#include <Hash_Naming_Context.h>
Inheritance diagram for TAO_Hash_Naming_Context:

Public Member Functions | |
| TAO_Hash_Naming_Context (PortableServer::POA_ptr poa, const char *poa_id) | |
| Constructor. | |
| void | interface (TAO_Naming_Context *i) |
| Set our pointer. | |
| virtual | ~TAO_Hash_Naming_Context (void) |
| Destructor. | |
| TAO_Naming_Context * | interface (void) |
| Get the pointer to our . | |
| int | root (void) |
| int | destroyed (void) |
| virtual void | bind (const CosNaming::Name &n, CORBA::Object_ptr obj) |
| virtual void | rebind (const CosNaming::Name &n, CORBA::Object_ptr obj) |
| virtual void | bind_context (const CosNaming::Name &n, CosNaming::NamingContext_ptr nc) |
| virtual void | rebind_context (const CosNaming::Name &n, CosNaming::NamingContext_ptr nc) |
| virtual CORBA::Object_ptr | resolve (const CosNaming::Name &n) |
| virtual void | unbind (const CosNaming::Name &n) |
| virtual CosNaming::NamingContext_ptr | bind_new_context (const CosNaming::Name &n) |
| virtual void | destroy (void) |
| virtual PortableServer::POA_ptr | _default_POA (void) |
| Returns the Default POA of this Servant object. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| CosNaming::NamingContext_ptr | get_context (const CosNaming::Name &name) |
Protected Attributes | |
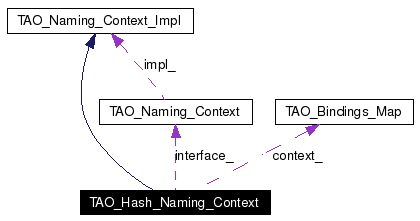
| TAO_Bindings_Map * | context_ |
| TAO_Naming_Context * | interface_ |
| TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX | lock_ |
| Lock used to serialize access to the underlying data structure. | |
| int | destroyed_ |
| PortableServer::POA_var | poa_ |
| POA we are registered with. | |
| ACE_CString | poa_id_ |
This class contains 'algorithm' code that is common to two hash-table-based implementations of the NamingContext: TAO_Transient_Naming_Context and TAO_Persistent_Naming_Context. To help achieve this 'templatization', we use the abstract base class TAO_Bindings_Map, which provides a common interface to the data structures used in TAO_Persistent_Namng_Context and TAO_Transient_Naming_Context.
Definition at line 116 of file Hash_Naming_Context.h.
|
||||||||||||
|
Constructor.
Definition at line 31 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp.
00033 : context_ (0), 00034 interface_ (0), 00035 destroyed_ (0), 00036 poa_ (PortableServer::POA::_duplicate (poa)), 00037 poa_id_ (poa_id) 00038 { 00039 } |
|
|
Destructor.
Definition at line 47 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp.
00048 {
00049 delete context_;
00050 }
|
|
|
Returns the Default POA of this Servant object.
Implements TAO_Naming_Context_Impl. Definition at line 53 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. Referenced by TAO_Storable_Naming_Context::destroy(), and destroy().
00054 {
00055 return PortableServer::POA::_duplicate (this->poa_.in ());
00056 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Create a binding for name and object in the naming context. Compound names are treated as follows: ctx->bind (<c1; c2; c3; cn>, obj) = (ctx->resolve (<c1; c2; cn-1>))->bind (, obj) if the there already exists a binding for the specified name, exception is thrown. Naming contexts should be bound using and in order to participate in name resolution later. Implements TAO_Naming_Context_Impl. Reimplemented in TAO_Storable_Naming_Context. Definition at line 107 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX, TAO_Bindings_Map::bind(), get_context(), CosNaming::Name, and TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX.
00108 {
00109 ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX (TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX,
00110 ace_mon, this->lock_,
00111 CORBA::INTERNAL ());
00112
00113 // Check to make sure this object didn't have <destroy> method
00114 // invoked on it.
