Stores messages for use throughout ACE (particularly in an ACE_Message_Queue). More...
#include <Message_Block.h>
Public Types | |
| enum | { MB_DATA = 0x01, MB_PROTO = 0x02, MB_BREAK = 0x03, MB_PASSFP = 0x04, MB_EVENT = 0x05, MB_SIG = 0x06, MB_IOCTL = 0x07, MB_SETOPTS = 0x08, MB_IOCACK = 0x81, MB_IOCNAK = 0x82, MB_PCPROTO = 0x83, MB_PCSIG = 0x84, MB_READ = 0x85, MB_FLUSH = 0x86, MB_STOP = 0x87, MB_START = 0x88, MB_HANGUP = 0x89, MB_ERROR = 0x8a, MB_PCEVENT = 0x8b, MB_NORMAL = 0x00, MB_PRIORITY = 0x80, MB_USER = 0x200 } |
| enum | { DONT_DELETE = 01, USER_FLAGS = 0x1000 } |
| typedef int | ACE_Message_Type |
| typedef unsigned long | Message_Flags |
Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_Message_Block (ACE_Allocator *message_block_allocator=0) | |
| Create an empty message. | |
| ACE_Message_Block (ACE_Data_Block *data_block, Message_Flags flags=0, ACE_Allocator *message_block_allocator=0) | |
| ACE_Message_Block (const char *data, size_t size=0, unsigned long priority=ACE_DEFAULT_MESSAGE_BLOCK_PRIORITY) | |
| ACE_Message_Block (size_t size, ACE_Message_Type type=MB_DATA, ACE_Message_Block *cont=0, const char *data=0, ACE_Allocator *allocator_strategy=0, ACE_Lock *locking_strategy=0, unsigned long priority=ACE_DEFAULT_MESSAGE_BLOCK_PRIORITY, const ACE_Time_Value &execution_time=ACE_Time_Value::zero, const ACE_Time_Value &deadline_time=ACE_Time_Value::max_time, ACE_Allocator *data_block_allocator=0, ACE_Allocator *message_block_allocator=0) | |
| ACE_Message_Block (const ACE_Message_Block &mb, size_t align) | |
| int | init (const char *data, size_t size=0) |
| int | init (size_t size, ACE_Message_Type type=MB_DATA, ACE_Message_Block *cont=0, const char *data=0, ACE_Allocator *allocator_strategy=0, ACE_Lock *locking_strategy=0, unsigned long priority=ACE_DEFAULT_MESSAGE_BLOCK_PRIORITY, const ACE_Time_Value &execution_time=ACE_Time_Value::zero, const ACE_Time_Value &deadline_time=ACE_Time_Value::max_time, ACE_Allocator *data_block_allocator=0, ACE_Allocator *message_block_allocator=0) |
| virtual | ~ACE_Message_Block (void) |
| ACE_Message_Type | msg_type (void) const |
| Get type of the message. | |
| void | msg_type (ACE_Message_Type type) |
| Set type of the message. | |
| int | is_data_msg (void) const |
| Find out what type of message this is. | |
| ACE_Message_Type | msg_class (void) const |
| Message_Flags | set_flags (Message_Flags more_flags) |
| Message_Flags | clr_flags (Message_Flags less_flags) |
| Message_Flags | flags (void) const |
| Get the current message flags. | |
| Message_Flags | set_self_flags (ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags more_flags) |
| Message_Flags | clr_self_flags (ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags less_flags) |
| Message_Flags | self_flags (void) const |
| Get the current message flags. | |
| unsigned long | msg_priority (void) const |
| Get priority of the message. | |
| void | msg_priority (unsigned long priority) |
| Set priority of the message. | |
| const ACE_Time_Value & | msg_execution_time (void) const |
| Get execution time associated with the message. | |
| void | msg_execution_time (const ACE_Time_Value &et) |
| Set execution time associated with the message. | |
| const ACE_Time_Value & | msg_deadline_time (void) const |
| Get absolute time of deadline associated with the message. | |
| void | msg_deadline_time (const ACE_Time_Value &dt) |
| Set absolute time of deadline associated with the message. | |
| virtual ACE_Message_Block * | clone (Message_Flags mask=0) const |
| virtual ACE_Message_Block * | duplicate (void) const |
| Return a "shallow" copy that increments our reference count by 1. | |
| virtual ACE_Message_Block * | release (void) |
| int | copy (const char *buf, size_t n) |
| int | copy (const char *buf) |
| int | crunch (void) |
| void | reset (void) |
| void | access_allocators (ACE_Allocator *&allocator_strategy, ACE_Allocator *&data_block_allocator, ACE_Allocator *&message_block_allocator) |
| void | reset_allocators (ACE_Allocator *allocator_strategy=0, ACE_Allocator *data_block_allocator=0, ACE_Allocator *message_block_allocator=0) |
| char * | base (void) const |
| Get message data. | |
| void | base (char *data, size_t size, Message_Flags=DONT_DELETE) |
| Set message data (doesn't reallocate). | |
| char * | end (void) const |
| Return a pointer to 1 past the end of the allocated data in a message. | |
| char * | mark (void) const |
| char * | rd_ptr (void) const |
| Get the read pointer. | |
| void | rd_ptr (char *ptr) |
| Set the read pointer to ptr. | |
| void | rd_ptr (size_t n) |
| Set the read pointer ahead n bytes. | |
| char * | wr_ptr (void) const |
| Get the write pointer. | |
| void | wr_ptr (char *ptr) |
| Set the write pointer to ptr. | |
| void | wr_ptr (size_t n) |
| ACE_Data_Block * | data_block (void) const |
| void | data_block (ACE_Data_Block *) |
| ACE_Data_Block * | replace_data_block (ACE_Data_Block *) |
| ACE_Message_Block * | cont (void) const |
| Get the continuation field. | |
| void | cont (ACE_Message_Block *) |
| Set the continuation field. | |
| ACE_Message_Block * | next (void) const |
| Get link to next message. | |
| void | next (ACE_Message_Block *) |
| Set link to next message. | |
| ACE_Message_Block * | prev (void) const |
| Get link to prev message. | |
| void | prev (ACE_Message_Block *) |
| Set link to prev message. | |
| ACE_Lock * | locking_strategy (void) |
| Get the locking strategy. | |
| ACE_Lock * | locking_strategy (ACE_Lock *) |
| Set a new locking strategy and return the hold one. | |
| int | reference_count (void) const |
| Get the current reference count. | |
| void | dump (void) const |
| Dump the state of an object. | |
Message length and size operations | |
| size_t | length (void) const |
| Get the length of the message. | |
| void | length (size_t n) |
| Set the length of the message. | |
| size_t | total_length (void) const |
| size_t | total_size (void) const |
