg::thr_desc.
Definition at line 272 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
{
// Just try to acquire the lock then release it.
#if defined (ACE_THREAD_MANAGER_USES_SAFE_SPAWN)
if (ACE_BIT_DISABLED (this->thr_state_, ACE_Thread_Manager::ACE_THR_SPAWNED))
#endif /* ACE_THREAD_MANAGER_USES_SAFE_SPAWN */
{
this->sync_->acquire ();
// Acquire the lock before removing <td> from the thread table. If
// this thread is in the table already, it should simply acquire the
// lock easily.
// Once we get the lock, we must have registered.
ACE_ASSERT (ACE_BIT_ENABLED (this->thr_state_, ACE_Thread_Manager::ACE_THR_SPAWNED));
this->sync_->release ();
// Release the lock before putting it back to freelist.
}
}
| int ACE_Thread_Descriptor::at_exit | ( | ACE_At_Thread_Exit * | cleanup | ) |
Register an At_Thread_Exit hook and the ownership is acquire by Thread_Descriptor, this is the usual case when the AT is dynamically allocated.
Definition at line 135 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
| int ACE_Thread_Descriptor::at_exit | ( | ACE_At_Thread_Exit & | cleanup | ) |
Register an At_Thread_Exit hook and the ownership is retained for the caller. Normally used when the at_exit hook is created in stack.
Definition at line 127 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
| int ACE_Thread_Descriptor::at_exit | ( | void * | object, | |
| ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC | cleanup_hook, | |||
| void * | param | |||
| ) |
Register an object (or array) for cleanup at thread termination. "cleanup_hook" points to a (global, or static member) function that is called for the object or array when it to be destroyed. It may perform any necessary cleanup specific for that object or its class. "param" is passed as the second parameter to the "cleanup_hook" function; the first parameter is the object (or array) to be destroyed. Returns 0 on success, non-zero on failure: -1 if virtual memory is exhausted or 1 if the object (or arrayt) had already been registered.
Definition at line 219 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Thread_Descriptor::at_exit");
// To keep compatibility, when cleanup_hook is null really is a at_pop
// without apply.
if (cleanup_hook == 0)
{
if (this->at_exit_list_!= 0)
this->at_pop(0);
}
else
{
ACE_At_Thread_Exit* cleanup = 0;
ACE_NEW_RETURN (cleanup,
ACE_At_Thread_Exit_Func (object,
cleanup_hook,
param),
-1);
this->at_push (cleanup);
}
return 0;
}
| void ACE_Thread_Descriptor::at_pop | ( | int | apply = 1 |
) | [private] |
Pop an At_Thread_Exit from at thread termination list, apply the at if apply is true.
Definition at line 95 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Thread_Descriptor::at_pop");
// Get first at from at_exit_list
ACE_At_Thread_Exit* at = this->at_exit_list_;
// Remove at from at_exit list
this->at_exit_list_ = at->next_;
// Apply if required
if (apply)
{
at->apply ();
// Do the apply method
at->was_applied (true);
// Mark at has been applied to avoid double apply from
// at destructor
}
// If at is not owner delete at.
if (!at->is_owner ())
delete at;
}
| void ACE_Thread_Descriptor::at_push | ( | ACE_At_Thread_Exit * | cleanup, | |
| bool | is_owner = false | |||
| ) | [private] |
Push an At_Thread_Exit to at thread termination list and set the ownership of at.
Definition at line 117 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Thread_Descriptor::at_push");
cleanup->is_owner (is_owner);
cleanup->td_ = this;
cleanup->next_ = at_exit_list_;
at_exit_list_ = cleanup;
}
| void ACE_Thread_Descriptor::do_at_exit | ( | void | ) | [private] |
Run the AT_Thread_Exit hooks.
Definition at line 148 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Thread_Descriptor::do_at_exit");
while (at_exit_list_!=0)
this->at_pop ();
}
| void ACE_Thread_Descriptor::dump | ( | void | ) | const |
Dump the state of an object.
Definition at line 245 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
{
#if defined (ACE_HAS_DUMP)
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Thread_Descriptor::dump");
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_BEGIN_DUMP, this));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\nthr_id_ = %d"), this->thr_id_));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\nthr_handle_ = %d"), this->thr_handle_));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\ngrp_id_ = %d"), this->grp_id_));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\nthr_state_ = %d"), this->thr_state_));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\nflags_ = %x\n"), this->flags_));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_END_DUMP));
#endif /* ACE_HAS_DUMP */
}
| ACE_Thread_Descriptor * ACE_Thread_Descriptor::get_next | ( | void | ) | const |
Definition at line 165 of file Thread_Manager.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Thread_Descriptor::get_next");
return static_cast<ACE_Thread_Descriptor * ACE_CAST_CONST> (this->next_);
}
| void ACE_Thread_Descriptor::log_msg_cleanup | ( | ACE_Log_Msg * | log_msg | ) |
This cleanup function must be called only for ACE_TSS_cleanup. The ACE_TSS_cleanup delegate Log_Msg instance destruction when Log_Msg cleanup is called before terminate.
Definition at line 149 of file Thread_Manager.inl.
{
log_msg_ = log_msg;
}
| void ACE_Thread_Descriptor::release | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 305 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
{
// Just try to acquire the lock then release it.
