#include <MEM_IO.h>
Inheritance diagram for ACE_MT_MEM_IO:

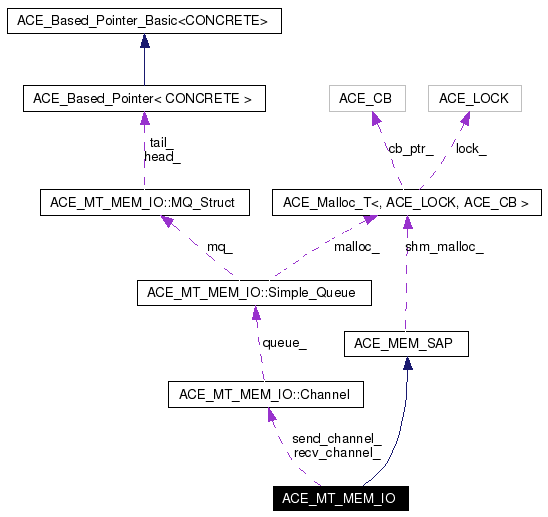
Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_MT_MEM_IO (void) | |
| virtual | ~ACE_MT_MEM_IO (void) |
| virtual int | init (ACE_HANDLE handle, const ACE_TCHAR *name, MALLOC_OPTIONS *options) |
| virtual ssize_t | recv_buf (ACE_MEM_SAP_Node *&buf, int flags, const ACE_Time_Value *timeout) |
| virtual ssize_t | send_buf (ACE_MEM_SAP_Node *buf, int flags, const ACE_Time_Value *timeout) |
Private Attributes | |
| Channel | recv_channel_ |
| Channel | send_channel_ |
|
|
Definition at line 22 of file MEM_IO.inl. References ACE_MT_MEM_IO::Channel::lock_, recv_channel_, ACE_MT_MEM_IO::Channel::sema_, and send_channel_.
00023 {
00024 this->recv_channel_.sema_ = 0;
00025 this->recv_channel_.lock_ = 0;
00026 this->send_channel_.sema_ = 0;
00027 this->send_channel_.lock_ = 0;
00028 }
|
|
|
Definition at line 147 of file MEM_IO.cpp. References ACE_MT_MEM_IO::Channel::lock_, recv_channel_, ACE_MT_MEM_IO::Channel::sema_, and send_channel_.
00148 {
00149 delete this->recv_channel_.sema_;
00150 delete this->recv_channel_.lock_;
00151 delete this->send_channel_.sema_;
00152 delete this->send_channel_.lock_;
00153 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Initialize the MEM_SAP object. Implements ACE_MEM_SAP. Definition at line 156 of file MEM_IO.cpp. References ACE_ALLOCATOR_RETURN, ACE_LIB_TEXT, ACE_NEW_RETURN, ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_MUTEX, ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_SEMAPHORE, ACE_TCHAR, ACE_TRACE, ACE::basename(), ACE_MEM_SAP::create_shm_malloc(), ACE_MT_MEM_IO::MQ_Struct::head_, ACE_MT_MEM_IO::Simple_Queue::init(), MAXPATHLEN, ACE_MT_MEM_IO::Channel::queue_, recv_channel_, send_channel_, ACE_OS::strcat(), ACE_OS::strcpy(), and ACE_MT_MEM_IO::MQ_Struct::tail_.
00159 {
00160 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_MT_MEM_IO::init");
00161 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (handle);
00162
00163 // @@ Give me a rule on naming and how the queue should
00164 // be kept in the shared memory and we are done
00165 // with this.
00166 if (this->create_shm_malloc (name, options) == -1)
00167 return -1;
00168
00169 ACE_TCHAR server_sema [MAXPATHLEN];
00170 ACE_TCHAR client_sema [MAXPATHLEN];
00171 ACE_TCHAR server_lock [MAXPATHLEN];
00172 ACE_TCHAR client_lock [MAXPATHLEN];
00173 const ACE_TCHAR *basename = ACE::basename (name);
00174 // size_t baselen = ACE_OS::strlen (basename);
00175
00176 // Building names. @@ Check buffer overflow?
00177 ACE_OS::strcpy (server_sema, basename);
00178 ACE_OS::strcat (server_sema, ACE_LIB_TEXT ("_sema_to_server"));
00179 ACE_OS::strcpy (client_sema, basename);
00180 ACE_OS::strcat (client_sema, ACE_LIB_TEXT ("_sema_to_client"));
00181 ACE_OS::strcpy (server_lock, basename);
00182 ACE_OS::strcat (server_lock, ACE_LIB_TEXT ("_lock_to_server"));
00183 ACE_OS::strcpy (client_lock, basename);
00184 ACE_OS::strcat (client_lock, ACE_LIB_TEXT ("_lock_to_client"));
00185
00186 void *to_server_ptr = 0;
00187 // @@ Here, we assume the shared memory fill will never be resued.
00188 // So we can determine whether we are server or client by examining
00189 // if the simple message queues have already been set up in
00190 // the Malloc object or not.
00191 if (this->shm_malloc_->find ("to_server", to_server_ptr) == -1)
00192 {
00193 void *ptr = 0;
00194 // We are server.