00115 if (this->destroyed_)
00116 throw CORBA::OBJECT_NOT_EXIST ();
00117
00118 // Get the length of the name.
00119 CORBA::ULong const name_len = n.length ();
00120
00121 // Check for invalid name.
00122 if (name_len == 0)
00123 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::InvalidName();
00124
00125 // If we received compound name, resolve it to get the context in
00126 // which the binding should take place, then perform the binding on
00127 // target context.
00128 if (name_len > 1)
00129 {
00130 CosNaming::NamingContext_var context = this->get_context (n);
00131
00132 CosNaming::Name simple_name;
00133 simple_name.length (1);
00134 simple_name[0] = n[name_len - 1];
00135 try
00136 {
00137 context->bind (simple_name, obj);
00138 }
00139 catch (const CORBA::SystemException&)
00140 {
00141 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::CannotProceed(
00142 context.in (), simple_name);
00143 }
00144 }
00145 // If we received a simple name, we need to bind it in this context.
00146 else
00147 {
00148 // Try binding the name.
00149 int result = this->context_->bind (n[0].id,
00150 n[0].kind,
00151 obj,
00152 CosNaming::nobject);
00153 if (result == 1)
00154 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::AlreadyBound();
00155
00156 // Something went wrong with the internal structure
00157 else if (result == -1)
00158 throw CORBA::INTERNAL ();
00159 }
00160 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
This is the version of specifically for binding naming contexts, so that they will participate in name resolution when compound names are passed to be resolved. Implements TAO_Naming_Context_Impl. Reimplemented in TAO_Storable_Naming_Context. Definition at line 221 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX, TAO_Bindings_Map::bind(), get_context(), CORBA::is_nil(), CosNaming::Name, and TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX. Referenced by bind_new_context().
00223 {
00224 ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX (TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX, ace_mon,
00225 this->lock_,
00226 CORBA::INTERNAL ());
00227
00228 // Check to make sure this object didn't have <destroy> method
00229 // invoked on it.
00230 if (this->destroyed_)
00231 throw CORBA::OBJECT_NOT_EXIST ();
00232
00233 // Do not allow binding of nil context reference.
00234 if (CORBA::is_nil (nc))
00235 throw CORBA::BAD_PARAM ();
00236
00237 // Get the length of the name.
00238 CORBA::ULong const name_len = n.length ();
00239
00240 // Check for invalid name.
00241 if (name_len == 0)
00242 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::InvalidName();
00243
00244 // If we received compound name, resolve it to get the context in
00245 // which the binding should take place, then perform the binding on
00246 // target context.
00247 if (name_len > 1)
00248 {
00249 CosNaming::NamingContext_var context = get_context (n);
00250
00251 CosNaming::Name simple_name;
00252 simple_name.length (1);
00253 simple_name[0] = n[name_len - 1];
00254 try
00255 {
00256 context->bind_context (simple_name, nc);
00257 }
00258 catch (const CORBA::SystemException&)
00259 {
00260 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::CannotProceed(
00261 context.in (), simple_name);
00262 }
00263 }
00264 // If we received a simple name, we need to bind it in this context.
00265 else
00266 {
00267 // Try binding the name.
00268 int result = this->context_->bind (n[0].id,
00269 n[0].kind,
00270 nc,
00271 CosNaming::ncontext);
00272 if (result == 1)
00273 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::AlreadyBound();
00274
00275 // Something went wrong with the internal structure
00276 else if (result == -1)
00277 throw CORBA::INTERNAL ();
00278 }
00279 }
|
|
|
This operation creates a new context and binds it to the name supplied as an argument. The newly-created context is implemented by the same server as the context in which it was bound (the name argument excluding the last component). Implements TAO_Naming_Context_Impl. Reimplemented in TAO_Storable_Naming_Context. Definition at line 482 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX, bind_context(), get_context(), CosNaming::Name, TAO_Naming_Context_Impl::new_context(), and TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX.
00483 {
00484 ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX (TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX,
00485 ace_mon,
00486 this->lock_,
00487 CORBA::INTERNAL ());
00488
00489 // Check to make sure this object didn't have <destroy> method
00490 // invoked on it.