| void | total_size_and_length (size_t &mb_size, size_t &mb_length) const |
| size_t | size (void) const |
| int | size (size_t length) |
| size_t | total_capacity (void) const |
| size_t | capacity (void) const |
| Get the number of allocated bytes in the top-level Message_Block. | |
| size_t | space (void) const |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static ACE_Message_Block * | duplicate (const ACE_Message_Block *mb) |
| static ACE_Message_Block * | release (ACE_Message_Block *mb) |
Public Attributes | |
| ACE_ALLOC_HOOK_DECLARE | |
| Declare the dynamic allocation hooks. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| ACE_Message_Block (size_t size, ACE_Message_Type type, ACE_Message_Block *cont, const char *data, ACE_Allocator *allocator_strategy, ACE_Lock *locking_strategy, Message_Flags flags, unsigned long priority, const ACE_Time_Value &execution_time, const ACE_Time_Value &deadline_time, ACE_Data_Block *db, ACE_Allocator *data_block_allocator, ACE_Allocator *message_block_allocator) | |
| Perform the actual initialization. | |
| int | release_i (ACE_Lock *lock) |
| int | init_i (size_t size, ACE_Message_Type type, ACE_Message_Block *cont, const char *data, ACE_Allocator *allocator_strategy, ACE_Lock *locking_strategy, Message_Flags flags, unsigned long priority, const ACE_Time_Value &execution_time, const ACE_Time_Value &deadline_time, ACE_Data_Block *db, ACE_Allocator *data_block_allocator, ACE_Allocator *message_block_allocator) |
| Perform the actual initialization. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| size_t | rd_ptr_ |
| Pointer to beginning of next read. | |
| size_t | wr_ptr_ |
| Pointer to beginning of next write. | |
| unsigned long | priority_ |
| Priority of message. | |
| ACE_Message_Block * | cont_ |
| Pointer to next message block in the chain. | |
| ACE_Message_Block * | next_ |
| Pointer to next message in the list. | |
| ACE_Message_Block * | prev_ |
| Pointer to previous message in the list. | |
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | flags_ |
| Misc flags (e.g., DONT_DELETE and USER_FLAGS). | |
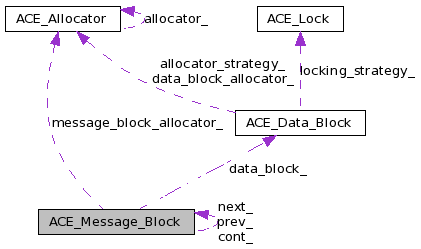
| ACE_Data_Block * | data_block_ |
| ACE_Allocator * | message_block_allocator_ |
Private Member Functions | |
| ACE_Message_Block & | operator= (const ACE_Message_Block &) |
| ACE_Message_Block (const ACE_Message_Block &) | |
Friends | |
| class | ACE_Data_Block |
Stores messages for use throughout ACE (particularly in an ACE_Message_Queue).
An ACE_Message_Block is modeled after the message data structures used in System V STREAMS. Its purpose is to enable efficient manipulation of arbitrarily large messages without incurring much memory copying overhead. Here are the main characteristics of an ACE_Message_Block:
Definition at line 59 of file Message_Block.h.
| typedef int ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Type |
Definition at line 119 of file Message_Block.h.
| typedef unsigned long ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags |
Definition at line 120 of file Message_Block.h.
| anonymous enum |
Definition at line 64 of file Message_Block.h.
{
// = Data and proto
/// Undifferentiated data message
MB_DATA = 0x01,
/// Undifferentiated protocol control
MB_PROTO = 0x02,
// = Control messages
/// Line break (regular and priority)
MB_BREAK = 0x03,
/// Pass file pointer
MB_PASSFP = 0x04,
/// Post an event to an event queue
MB_EVENT = 0x05,
/// Generate process signal
MB_SIG = 0x06,
/// ioctl; set/get params
MB_IOCTL = 0x07,
/// Set various stream head options
MB_SETOPTS = 0x08,
// = Control messages
/// Acknowledge ioctl (high priority; go to head of queue)
MB_IOCACK = 0x81,
/// Negative ioctl acknowledge
MB_IOCNAK = 0x82,
/// Priority proto message
MB_PCPROTO = 0x83,
/// Generate process signal
MB_PCSIG = 0x84,
/// Generate read notification
MB_READ = 0x85,
/// Flush your queues
MB_FLUSH = 0x86,
/// Stop transmission immediately
MB_STOP = 0x87,
/// Restart transmission after stop
MB_START = 0x88,
/// Line disconnect
MB_HANGUP = 0x89,
/// Fatal error used to set u.u_error
MB_ERROR = 0x8a,
/// Post an event to an event queue
MB_PCEVENT = 0x8b,
// = Message class masks
/// Normal priority message mask
MB_NORMAL = 0x00,
/// High priority control message mask
MB_PRIORITY = 0x80,
/// User-defined message mask
MB_USER = 0x200
};
| anonymous enum |
| DONT_DELETE |
Don't delete the data on exit since we don't own it. |
| USER_FLAGS |
user defined flags start here |
Definition at line 122 of file Message_Block.h.
{
/// Don't delete the data on exit since we don't own it.
DONT_DELETE = 01,
/// user defined flags start here
USER_FLAGS = 0x1000
};
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block | ( | ACE_Allocator * | message_block_allocator = 0 |
) |
Create an empty message.
Definition at line 414 of file Message_Block.cpp.
: flags_ (0), data_block_ (0) { ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block"); if (this->init_i (0, // size MB_DATA, // type 0, // cont 0, // data 0, // allocator 0, // locking strategy ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE, // flags 0, // priority ACE_Time_Value::zero, // execution time ACE_Time_Value::max_time, // absolute time of deadline 0, // data block 0, // data_block allocator message_block_allocator) == -1) // message_block allocator ACE_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, ACE_TEXT ("ACE_Message_Block"))); }
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block | ( | ACE_Data_Block * | data_block, | |
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | flags = 0, |
|||
| ACE_Allocator * | message_block_allocator = 0 | |||
| ) |
Create an ACE_Message_Block that owns the specified ACE_Data_Block without copying it. If the flags is set to DONT_DELETE we don't delete the ACE_Data_Block. It is left to the client's responsibility to take care of the memory allocated for the data_block
Definition at line 557 of file Message_Block.cpp.