00195 ACE_ALLOCATOR_RETURN (ptr,
00196 this->shm_malloc_->malloc (2 * sizeof (MQ_Struct)),
00197 -1);
00198
00199 MQ_Struct *mymq = reinterpret_cast<MQ_Struct *> (ptr);
00200 mymq->tail_ = 0;
00201 mymq->head_ = 0;
00202 (mymq + 1)->tail_ = 0;
00203 (mymq + 1)->head_ = 0;
00204 if (this->shm_malloc_->bind ("to_server", mymq) == -1)
00205 return -1;
00206
00207 if (this->shm_malloc_->bind ("to_client", mymq + 1) == -1)
00208 return -1;
00209
00210 this->recv_channel_.queue_.init (mymq, this->shm_malloc_);
00211 ACE_NEW_RETURN (this->recv_channel_.sema_,
00212 ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_SEMAPHORE (0, server_sema),
00213 -1);
00214 ACE_NEW_RETURN (this->recv_channel_.lock_,
00215 ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_MUTEX (server_lock),
00216 -1);
00217
00218 this->send_channel_.queue_.init (mymq + 1, this->shm_malloc_);
00219 ACE_NEW_RETURN (this->send_channel_.sema_,
00220 ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_SEMAPHORE (0, client_sema),
00221 -1);
00222 ACE_NEW_RETURN (this->send_channel_.lock_,
00223 ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_MUTEX (client_lock),
00224 -1);
00225 }
00226 else
00227 {
00228 // we are client.
00229 MQ_Struct *mymq = reinterpret_cast<MQ_Struct *> (to_server_ptr);
00230 this->recv_channel_.queue_.init (mymq +1, this->shm_malloc_);
00231 ACE_NEW_RETURN (this->recv_channel_.sema_,
00232 ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_SEMAPHORE (0, client_sema),
00233 -1);
00234 ACE_NEW_RETURN (this->recv_channel_.lock_,
00235 ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_MUTEX (client_lock),
00236 -1);
00237
00238 this->send_channel_.queue_.init (mymq, this->shm_malloc_);
00239 ACE_NEW_RETURN (this->send_channel_.sema_,
00240 ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_SEMAPHORE (0, server_sema),
00241 -1);
00242 ACE_NEW_RETURN (this->send_channel_.lock_,
00243 ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_MUTEX (server_lock),
00244 -1);
00245 }
00246 return 0;
00247 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Fetch location of next available data into . As this operation read the address of the data off the socket using ACE::recv, only applies to ACE::recv. Implements ACE_MEM_SAP. Definition at line 250 of file MEM_IO.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_MUTEX, ACE_TRACE, ACE_MT_MEM_IO::Channel::queue_, ACE_MT_MEM_IO::Simple_Queue::read(), recv_channel_, ACE_MT_MEM_IO::Channel::sema_, and ACE_MEM_SAP_Node::size().
00253 {
00254 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_MT_MEM_IO::recv_buf");
00255
00256 // @@ Don't know how to handle timeout yet.
00257 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (timeout);
00258 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (flags);
00259
00260 if (this->shm_malloc_ == 0)
00261 return -1;
00262
00263 // Need to handle timeout here.
00264 if (this->recv_channel_.sema_->acquire () == -1)
00265 return -1;
00266
00267 {
00268 // @@ We can probably skip the lock in certain circumstance.
00269 ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_MUTEX, ace_mon, *this->recv_channel_.lock_, -1);
00270
00271 buf = this->recv_channel_.queue_.read ();
00272 if (buf != 0)
00273 return buf->size ();
00274 return -1;
00275 }
00276 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Wait to to amount of time to send . If times out a -1 is returned with <errno == ETIME>. If it succeeds the number of bytes sent is returned. Implements ACE_MEM_SAP. Definition at line 279 of file MEM_IO.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_MUTEX, ACE_TRACE, ACE_MT_MEM_IO::Channel::queue_, ACE_MEM_SAP::release_buffer(), ACE_MT_MEM_IO::Channel::sema_, send_channel_, ACE_MEM_SAP_Node::size(), and ACE_MT_MEM_IO::Simple_Queue::write().
00282 {
00283 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_MT_MEM_IO::send_buf");
00284
00285 // @@ Don't know how to handle timeout yet.
00286 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (timeout);
00287 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (flags);
00288
00289 if (this->shm_malloc_ == 0)
00290 return -1;
00291
00292 {
00293 // @@ We can probably skip the lock in certain curcumstances.
00294 ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_SYNCH_PROCESS_MUTEX, ace_mon, *this->send_channel_.lock_, -1);
00295
00296 if (this->send_channel_.queue_.write (buf) == -1)
00297 {
00298 this->release_buffer (buf);
00299 return -1;
00300 }
00301 }
00302
00303 if (this->send_channel_.sema_->release () == -1)
00304 return -1;
00305
00306 return buf->size ();
00307 }
|
|
|
Definition at line 139 of file MEM_IO.h. Referenced by ACE_MT_MEM_IO(), init(), recv_buf(), and ~ACE_MT_MEM_IO(). |
|
|
Definition at line 140 of file MEM_IO.h. Referenced by ACE_MT_MEM_IO(), init(), send_buf(), and ~ACE_MT_MEM_IO(). |
 1.3.6
1.3.6