00491 if (this->destroyed_)
00492 throw CORBA::OBJECT_NOT_EXIST ();
00493
00494 // Get the length of the name.
00495 CORBA::ULong name_len = n.length ();
00496
00497 // Check for invalid name.
00498 if (name_len == 0)
00499 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::InvalidName();
00500
00501 // If we received compound name, resolve it to get the context in
00502 // which the binding should take place, then perform the operation on
00503 // target context.
00504 if (name_len > 1)
00505 {
00506 CosNaming::NamingContext_var context =
00507 get_context (n);
00508
00509 CosNaming::Name simple_name;
00510 simple_name.length (1);
00511 simple_name[0] = n[name_len - 1];
00512 return context->bind_new_context (simple_name);
00513 }
00514
00515 // If we received a simple name, we need to bind it in this context.
00516
00517 // Stores our new Naming Context.
00518 CosNaming::NamingContext_var result =
00519 CosNaming::NamingContext::_nil ();
00520
00521 // Create new context.
00522 result = new_context ();
00523
00524 // Bind the new context to the name.
00525 try
00526 {
00527 bind_context (n, result.in ());
00528 }
00529 catch (const CORBA::Exception&)
00530 {
00531 // If the bind() operation fails we must destroy the recently
00532 // created context, should any exceptions be raised by the
00533 // destroy() operation we want to ignore them.
00534 {
00535 try
00536 {
00537 result->destroy ();
00538 }
00539 catch (const CORBA::Exception&)
00540 {
00541 }
00542 }
00543 // Re-raise the exception in bind_context()
00544 throw;
00545 }
00546 return result._retn ();
00547 }
|
|
|
Delete the naming context. The user should take care to any bindings in which the given context is bound to some names, to avoid dangling references when invoking operation. NOTE: is a no-op on the root context. NOTE: after is invoked on a Naming Context, all BindingIterators associated with that Naming Context are also destroyed. Implements TAO_Naming_Context_Impl. Reimplemented in TAO_Storable_Naming_Context. Definition at line 550 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. References _default_POA(), ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX, TAO_Bindings_Map::current_size(), poa_id_, root(), and TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX.
00551 {
00552 ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX (TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX,
00553 ace_mon,
00554 this->lock_,
00555 CORBA::INTERNAL ());
00556
00557 // Check to make sure this object didn't have <destroy> method
00558 // invoked on it.
00559 if (this->destroyed_)
00560 throw CORBA::OBJECT_NOT_EXIST ();
00561
00562 if (this->context_->current_size () != 0)
00563 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::NotEmpty();
00564
00565 // Destroy is a no-op on a root context.
00566 if (root ())
00567 return;
00568
00569 else
00570 {
00571 this->destroyed_ = 2;
00572
00573 // Remove self from POA. Because of reference counting, the POA
00574 // will automatically delete the servant when all pending requests
00575 // on this servant are complete.
00576
00577 PortableServer::POA_var poa =
00578 this->_default_POA ();
00579
00580 PortableServer::ObjectId_var id =
00581 PortableServer::string_to_ObjectId (poa_id_.fast_rep ());
00582
00583 poa->deactivate_object (id.in ());
00584 }
00585 }
|
|
|
Returns true if this context had operation invoked on it, and false otherwise. Definition at line 595 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. Referenced by TAO_Bindings_Iterator< ITERATOR, TABLE_ENTRY >::next_n(), and TAO_Bindings_Iterator< ITERATOR, TABLE_ENTRY >::next_one().
00596 {
00597 return this->destroyed_;
00598 }
|
|
|
is used by methods that need to resolve a compound name before performing the actual operation (e.g., bind, unbind, etc.) takes a full name (including the last component that doesn't need to be resolved), and returns a pointer to the target context. Definition at line 59 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. References CORBA::is_nil(), CosNaming::Name, and resolve(). Referenced by TAO_Storable_Naming_Context::bind(), bind(), TAO_Storable_Naming_Context::bind_context(), bind_context(), TAO_Storable_Naming_Context::bind_new_context(), bind_new_context(), TAO_Storable_Naming_Context::rebind(), rebind(), TAO_Storable_Naming_Context::rebind_context(), rebind_context(), TAO_Storable_Naming_Context::unbind(), and unbind().