: flags_ (flags), data_block_ (0) { ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block"); if (this->init_i (0, // size MB_NORMAL, // type 0, // cont 0, // data 0, // allocator 0, // locking strategy 0, // flags 0, // priority ACE_Time_Value::zero, // execution time ACE_Time_Value::max_time, // absolute time of deadline data_block, // data block data_block->data_block_allocator (), message_block_allocator) == -1) ACE_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, ACE_TEXT ("ACE_Message_Block"))); }
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block | ( | const char * | data, | |
| size_t | size = 0, |
|||
| unsigned long | priority = ACE_DEFAULT_MESSAGE_BLOCK_PRIORITY | |||
| ) |
Create an ACE_Message_Block that refers to data without copying it. The data memory will not be freed when this block is destroyed; memory management of data is left to the caller. Note that the size of the new ACE_Message_Block will be size, but the length will be 0 until the write pointer is changed.
Definition at line 389 of file Message_Block.cpp.
: flags_ (0), data_block_ (0) { ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block"); if (this->init_i (size, // size MB_DATA, // type 0, // cont data, // data 0, // allocator 0, // locking strategy ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE, // flags priority, // priority ACE_Time_Value::zero, // execution time ACE_Time_Value::max_time, // absolute time of deadline 0, // data block 0, // data_block allocator 0) == -1) // message_block allocator ACE_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, ACE_TEXT ("ACE_Message_Block"))); }
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block | ( | size_t | size, | |
| ACE_Message_Type | type = MB_DATA, |
|||
| ACE_Message_Block * | cont = 0, |
|||
| const char * | data = 0, |
|||
| ACE_Allocator * | allocator_strategy = 0, |
|||
| ACE_Lock * | locking_strategy = 0, |
|||
| unsigned long | priority = ACE_DEFAULT_MESSAGE_BLOCK_PRIORITY, |
|||
| const ACE_Time_Value & | execution_time = ACE_Time_Value::zero, |
|||
| const ACE_Time_Value & | deadline_time = ACE_Time_Value::max_time, |
|||
| ACE_Allocator * | data_block_allocator = 0, |
|||
| ACE_Allocator * | message_block_allocator = 0 | |||
| ) |
Create an initialized message of type type containing size bytes. The cont argument initializes the continuation field in the ACE_Message_Block. If data == 0 then this block allocates and owns the block's memory, using allocator to get the data if it's non-0. If data != 0 then this block refers to that memory until this this block ceases to exist; this object will not free data on destruction. If locking_strategy is non-0 then this is used to protect regions of code that access shared state (e.g., reference counting) from race conditions. Note that the size of the ACE_Message_Block will be size, but the length will be 0 until the write pointer is set. The data_block_allocator is used to allocate the data blocks while the allocator_strategy is used to allocate the buffers contained by those. The message_block_allocator is used to allocate new ACE_Message_Block objects when the duplicate() method is called. If a message_block_allocator is given, this ACE_Message_Block and future ACE_Message_Block objects created by duplicate() will be freed using this allocator when they are released.
Definition at line 437 of file Message_Block.cpp.
:flags_ (0), data_block_ (0) { ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block"); if (this->init_i (size, msg_type, msg_cont, msg_data, allocator_strategy, locking_strategy, msg_data ? ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE : 0, priority, execution_time, deadline_time, 0, // data block data_block_allocator, message_block_allocator) == -1) ACE_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, ACE_TEXT ("ACE_Message_Block"))); }
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block | ( | const ACE_Message_Block & | mb, | |
| size_t | align | |||
| ) |
A copy constructor. This constructor is a bit different. If the incoming Message Block has a data block from the stack this constructor does a deep copy ie. allocates a new data block on the heap and does a copy of the data from the incoming message block. As a final note, the alignment information is used to align the data block if it is created afresh. If the incoming mb has a data block has a data block allocated from the heap, then this constructor just duplicates (ie. a shallow copy) the data block of the incoming mb.
Definition at line 582 of file Message_Block.cpp.
:flags_ (0), data_block_ (0) { ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block"); if (ACE_BIT_DISABLED (mb.flags_, ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE)) { if (this->init_i (0, // size MB_NORMAL, // type 0, // cont 0, // data 0, // allocator 0, // locking strategy 0, // flags 0, // priority ACE_Time_Value::zero, // execution time ACE_Time_Value::max_time, // absolute time of deadline mb.data_block ()->duplicate (), // data block mb.data_block ()->data_block_allocator (), mb.message_block_allocator_) == -1) ACE_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, ACE_TEXT ("ACE_Message_Block"))); #if !defined (ACE_LACKS_CDR_ALIGNMENT) // Align ourselves char *start = ACE_ptr_align_binary (this->base (), align); #else char *start = this->base (); #endif /* ACE_LACKS_CDR_ALIGNMENT */ // Set our rd & wr pointers this->rd_ptr (start); this->wr_ptr (start); } else { if (this->init_i (0, // size MB_NORMAL, // type 0, // cont 0, // data 0, // allocator 0, // locking strategy 0, // flags 0, // priority ACE_Time_Value::zero, // execution time ACE_Time_Value::max_time, // absolute time of deadline mb.data_block ()->clone_nocopy (),// data block mb.data_block ()->data_block_allocator (), mb.message_block_allocator_) == -1) ACE_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, ACE_TEXT ("ACE_Message_Block"))); #if !defined (ACE_LACKS_CDR_ALIGNMENT) // Align ourselves char *start = ACE_ptr_align_binary (this->base (), align); #else char *start = this->base (); #endif /* ACE_LACKS_CDR_ALIGNMENT */ // Set our rd & wr pointers this->rd_ptr (start); this->wr_ptr (start); #if !defined (ACE_LACKS_CDR_ALIGNMENT) // Get the alignment offset of the incoming ACE_Message_Block start = ACE_ptr_align_binary (mb.base (), align); #else start = mb.base (); #endif /* ACE_LACKS_CDR_ALIGNMENT */ // Actual offset for the incoming message block assuming that it // is also aligned to the same "align" byte size_t const wr_offset = mb.wr_ptr_ - (start - mb.base ()); // Copy wr_offset amount of data in to <this->data_block> (void) ACE_OS::memcpy (this->wr_ptr (), start, wr_offset); // Dont move the write pointer, just leave it to the application // to do what it wants } #if defined (ACE_LACKS_CDR_ALIGNMENT) ACE_UNUSED_ARG (align); #endif /* ACE_LACKS_CDR_ALIGNMENT */ }
| ACE_Message_Block::~ACE_Message_Block | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Delete all the resources held in the message.
