Primary interface for application message processing, as well as input and output message queueing. More...
#include <Task_Ex_T.h>
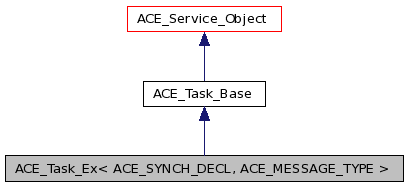
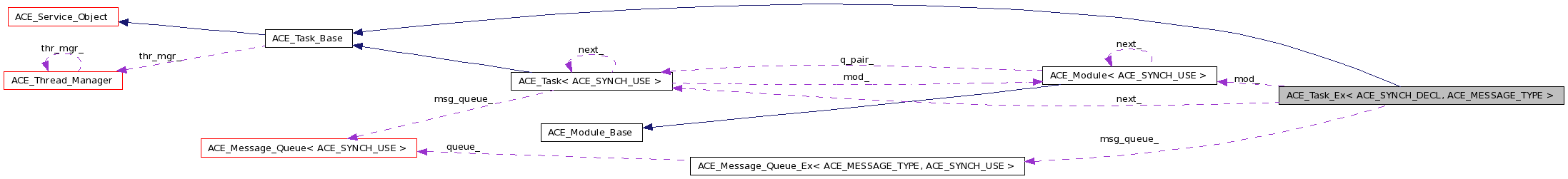
Public Types | |
| typedef ACE_Message_Queue_Ex < ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE, ACE_SYNCH_USE > | MESSAGE_QUEUE_EX |
Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_Task_Ex (ACE_Thread_Manager *thr_mgr=0, MESSAGE_QUEUE_EX *mq=0) | |
| virtual | ~ACE_Task_Ex (void) |
| Destructor. | |
| MESSAGE_QUEUE_EX * | msg_queue (void) |
| Gets the message queue associated with this task. | |
| void | msg_queue (MESSAGE_QUEUE_EX *) |
| Sets the message queue associated with this task. | |
| int | putq (ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE *, ACE_Time_Value *timeout=0) |
| int | getq (ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE *&mb, ACE_Time_Value *timeout=0) |
| int | ungetq (ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE *, ACE_Time_Value *timeout=0) |
| int | reply (ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE *, ACE_Time_Value *timeout=0) |
| int | put_next (ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE *msg, ACE_Time_Value *timeout=0) |
| int | can_put (ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE *) |
| const ACE_TCHAR * | name (void) const |
| ACE_Task< ACE_SYNCH_USE > * | next (void) |
| Get next Task pointer. | |
| void | next (ACE_Task< ACE_SYNCH_USE > *) |
| Set next Task pointer. | |
| ACE_Task< ACE_SYNCH_USE > * | sibling (void) |
| Alwasy return 0. | |
| ACE_Module< ACE_SYNCH_USE > * | module (void) const |
| Return the Task's Module if there is one, else returns 0. | |
| int | flush (u_long flag=ACE_Task_Flags::ACE_FLUSHALL) |
| void | water_marks (ACE_IO_Cntl_Msg::ACE_IO_Cntl_Cmds, size_t) |
| Manipulate watermarks. | |
| void | dump (void) const |
| Dump the state of an object. | |
Public Attributes | |
| MESSAGE_QUEUE_EX * | msg_queue_ |
| Queue of messages on the ACE_Task.. | |
| bool | delete_msg_queue_ |
| true if should delete Message_Queue, false otherwise. | |
| ACE_Module< ACE_SYNCH_USE > * | mod_ |
| Back-pointer to the enclosing module. | |
| ACE_Task< ACE_SYNCH_USE > * | next_ |
| Pointer to adjacent ACE_Task. | |
| ACE_ALLOC_HOOK_DECLARE | |
| Declare the dynamic allocation hooks. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | operator= (const ACE_Task_Ex< _ACE_SYNCH_MUTEX_T, _ACE_SYNCH_CONDITION_T, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE > &) |
| ACE_Task_Ex (const ACE_Task_Ex< _ACE_SYNCH_MUTEX_T, _ACE_SYNCH_CONDITION_T, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE > &) | |
Friends | |
| class | ACE_Module< ACE_SYNCH_USE > |
| class | ACE_Module_Type |
Primary interface for application message processing, as well as input and output message queueing.
Unlike ACE_Task, these class doesn't have the ability to be a part of a Stream chain. I.e. You cannot (yet) chain modules based on ACE_Task_Ex.
Now specialized version of ACE_Task with ACE_Message_Block as its ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE...
template <ACE_SYNCH_DECL> class ACE_Task <ACE_SYNCH_USE, ACE_Message_Block> : public ACE_Task_Base { // put here the good old ACE_Task code };
When User (and legacy code) write ACE_Task<ACE_MT_SYNCH>, specialized ACE_Task code is in action.