#if defined (ACE_THREAD_MANAGER_USES_SAFE_SPAWN)
if (ACE_BIT_DISABLED (this->thr_state_, ACE_Thread_Manager::ACE_THR_SPAWNED))
#endif /* ACE_THREAD_MANAGER_USES_SAFE_SPAWN */
{
this->sync_->release ();
// Release the lock before putting it back to freelist.
}
}
| void ACE_Thread_Descriptor::reset | ( | ACE_Thread_Manager * | tm | ) | [private] |
Reset this thread descriptor.
Definition at line 173 of file Thread_Manager.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Thread_Descriptor::reset");
this->ACE_Thread_Descriptor_Base::reset ();
this->at_exit_list_ = 0;
// Start the at_exit hook list.
this->tm_ = tm;
// Setup the Thread_Manager.
this->log_msg_ = 0;
this->terminated_ = false;
}
| void ACE_Thread_Descriptor::self | ( | ACE_hthread_t & | handle | ) |
Unique handle to thread (used by Win32 and AIX).
Definition at line 142 of file Thread_Manager.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Thread_Descriptor::self");
handle = this->thr_handle_;
}
| ACE_thread_t ACE_Thread_Descriptor::self | ( | void | ) | const |
Unique thread id.
Definition at line 133 of file Thread_Manager.inl.
| void ACE_Thread_Descriptor::set_next | ( | ACE_Thread_Descriptor * | td | ) |
Set/get the next_ pointer. These are required by the ACE_Free_List.
Definition at line 157 of file Thread_Manager.inl.
| void ACE_Thread_Descriptor::terminate | ( | void | ) | [private] |
Terminate realize the cleanup process to thread termination.
Definition at line 156 of file Thread_Manager.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Thread_Descriptor::terminate");
if (!terminated_)
{
ACE_Log_Msg* log_msg = this->log_msg_;
terminated_ = true;
// Run at_exit hooks
this->do_at_exit ();
// We must remove Thread_Descriptor from Thread_Manager list
if (this->tm_ != 0)
{
int close_handle = 0;
#if !defined (ACE_HAS_VXTHREADS)
// Threads created with THR_DAEMON shouldn't exist here, but
// just to be safe, let's put it here.
if (ACE_BIT_DISABLED (this->thr_state_, ACE_Thread_Manager::ACE_THR_JOINING))
{
if (ACE_BIT_DISABLED (this->flags_, THR_DETACHED | THR_DAEMON)
|| ACE_BIT_ENABLED (this->flags_, THR_JOINABLE))
{
// Mark thread as terminated.
ACE_SET_BITS (this->thr_state_, ACE_Thread_Manager::ACE_THR_TERMINATED);
tm_->register_as_terminated (this);
// Must copy the information here because td will be
// "freed" below.
}
#if defined (ACE_WIN32)
else
{
close_handle = 1;
}
#endif /* ACE_WIN32 */
}
#endif /* !ACE_HAS_VXTHREADS */
// Remove thread descriptor from the table.
if (this->tm_ != 0)
tm_->remove_thr (this, close_handle);
}
// Check if we need delete ACE_Log_Msg instance
// If ACE_TSS_cleanup was not executed first log_msg == 0
if (log_msg == 0)
{
// Only inform to ACE_TSS_cleanup that it must delete the log instance
// setting ACE_LOG_MSG thr_desc to 0.
ACE_LOG_MSG->thr_desc (0);
}
else
{
// Thread_Descriptor is the owner of the Log_Msg instance!!
// deleted.
this->log_msg_ = 0;
delete log_msg;
}
}
}
friend class ACE_At_Thread_Exit [friend] |
Definition at line 231 of file Thread_Manager.h.
friend class ACE_Double_Linked_List< ACE_Thread_Descriptor > [friend] |
Reimplemented from ACE_Thread_Descriptor_Base.
Definition at line 233 of file Thread_Manager.h.
friend class ACE_Double_Linked_List_Iterator< ACE_Thread_Descriptor > [friend] |
Reimplemented from ACE_Thread_Descriptor_Base.
Definition at line 234 of file Thread_Manager.h.
friend class ACE_Thread_Manager [friend] |
Reimplemented from ACE_Thread_Descriptor_Base.
Definition at line 232 of file Thread_Manager.h.
The AT_Thread_Exit list.
Definition at line 329 of file Thread_Manager.h.
ACE_Log_Msg* ACE_Thread_Descriptor::log_msg_ [private] |
Thread_Descriptor is the ownership of ACE_Log_Msg if log_msg_!=0 This can occur because ACE_TSS_cleanup was executed before terminate.
Definition at line 326 of file Thread_Manager.h.
ACE_DEFAULT_THREAD_MANAGER_LOCK* ACE_Thread_Descriptor::sync_ [private] |
Registration lock to prevent premature removal of thread descriptor.
Definition at line 345 of file Thread_Manager.h.
bool ACE_Thread_Descriptor::terminated_ [private] |
Keep track of termination status.
Definition at line 348 of file Thread_Manager.h.
ACE_Thread_Manager* ACE_Thread_Descriptor::tm_ [private] |
Pointer to an ACE_Thread_Manager or NULL if there's no ACE_Thread_Manager>
Definition at line 342 of file Thread_Manager.h.
 1.7.0
1.7.0