Definition at line 976 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::~ACE_Message_Block");
if (ACE_BIT_DISABLED (this->flags_,
ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE)&&
this->data_block ())
this->data_block ()->release ();
this->prev_ = 0;
this->next_ = 0;
this->cont_ = 0;
}
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block | ( | size_t | size, | |
| ACE_Message_Type | type, | |||
| ACE_Message_Block * | cont, | |||
| const char * | data, | |||
| ACE_Allocator * | allocator_strategy, | |||
| ACE_Lock * | locking_strategy, | |||
| Message_Flags | flags, | |||
| unsigned long | priority, | |||
| const ACE_Time_Value & | execution_time, | |||
| const ACE_Time_Value & | deadline_time, | |||
| ACE_Data_Block * | db, | |||
| ACE_Allocator * | data_block_allocator, | |||
| ACE_Allocator * | message_block_allocator | |||
| ) | [protected] |
Perform the actual initialization.
Definition at line 522 of file Message_Block.cpp.
: flags_ (0), data_block_ (0) { ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block"); if (this->init_i (size, msg_type, msg_cont, msg_data, allocator_strategy, locking_strategy, flags, priority, execution_time, deadline_time, db, data_block_allocator, message_block_allocator) == -1) ACE_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, ACE_TEXT ("ACE_Message_Block"))); }
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Block | ( | const ACE_Message_Block & | ) | [private] |
| void ACE_Message_Block::access_allocators | ( | ACE_Allocator *& | allocator_strategy, | |
| ACE_Allocator *& | data_block_allocator, | |||
| ACE_Allocator *& | message_block_allocator | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Access all the allocators in the message block.
This method returns the allocators only from the first message block in the chain.
| allocator_strategy | Strategy used to allocate the underlying buffer | |
| data_block_allocator | Strategy used to allocate the underlying data block | |
| message_block_allocator | Strategy used to allocate the message block |
Definition at line 272 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
allocator_strategy =
this->data_block_->allocator_strategy_;
data_block_allocator =
this->data_block_->data_block_allocator_;
message_block_allocator =
this->message_block_allocator_;
}
| char * ACE_Message_Block::base | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get message data.
Definition at line 285 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::base");
return this->data_block ()->base ();
}
| void ACE_Message_Block::base | ( | char * | data, | |
| size_t | size, | |||
| Message_Flags | msg_flags = DONT_DELETE | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Set message data (doesn't reallocate).
Definition at line 292 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::base");
this->rd_ptr_ = 0;
this->wr_ptr_ = 0;
this->data_block ()->base (msg_data, msg_length, msg_flags);
}
| size_t ACE_Message_Block::capacity | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the number of allocated bytes in the top-level Message_Block.
Definition at line 154 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::capacity");
return this->data_block ()->capacity ();
}
| ACE_Message_Block * ACE_Message_Block::clone | ( | Message_Flags | mask = 0 |
) | const [virtual] |
Return an exact "deep copy" of the message, i.e., create fresh new copies of all the Data_Blocks and continuations.
Definition at line 1175 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::clone");
// Get a pointer to a "cloned" <ACE_Data_Block> (will copy the
// values rather than increment the reference count).
ACE_Data_Block *db = this->data_block ()->clone (mask);
if (db == 0)
return 0;
ACE_Message_Block *nb = 0;
if(message_block_allocator_ == 0)
{
ACE_NEW_RETURN (nb,
ACE_Message_Block (0, // size
ACE_Message_Type (0), // type
0, // cont
0, // data
0, // allocator
0, // locking strategy
0, // flags
this->priority_, // priority
ACE_EXECUTION_TIME, // execution time
ACE_DEADLINE_TIME, // absolute time to deadline
// Get a pointer to a
// "duplicated" <ACE_Data_Block>
// (will simply increment the
// reference count).
db,
db->data_block_allocator (),
this->message_block_allocator_),
0);
}
else
{
// This is the ACE_NEW_MALLOC macro with the return check removed.
// We need to do it this way because if it fails we need to release
// the cloned data block that was created above. If we used
// ACE_NEW_MALLOC_RETURN, there would be a memory leak because the
// above db pointer would be left dangling.
nb = static_cast<ACE_Message_Block*> (message_block_allocator_->malloc (sizeof (ACE_Message_Block)));
if(nb != 0)
new (nb) ACE_Message_Block (0, // size
ACE_Message_Type (0), // type
0, // cont
0, // data
0, // allocator
0, // locking strategy
0, // flags
this->priority_, // priority
ACE_EXECUTION_TIME, // execution time
ACE_DEADLINE_TIME, // absolute time to deadline
db,
db->data_block_allocator (),
this->message_block_allocator_);
}
if (nb == 0)
{
db->release ();
return 0;
}
// Set the read and write pointers in the new <Message_Block> to the
// same relative offset as in the existing <Message_Block>.
nb->rd_ptr (this->rd_ptr_);
nb->wr_ptr (this->wr_ptr_);
// Clone all the continuation messages if necessary.
if (this->cont () != 0
&& (nb->cont_ = this->cont ()->clone (mask)) == 0)
{
nb->release ();
return 0;
}
return nb;
}
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags ACE_Message_Block::clr_flags | ( | ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | less_flags | ) | [inline] |
Clear the message flag bits specified in less_flags and return the new value.
Definition at line 112 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::clr_flags");
return this->data_block ()->clr_flags (less_flags);
}
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags ACE_Message_Block::clr_self_flags | ( | ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | less_flags | ) | [inline] |
Clear the message flag bits specified in less_flags and return the new value.
Definition at line 24 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::clr_self_flags");
// Later we might mask more_flags so that user can't change internal
// ones: less_flags &= ~(USER_FLAGS -1).
return ACE_CLR_BITS (this->flags_, less_flags);
}
| ACE_Message_Block * ACE_Message_Block::cont | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the continuation field.
Definition at line 416 of file Message_Block.inl.
| void ACE_Message_Block::cont | ( | ACE_Message_Block * | cont_msg | ) | [inline] |
Set the continuation field.
Definition at line 409 of file Message_Block.inl.
| int ACE_Message_Block::copy | ( | const char * | buf | ) |
Copies a 0-terminated character string into this ACE_Message_Block. The string is copied into the block starting at the current write pointer. The 0-terminator is included in the copied data.
| buf | Pointer to the character string to copy from. |
| 0 | on success; the write pointer is advanced by the string's length, including the 0 terminator. | |
| -1 | if the amount of free space following the write pointer in the block is less than required to hold the entire string. Free space can be checked by calling space(). |
Definition at line 102 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::copy");
/* size_t len = static_cast<size_t> (this->end () - this->wr_ptr ()); */
// Note that for this to work correct, end() *must* be >= wr_ptr().
size_t len = this->space ();
size_t buflen = ACE_OS::strlen (buf) + 1;
if (len < buflen)
{
errno = ENOSPC;
return -1;
}
else
{
(void) ACE_OS::memcpy (this->wr_ptr (),
buf,
buflen);
this->wr_ptr (buflen);
return 0;
}
}
| int ACE_Message_Block::copy | ( | const char * | buf, | |
| size_t | n | |||
| ) |
Copies data into this ACE_Message_Block. Data is copied into the block starting at the current write pointer.