Definition at line 61 of file Task_Ex_T.h.
| typedef ACE_Message_Queue_Ex<ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE, ACE_SYNCH_USE> ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::MESSAGE_QUEUE_EX |
Definition at line 66 of file Task_Ex_T.h.
| ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::ACE_Task_Ex | ( | ACE_Thread_Manager * | thr_mgr = 0, |
|
| MESSAGE_QUEUE_EX * | mq = 0 | |||
| ) |
Initialize a Task, supplying a thread manager and a message queue. If the user doesn't supply a ACE_Message_Queue pointer then we'll allocate one dynamically. Otherwise, we'll use the one passed as a parameter.
Definition at line 48 of file Task_Ex_T.cpp.
: ACE_Task_Base (thr_man), msg_queue_ (0), delete_msg_queue_ (false), mod_ (0), next_ (0) { ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::ACE_Task_Ex"); if (mq == 0) { ACE_NEW (mq, (ACE_Message_Queue_Ex<ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE, ACE_SYNCH_USE>)); this->delete_msg_queue_ = true; } this->msg_queue_ = mq; }
| ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::~ACE_Task_Ex | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Destructor.
Definition at line 69 of file Task_Ex_T.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::~ACE_Task_Ex");
if (this->delete_msg_queue_)
delete this->msg_queue_;
// These assignments aren't strickly necessary but they help guard
// against odd race conditions...
this->delete_msg_queue_ = false;
}
| ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::ACE_Task_Ex | ( | const ACE_Task_Ex< _ACE_SYNCH_MUTEX_T, _ACE_SYNCH_CONDITION_T, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE > & | ) | [private] |
| int ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::can_put | ( | ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE * | ) |
Tests whether we can enqueue a message without blocking.
Definition at line 26 of file Task_Ex_T.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE,ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::can_put");
ACE_NOTSUP_RETURN (-1);
}
| void ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::dump | ( | void | ) | const |
Dump the state of an object.
Definition at line 23 of file Task_Ex_T.cpp.
{
#if defined (ACE_HAS_DUMP)
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::dump");
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_BEGIN_DUMP, this));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\nthr_mgr_ = %x"), this->thr_mgr_));
this->msg_queue_->dump ();
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("delete_msg_queue_ = %d\n"), this->delete_msg_queue_));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\nflags = %x"), this->flags_));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\nmod_ = %x"), this->mod_));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\nnext_ = %x"), this->next_));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\ngrp_id_ = %d"), this->grp_id_));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\nthr_count_ = %d"), this->thr_count_));
#if defined (ACE_MT_SAFE) && (ACE_MT_SAFE != 0)
this->lock_.dump ();
#endif /* ACE_MT_SAFE */
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_END_DUMP));
#endif /* ACE_HAS_DUMP */
}
| int ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::flush | ( | u_long | flag = ACE_Task_Flags::ACE_FLUSHALL |
) |
Flush the task's queue, i.e., free all of the enqueued message blocks and releases any threads blocked on the queue. Note that if this conflicts with the C++ iostream <flush> function, just rewrite the iostream function as ::<flush>.
Definition at line 47 of file Task_Ex_T.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE,ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::flush");
if (ACE_BIT_ENABLED (flag, ACE_Task_Flags::ACE_FLUSHALL))
return this->msg_queue_ != 0 && this->msg_queue_->close ();
else
return -1; // Note, need to be more careful about what we free...
}
| int ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::getq | ( | ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE *& | mb, | |
| ACE_Time_Value * | timeout = 0 | |||
| ) |
Extract the first message from the queue (blocking). Note that timeout uses <{absolute}> time rather than <{relative}> time. Returns number of items in queue if the call succeeds or -1 otherwise.
Definition at line 19 of file Task_Ex_T.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE,ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::getq");
return this->msg_queue_->dequeue_head (mb, tv);
}
| ACE_Module< ACE_SYNCH_USE > * ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::module | ( | void | ) | const |
Return the Task's Module if there is one, else returns 0.
Definition at line 106 of file Task_Ex_T.cpp.
| ACE_Message_Queue_Ex< ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE, ACE_SYNCH_USE > * ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::msg_queue | ( | void | ) |
Gets the message queue associated with this task.
Definition at line 69 of file Task_Ex_T.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE,ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::msg_queue");
return this->msg_queue_;
}
| void ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::msg_queue | ( | MESSAGE_QUEUE_EX * | mq | ) |
Sets the message queue associated with this task.