| buf | Pointer to the buffer to copy from. | |
| n | The number of bytes to copy. |
| 0 | on success; the write pointer is advanced by
| |
| -1 | if the amount of free space following the write pointer in the block is less than
|
Definition at line 78 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::copy");
/*size_t len = static_cast<size_t> (this->end () - this->wr_ptr ());*/
// Note that for this to work correct, end () *must* be >= mark ().
size_t len = this->space ();
if (len < n)
{
errno = ENOSPC;
return -1;
}
else
{
(void) ACE_OS::memcpy (this->wr_ptr (),
buf,
n);
this->wr_ptr (n);
return 0;
}
}
| int ACE_Message_Block::crunch | ( | void | ) |
Normalizes data in the top-level Message_Block to align with the base, i.e., it "shifts" the data pointed to by <rd_ptr> down to the <base> and then readjusts <rd_ptr> to point to <base> and <wr_ptr> to point to <base> + the length of the moved data. Returns -1 and does nothing if the <rd_ptr> is > <wr_ptr>, else 0 on success.
Definition at line 128 of file Message_Block.cpp.
| ACE_Data_Block * ACE_Message_Block::data_block | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get a pointer to the data block. Note that the ACE_Message_Block still references the block; this call does not change the reference count.
Definition at line 8 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::data_block");
return this->data_block_;
}
| void ACE_Message_Block::data_block | ( | ACE_Data_Block * | ) |
Set a new data block pointer. The original ACE_Data_Block is released as a result of this call. If you need to keep the original block, call <replace_data_block> instead. Upon return, this ACE_Message_Block holds a pointer to the new ACE_Data_Block, taking over the reference you held on it prior to the call.
| void ACE_Message_Block::dump | ( | void | ) | const |
Dump the state of an object.
Definition at line 174 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
#if defined (ACE_HAS_DUMP)
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::dump");
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_BEGIN_DUMP, this));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG,
ACE_TEXT ("-----( Message Block )-----\n")
ACE_TEXT ("priority_ = %d\n")
ACE_TEXT ("next_ = %@\n")
ACE_TEXT ("prev_ = %@\n")
ACE_TEXT ("cont_ = %@\n")
ACE_TEXT ("rd_ptr_ = %@\n")
ACE_TEXT ("wr_ptr_ = %@\n")
ACE_TEXT ("---------------------------\n"),
this->priority_,
this->next_,
this->prev_,
this->cont_,
this->rd_ptr_,
this->wr_ptr_));
this->data_block ()->dump ();
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_END_DUMP));
#endif /* ACE_HAS_DUMP */
}
| ACE_Message_Block * ACE_Message_Block::duplicate | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
Return a "shallow" copy that increments our reference count by 1.
Definition at line 1018 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::duplicate");
ACE_Message_Block *nb = 0;
// Create a new <ACE_Message_Block> that contains unique copies of
// the message block fields, but a reference counted duplicate of
// the <ACE_Data_Block>.
// If there is no allocator, use the standard new and delete calls.
if (this->message_block_allocator_ == 0)
ACE_NEW_RETURN (nb,
ACE_Message_Block (0, // size
ACE_Message_Type (0), // type
0, // cont
0, // data
0, // allocator
0, // locking strategy
0, // flags
this->priority_, // priority
ACE_EXECUTION_TIME,
ACE_DEADLINE_TIME,
// Get a pointer to a
// "duplicated" <ACE_Data_Block>
// (will simply increment the
// reference count).
this->data_block ()->duplicate (),
this->data_block ()->data_block_allocator (),
this->message_block_allocator_),
0);
else // Otherwise, use the message_block_allocator passed in.
ACE_NEW_MALLOC_RETURN (nb,
static_cast<ACE_Message_Block*> (
message_block_allocator_->malloc (sizeof (ACE_Message_Block))),
ACE_Message_Block (0, // size
ACE_Message_Type (0), // type
0, // cont
0, // data
0, // allocator
0, // locking strategy
0, // flags
this->priority_, // priority
ACE_EXECUTION_TIME,
ACE_DEADLINE_TIME,
// Get a pointer to a
// "duplicated" <ACE_Data_Block>
// (will simply increment the
// reference count).
this->data_block ()->duplicate (),
this->data_block ()->data_block_allocator (),
this->message_block_allocator_),
0);
// Set the read and write pointers in the new <Message_Block> to the
// same relative offset as in the existing <Message_Block>. Note
// that we are assuming that the data_block()->base() pointer
// doesn't change when it's duplicated.
nb->rd_ptr (this->rd_ptr_);
nb->wr_ptr (this->wr_ptr_);
// Increment the reference counts of all the continuation messages.
if (this->cont_)
{
nb->cont_ = this->cont_->duplicate ();
// If things go wrong, release all of our resources and return
// 0.
if (nb->cont_ == 0)
{
nb->release ();
nb = 0;
}
}
return nb;
}
| ACE_Message_Block * ACE_Message_Block::duplicate | ( | const ACE_Message_Block * | mb | ) | [static] |
Return a "shallow" copy that increments our reference count by 1. This is similar to CORBA's <_duplicate> method, which is useful if you want to eliminate lots of checks for NULL mb pointers before calling <_duplicate> on them.
Definition at line 1097 of file Message_Block.cpp.
| char * ACE_Message_Block::end | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Return a pointer to 1 past the end of the allocated data in a message.
Definition at line 340 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::end");
return this->data_block ()->end ();
}
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags ACE_Message_Block::flags | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the current message flags.
Definition at line 119 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::flags");
return this->data_block ()->flags ();
}
| int ACE_Message_Block::init | ( | const char * | data, | |
| size_t | size = 0 | |||
| ) |
Create a Message Block that assumes it has ownership of data, but in reality it doesnt (i.e., cannot delete it since it didn't malloc it!). Note that the size of the Message_Block will be size, but the length will be 0 until <wr_ptr> is set.
Definition at line 501 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::init");
// Should we also initialize all the other fields, as well?
return this->init_i (size, // size
MB_DATA, // type
0, // cont
data, // data
0, // allocator
0, // locking strategy
ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE, // flags
0, // priority
ACE_Time_Value::zero, // execution time
ACE_Time_Value::max_time, // absolute time of deadline
0, // data block
0, // data_block allocator
0); // message_block allocator
}
| int ACE_Message_Block::init | ( | size_t | size, | |
| ACE_Message_Type | type = MB_DATA, |
|||
| ACE_Message_Block * | cont = 0, |
|||
| const char * | data = 0, |
|||
| ACE_Allocator * | allocator_strategy = 0, |
|||
| ACE_Lock * | locking_strategy = 0, |
|||
| unsigned long | priority = ACE_DEFAULT_MESSAGE_BLOCK_PRIORITY, |
|||
| const ACE_Time_Value & | execution_time = ACE_Time_Value::zero, |
|||
| const ACE_Time_Value & | deadline_time = ACE_Time_Value::max_time, |
|||
| ACE_Allocator * | data_block_allocator = 0, |
|||
| ACE_Allocator * | message_block_allocator = 0 | |||
| ) |
Create an initialized message of type type containing size bytes. The cont argument initializes the continuation field in the Message_Block. If data == 0 then we create and own the data, using allocator_strategy to get the data if it's non-0. If data != 0 we assume that we have ownership of the data till this object ceases to exist (and don't delete it during destruction). If locking_strategy is non-0 then this is used to protect regions of code that access shared state (e.g., reference counting) from race conditions. Note that the size of the Message_Block will be size, but the length will be 0 until <wr_ptr> is set. The data_block_allocator is use to allocate the data blocks while the allocator_strategy is used to allocate the buffers contained by those.
Definition at line 471 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::init");
return this->init_i (size,
msg_type,
msg_cont,
msg_data,
allocator_strategy,
locking_strategy,
msg_data ? ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE : 0,
priority,
execution_time,
deadline_time,
0, // data block
data_block_allocator,
message_block_allocator);
}
| int ACE_Message_Block::init_i | ( | size_t | size, | |
| ACE_Message_Type | type, | |||
| ACE_Message_Block * | cont, | |||
| const char * | data, | |||
| ACE_Allocator * | allocator_strategy, | |||
| ACE_Lock * | locking_strategy, | |||
| Message_Flags | flags, | |||
| unsigned long | priority, | |||
| const ACE_Time_Value & | execution_time, | |||
| const ACE_Time_Value & | deadline_time, | |||
| ACE_Data_Block * | db, | |||
| ACE_Allocator * | data_block_allocator, | |||
| ACE_Allocator * | message_block_allocator | |||
| ) | [protected] |
Perform the actual initialization.
Definition at line 677 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::init_i");
ACE_FUNCTION_TIMEPROBE (ACE_MESSAGE_BLOCK_INIT_I_ENTER);
this->rd_ptr_ = 0;
this->wr_ptr_ = 0;
this->priority_ = priority;
#if defined (ACE_HAS_TIMED_MESSAGE_BLOCKS)
this->execution_time_ = execution_time;
this->deadline_time_ = deadline_time;
#else
ACE_UNUSED_ARG (execution_time);
ACE_UNUSED_ARG (deadline_time);
#endif /* ACE_HAS_TIMED_MESSAGE_BLOCKS */
this->cont_ = msg_cont;
this->next_ = 0;
this->prev_ = 0;
this->message_block_allocator_ = message_block_allocator;
if (this->data_block_ != 0)
{
this->data_block_->release ();
this->data_block_ = 0;
}
if (db == 0)
{
if (data_block_allocator == 0)
ACE_ALLOCATOR_RETURN (data_block_allocator,
ACE_Allocator::instance (),
-1);
ACE_TIMEPROBE (ACE_MESSAGE_BLOCK_INIT_I_DB_ALLOC);
// Allocate the <ACE_Data_Block> portion, which is reference
// counted.
ACE_NEW_MALLOC_RETURN (db,
static_cast<ACE_Data_Block *> (
data_block_allocator->malloc (sizeof (ACE_Data_Block))),
ACE_Data_Block (size,
msg_type,
msg_data,
allocator_strategy,
locking_strategy,
flags,
data_block_allocator),
-1);
ACE_TIMEPROBE (ACE_MESSAGE_BLOCK_INIT_I_DB_CTOR);
// Message block initialization may fail, while the construction
// succeds. Since ACE may throw no exceptions, we have to do a
// separate check and clean up, like this:
if (db != 0 && db->size () < size)
{
db->ACE_Data_Block::~ACE_Data_Block(); // placement destructor ...
data_block_allocator->free (db); // free ...
errno = ENOMEM;
return -1;
}
}
// Reset the data_block_ pointer.
this->data_block (db);
return 0;
}
| int ACE_Message_Block::is_data_msg | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Find out what type of message this is.
Definition at line 202 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::is_data_msg");
ACE_Message_Type mt = this->msg_type ();
return
mt == ACE_Message_Block::MB_DATA
|| mt == ACE_Message_Block::MB_PROTO
|| mt == ACE_Message_Block::MB_PCPROTO;
}
| size_t ACE_Message_Block::length | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the length of the message.
Definition at line 128 of file Message_Block.inl.
| void ACE_Message_Block::length | ( | size_t | n | ) | [inline] |
| ACE_Lock * ACE_Message_Block::locking_strategy | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
Get the locking strategy.
Definition at line 493 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::locking_strategy");
return this->data_block ()->locking_strategy ();
}
Set a new locking strategy and return the hold one.
Definition at line 500 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::locking_strategy");
ACE_Lock *ols = this->data_block ()->locking_strategy ();
this->data_block ()->locking_strategy (nls);
return ols;
}
| char * ACE_Message_Block::mark | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Return a pointer to 1 past the end of the allotted data in a message. Allotted data may be less than allocated data if a value smaller than capacity() to is passed to size().
Definition at line 326 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::mark");
return this->data_block ()->mark ();
}
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Type ACE_Message_Block::msg_class | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Find out what class of message this is (there are two classes, normal messages and high-priority messages).
Definition at line 189 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::msg_class");
if (this->msg_type () < ACE_Message_Block::MB_PRIORITY)
return ACE_Message_Block::MB_NORMAL;
else if (this->msg_type () < ACE_Message_Block::MB_USER)
return ACE_Message_Block::MB_PRIORITY;
else
return ACE_Message_Block::MB_USER;
}
| const ACE_Time_Value & ACE_Message_Block::msg_deadline_time | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get absolute time of deadline associated with the message.
Definition at line 249 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::msg_deadline_time (void)");
#if defined (ACE_HAS_TIMED_MESSAGE_BLOCKS)
return this->deadline_time_;
#else
return ACE_Time_Value::max_time; // absolute time of deadline
#endif /* ACE_HAS_TIMED_MESSAGE_BLOCKS */
}
| void ACE_Message_Block::msg_deadline_time | ( | const ACE_Time_Value & | dt | ) | [inline] |
Set absolute time of deadline associated with the message.