Definition at line 57 of file Task_Ex_T.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE,ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::msg_queue");
if (this->delete_msg_queue_)
{
delete this->msg_queue_;
this->delete_msg_queue_ = false;
}
this->msg_queue_ = mq;
}
| const ACE_TCHAR * ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::name | ( | void | ) | const |
| void ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::next | ( | ACE_Task< ACE_SYNCH_USE > * | q | ) |
Set next Task pointer.
Definition at line 92 of file Task_Ex_T.inl.
| ACE_Task< ACE_SYNCH_USE > * ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::next | ( | void | ) |
Get next Task pointer.
Definition at line 85 of file Task_Ex_T.inl.
| void ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::operator= | ( | const ACE_Task_Ex< _ACE_SYNCH_MUTEX_T, _ACE_SYNCH_CONDITION_T, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE > & | ) | [private] |
| int ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::put_next | ( | ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE * | msg, | |
| ACE_Time_Value * | timeout = 0 | |||
| ) |
Transfer message to the adjacent ACE_Task_Ex in a ACE_Stream. Note that timeout uses <{absolute}> time rather than <{relative}> time.
Definition at line 101 of file Task_Ex_T.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE,ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::put_next");
return -1; // this->next_ == 0 ? -1 : this->next_->put (msg, tv);
}
| int ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::putq | ( | ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE * | mb, | |
| ACE_Time_Value * | timeout = 0 | |||
| ) |
Insert message into the message queue. Note that timeout uses <{absolute}> time rather than <{relative}> time.
Definition at line 33 of file Task_Ex_T.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE,ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::putq");
return this->msg_queue_->enqueue_tail (mb, tv);
}
| int ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::reply | ( | ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE * | mb, | |
| ACE_Time_Value * | timeout = 0 | |||
| ) |
Turn the message around and send it back down the Stream. Note that timeout uses <{absolute}> time rather than <{relative}> time.
Definition at line 76 of file Task_Ex_T.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE,ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::reply");
ACE_UNUSED_ARG (mb);
ACE_UNUSED_ARG (tv);
return -1 ; // this->sibling ()->put_next (mb, tv);
}
| ACE_Task< ACE_SYNCH_USE > * ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::sibling | ( | void | ) |
Alwasy return 0.
Definition at line 81 of file Task_Ex_T.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::sibling");
/// @todo FIXME Need to impl ACE_Moudle to support ACE_Task as well.
/// Now always return 0 for sibling
return 0;
/*
if (this->mod_ == 0)
return 0;
else
return this->mod_->sibling (this);
*/
}
| int ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::ungetq | ( | ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE * | mb, | |
| ACE_Time_Value * | timeout = 0 | |||
| ) |
Return a message to the queue. Note that timeout uses <{absolute}> time rather than <{relative}> time.
Definition at line 40 of file Task_Ex_T.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE,ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::ungetq");
return this->msg_queue_->enqueue_head (mb, tv);
}
| void ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::water_marks | ( | ACE_IO_Cntl_Msg::ACE_IO_Cntl_Cmds | cmd, | |
| size_t | wm_size | |||
| ) |
Manipulate watermarks.
Definition at line 8 of file Task_Ex_T.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Task_Ex<ACE_SYNCH_USE,ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE>::water_marks");
if (cmd == ACE_IO_Cntl_Msg::SET_LWM)
this->msg_queue_->low_water_mark (wm_size);
else /* cmd == ACE_IO_Cntl_Msg::SET_HWM */
this->msg_queue_->high_water_mark (wm_size);
}
friend class ACE_Module< ACE_SYNCH_USE > [friend] |
Definition at line 64 of file Task_Ex_T.h.
friend class ACE_Module_Type [friend] |
Definition at line 65 of file Task_Ex_T.h.
| ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::ACE_ALLOC_HOOK_DECLARE |
Declare the dynamic allocation hooks.
Definition at line 181 of file Task_Ex_T.h.
| bool ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::delete_msg_queue_ |
true if should delete Message_Queue, false otherwise.
Definition at line 169 of file Task_Ex_T.h.
| ACE_Module<ACE_SYNCH_USE>* ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::mod_ |
Back-pointer to the enclosing module.
Definition at line 172 of file Task_Ex_T.h.
| MESSAGE_QUEUE_EX* ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::msg_queue_ |
Queue of messages on the ACE_Task..
Definition at line 166 of file Task_Ex_T.h.
| ACE_Task<ACE_SYNCH_USE>* ACE_Task_Ex< ACE_SYNCH_DECL, ACE_MESSAGE_TYPE >::next_ |
Pointer to adjacent ACE_Task.
Definition at line 175 of file Task_Ex_T.h.
 1.7.0
1.7.0