Definition at line 261 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::msg_deadline_time (const ACE_Time_Value & et)");
#if defined (ACE_HAS_TIMED_MESSAGE_BLOCKS)
this->deadline_time_ = dt;
#else
ACE_UNUSED_ARG (dt);
#endif /* ACE_HAS_TIMED_MESSAGE_BLOCKS */
}
| void ACE_Message_Block::msg_execution_time | ( | const ACE_Time_Value & | et | ) | [inline] |
Set execution time associated with the message.
Definition at line 238 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::msg_execution_time (const ACE_Time_Value & et)");
#if defined (ACE_HAS_TIMED_MESSAGE_BLOCKS)
this->execution_time_ = et;
#else
ACE_UNUSED_ARG (et);
#endif /* ACE_HAS_TIMED_MESSAGE_BLOCKS */
}
| const ACE_Time_Value & ACE_Message_Block::msg_execution_time | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get execution time associated with the message.
Definition at line 227 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::msg_execution_time (void)");
#if defined (ACE_HAS_TIMED_MESSAGE_BLOCKS)
return this->execution_time_;
#else
return ACE_Time_Value::zero;
#endif /* ACE_HAS_TIMED_MESSAGE_BLOCKS */
}
| void ACE_Message_Block::msg_priority | ( | unsigned long | priority | ) | [inline] |
Set priority of the message.
Definition at line 220 of file Message_Block.inl.
| unsigned long ACE_Message_Block::msg_priority | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get priority of the message.
Definition at line 213 of file Message_Block.inl.
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Type ACE_Message_Block::msg_type | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get type of the message.
Definition at line 175 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::msg_type");
return this->data_block ()->msg_type ();
}
| void ACE_Message_Block::msg_type | ( | ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Type | t | ) | [inline] |
Set type of the message.
Definition at line 182 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::msg_type");
this->data_block ()->msg_type (t);
}
| ACE_Message_Block * ACE_Message_Block::next | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get link to next message.
Definition at line 448 of file Message_Block.inl.
| void ACE_Message_Block::next | ( | ACE_Message_Block * | next_msg | ) | [inline] |
Set link to next message.
Definition at line 441 of file Message_Block.inl.
| ACE_Message_Block & ACE_Message_Block::operator= | ( | const ACE_Message_Block & | ) | [private] |
Definition at line 1257 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::operator=");
return *this;
}
| ACE_Message_Block * ACE_Message_Block::prev | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get link to prev message.
Definition at line 462 of file Message_Block.inl.
| void ACE_Message_Block::prev | ( | ACE_Message_Block * | next_msg | ) | [inline] |
Set link to prev message.
Definition at line 455 of file Message_Block.inl.
| char * ACE_Message_Block::rd_ptr | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the read pointer.
Definition at line 303 of file Message_Block.inl.
| void ACE_Message_Block::rd_ptr | ( | char * | ptr | ) | [inline] |
Set the read pointer to ptr.
Definition at line 348 of file Message_Block.inl.
| void ACE_Message_Block::rd_ptr | ( | size_t | n | ) | [inline] |
Set the read pointer ahead n bytes.
Definition at line 355 of file Message_Block.inl.
| int ACE_Message_Block::reference_count | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the current reference count.
Definition at line 46 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
return data_block () ? data_block ()->reference_count () : 0;
}
| ACE_Message_Block * ACE_Message_Block::release | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Decrease the shared ACE_Data_Block's reference count by 1. If the ACE_Data_Block's reference count goes to 0, it is deleted. In all cases, this ACE_Message_Block is deleted - it must have come from the heap, or there will be trouble.
release() is designed to release the continuation chain; the destructor is not. If we make the destructor release the continuation chain by calling release() or delete on the message blocks in the continuation chain, the following code will not work since the message block in the continuation chain is not off the heap:
ACE_Message_Block mb1 (1024); ACE_Message_Block mb2 (1024);
mb1.cont (&mb2);
And hence, call release() on a dynamically allocated message block. This will release all the message blocks in the continuation chain. If you call delete or let the message block fall off the stack, cleanup of the message blocks in the continuation chain becomes the responsibility of the user.
| 0,always,and | the object this method was invoked on is no longer valid. |
Definition at line 859 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::release");
// We want to hold the data block in a temporary variable because we
// invoked "delete this;" at some point, so using this->data_block_
// could be a bad idea.
ACE_Data_Block *tmp = this->data_block ();
// This flag is set to 1 when we have to destroy the data_block
int destroy_dblock = 0;
ACE_Lock *lock = 0;
// Do we have a valid data block
if (this->data_block ())
{
// Grab the lock that belongs to my data block
lock = this->data_block ()->locking_strategy ();
// if we have a lock
if (lock != 0)
{
// One guard for all
ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Lock, ace_mon, *lock, 0);
// Call non-guarded release with @a lock
destroy_dblock = this->release_i (lock);
}
// This is the case when we have a valid data block but no lock
else
// Call non-guarded release with no lock
destroy_dblock = this->release_i (0);
}
else
// This is the case when we don't even have a valid data block
destroy_dblock = this->release_i (0);
if (destroy_dblock != 0)
{
ACE_Allocator *allocator = tmp->data_block_allocator ();
ACE_DES_FREE (tmp,
allocator->free,
ACE_Data_Block);
}
return 0;
}
| ACE_Message_Block * ACE_Message_Block::release | ( | ACE_Message_Block * | mb | ) | [static] |
This behaves like the non-static method <release>, except that it checks if mb is 0. This is similar to <CORBA::release>, which is useful if you want to eliminate lots of checks for NULL pointers before calling <release> on them. Returns mb.
Definition at line 966 of file Message_Block.cpp.
| int ACE_Message_Block::release_i | ( | ACE_Lock * | lock | ) | [protected] |
Internal release implementation Returns 1 if the data block has to be destroyed.
Definition at line 909 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::release_i");
// Free up all the continuation messages.
if (this->cont_)
{
ACE_Message_Block *mb = this->cont_;
ACE_Message_Block *tmp = 0;
do
{
tmp = mb;
mb = mb->cont_;
tmp->cont_ = 0;
ACE_Data_Block *db = tmp->data_block ();
if (tmp->release_i (lock) != 0)
{
ACE_Allocator *allocator = db->data_block_allocator ();
ACE_DES_FREE (db,
allocator->free,
ACE_Data_Block);
}
}
while (mb);
this->cont_ = 0;
}
int result = 0;
if (ACE_BIT_DISABLED (this->flags_,
ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE) &&
this->data_block ())
{
if (this->data_block ()->release_no_delete (lock) == 0)
result = 1;
this->data_block_ = 0;
}
// We will now commit suicide: this object *must* have come from the
// allocator given.
if (this->message_block_allocator_ == 0)
delete this;
else
{
ACE_Allocator *allocator = this->message_block_allocator_;
ACE_DES_FREE (this,
allocator->free,
ACE_Message_Block);
}
return result;
}
| ACE_Data_Block * ACE_Message_Block::replace_data_block | ( | ACE_Data_Block * | db | ) | [inline] |
Set a new data block pointer. A pointer to the original ACE_Data_Block is returned, and not released (as it is with <data_block>).
Definition at line 391 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::replace_data_block");
ACE_Data_Block *old = this->data_block_;
this->data_block_ = db;
if (db != 0)
{
// Set the read and write pointers in the <Message_Block> to point
// to the buffer in the ACE_Data_Block.
this->rd_ptr (this->data_block ()->base ());
this->wr_ptr (this->data_block ()->base ());
}
return old;
}
| void ACE_Message_Block::reset | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
Resets the Message Block data to contain nothing, i.e., sets the read and write pointers to align with the base.
Definition at line 376 of file Message_Block.inl.
| void ACE_Message_Block::reset_allocators | ( | ACE_Allocator * | allocator_strategy = 0, |
|
| ACE_Allocator * | data_block_allocator = 0, |
|||
| ACE_Allocator * | message_block_allocator = 0 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Reset all the allocators in the message block.
This method resets the allocators in all the message blocks in the chain.
Definition at line 423 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
this->data_block_->allocator_strategy_ =
allocator_strategy;
this->data_block_->data_block_allocator_ =
data_block_allocator;
this->message_block_allocator_ =
message_block_allocator;
if (this->cont () != 0)
this->cont ()->reset_allocators (allocator_strategy,
data_block_allocator,
message_block_allocator);
}
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags ACE_Message_Block::self_flags | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the current message flags.
Definition at line 33 of file Message_Block.inl.
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags ACE_Message_Block::set_flags | ( | ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | more_flags | ) | [inline] |
Bitwise-or the more_flags into the existing message flags and return the new value.
Definition at line 105 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::set_flags");
return this->data_block ()->set_flags (more_flags);
}
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags ACE_Message_Block::set_self_flags | ( | ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | more_flags | ) | [inline] |
Bitwise-or the more_flags into the existing message flags and return the new value.
Definition at line 15 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::set_self_flags");
// Later we might mask more_glags so that user can't change internal
// ones: more_flags &= ~(USER_FLAGS -1).
return ACE_SET_BITS (this->flags_, more_flags);
}
| int ACE_Message_Block::size | ( | size_t | length | ) |
Set the number of bytes in the top-level Message_Block, reallocating space if necessary. However, the rd_ptr_ and wr_ptr_ remain at the original offsets into the buffer, even if it is reallocated. Returns 0 if successful, else -1.
Definition at line 246 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::size");
// Resize the underlying <ACE_Data_Block>.
if (this->data_block ()->size (length) == -1)
return -1;
return 0;
}
| size_t ACE_Message_Block::size | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the number of bytes in the top-level Message_Block (i.e., does not consider the bytes in chained Message_Blocks).
Definition at line 147 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::size");
return this->data_block ()->size ();
}
| size_t ACE_Message_Block::space | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the number of bytes available after the <wr_ptr_> in the top-level Message_Block.
Definition at line 384 of file Message_Block.inl.
| size_t ACE_Message_Block::total_capacity | ( | void | ) | const |
Get the number of allocated bytes in all Message_Block, including chained Message_Blocks.
Definition at line 301 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::total_capacity");
size_t size = 0;
for (const ACE_Message_Block *i = this;
i != 0;
i = i->cont ())
size += i->capacity ();
return size;
}
| size_t ACE_Message_Block::total_length | ( | void | ) | const |
Get the length of the Message_Blocks, including chained Message_Blocks.
Definition at line 287 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::total_length");
size_t length = 0;
for (const ACE_Message_Block *i = this;
i != 0;
i = i->cont ())
length += i->length ();
return length;
}
| size_t ACE_Message_Block::total_size | ( | void | ) | const |
Get the total number of bytes in all Message_Blocks, including chained Message_Blocks.
Definition at line 273 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::total_size");
size_t size = 0;
for (const ACE_Message_Block *i = this;
i != 0;
i = i->cont ())
size += i->size ();
return size;
}
| void ACE_Message_Block::total_size_and_length | ( | size_t & | mb_size, | |
| size_t & | mb_length | |||
| ) | const |
Get the total number of bytes and total length in all Message_Blocks, including chained Message_Blocks.
Definition at line 258 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Message_Block::total_size_and_length");
for (const ACE_Message_Block *i = this;
i != 0;
i = i->cont ())
{
mb_size += i->size ();
mb_length += i->length ();
}
}
| void ACE_Message_Block::wr_ptr | ( | char * | ptr | ) | [inline] |
Set the write pointer to ptr.
Definition at line 310 of file Message_Block.inl.
| void ACE_Message_Block::wr_ptr | ( | size_t | n | ) | [inline] |
Set the write pointer ahead n bytes. This is used to compute the <length> of a message.
Definition at line 369 of file Message_Block.inl.
| char * ACE_Message_Block::wr_ptr | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the write pointer.
Definition at line 362 of file Message_Block.inl.
friend class ACE_Data_Block [friend] |
Definition at line 62 of file Message_Block.h.
Declare the dynamic allocation hooks.
Definition at line 583 of file Message_Block.h.
ACE_Message_Block* ACE_Message_Block::cont_ [protected] |
Pointer to next message block in the chain.
Definition at line 640 of file Message_Block.h.
ACE_Data_Block* ACE_Message_Block::data_block_ [protected] |
Pointer to the reference counted data structure that contains the actual memory buffer.
Definition at line 653 of file Message_Block.h.
Misc flags (e.g., DONT_DELETE and USER_FLAGS).
Definition at line 649 of file Message_Block.h.
ACE_Allocator* ACE_Message_Block::message_block_allocator_ [protected] |
The allocator used to destroy ourselves when release is called and create new message blocks on duplicate.
Definition at line 657 of file Message_Block.h.
ACE_Message_Block* ACE_Message_Block::next_ [protected] |
Pointer to next message in the list.
Definition at line 643 of file Message_Block.h.
ACE_Message_Block* ACE_Message_Block::prev_ [protected] |
Pointer to previous message in the list.
Definition at line 646 of file Message_Block.h.
unsigned long ACE_Message_Block::priority_ [protected] |
Priority of message.
Definition at line 628 of file Message_Block.h.
size_t ACE_Message_Block::rd_ptr_ [protected] |
Pointer to beginning of next read.
Definition at line 622 of file Message_Block.h.
size_t ACE_Message_Block::wr_ptr_ [protected] |
Pointer to beginning of next write.
Definition at line 625 of file Message_Block.h.
 1.7.0
1.7.0