00060 {
00061 // Naming context we will return.
00062 CosNaming::NamingContext_var result =
00063 CosNaming::NamingContext::_nil ();
00064
00065 // Create compound name to be resolved, i.e.,
00066 // (<name> - last component). To avoid copying, we can just reuse
00067 // <name>'s buffer, since we will not be modifying it.
00068 CORBA::ULong name_len = name.length ();
00069 CosNaming::Name comp_name (name.maximum (),
00070 name_len - 1,
00071 const_cast<CosNaming::NameComponent*> (name.get_buffer ()));
00072 try
00073 {
00074 // Resolve the name.
00075 CORBA::Object_var context = resolve (comp_name);
00076
00077 // Try narrowing object reference to the NamingContext type.
00078 result = CosNaming::NamingContext::_narrow (context.in ());
00079 }
00080 catch (CosNaming::NamingContext::NotFound& ex)
00081 {
00082 // Add the last component of the name, which was stripped before
00083 // the call to resolve.
00084 CORBA::ULong rest_len = ex.rest_of_name.length () + 1;
00085 ex.rest_of_name.length (rest_len);
00086 ex.rest_of_name[rest_len - 1] = name[name_len - 1];
00087
00088 throw;
00089 }
00090
00091 if (CORBA::is_nil (result.in ()))
00092 {
00093 CosNaming::Name rest;
00094 rest.length (2);
00095 rest[0] = name[name_len - 2];
00096 rest[1] = name[name_len - 1];
00097 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::NotFound(
00098 CosNaming::NamingContext::not_context,
00099 rest);
00100 }
00101 // Finally, if everything went smoothly, just return the resolved
00102 // context.
00103 return result._retn ();
00104 }
|
|
|
Get the pointer to our .
Definition at line 601 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. References interface_.
00602 {
00603 return this->interface_;
00604 }
|
|
|
Set our pointer.
Definition at line 42 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. References interface_. Referenced by TAO_Bindings_Iterator< ITERATOR, TABLE_ENTRY >::~TAO_Bindings_Iterator().
00043 {
00044 this->interface_ = i;
00045 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
This is similar to operation above, except for when the binding for the specified name already exists in the specified context. In that case, the existing binding is replaced with the new one. Implements TAO_Naming_Context_Impl. Reimplemented in TAO_Storable_Naming_Context. Definition at line 163 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX, get_context(), CosNaming::Name, TAO_Bindings_Map::rebind(), and TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX.
00165 {
00166 ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX (TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX, ace_mon,
00167 this->lock_,
00168 CORBA::INTERNAL ());
00169
00170 // Check to make sure this object didn't have <destroy> method
00171 // invoked on it.
00172 if (this->destroyed_)
00173 throw CORBA::OBJECT_NOT_EXIST ();
00174
00175 // Get the length of the name.
00176 CORBA::ULong const name_len = n.length ();
00177
00178 // Check for invalid name.
00179 if (name_len == 0)
00180 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::InvalidName();
00181
00182 // If we received compound name, resolve it to get the context in
00183 // which the rebinding should take place, then perform the rebinding
00184 // on target context.
00185 if (name_len > 1)
00186 {
00187 CosNaming::NamingContext_var context = get_context (n);
00188
00189 CosNaming::Name simple_name;
00190 simple_name.length (1);
00191 simple_name[0] = n[name_len - 1];
00192 try
00193 {
00194 context->rebind (simple_name, obj);
00195 }
00196 catch (const CORBA::SystemException&)
00197 {
00198 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::CannotProceed(
00199 context.in (), simple_name);
00200 }
00201 }
00202 else
00203 // If we received a simple name, we need to rebind it in this
00204 // context.
00205 {
00206 int result = this->context_->rebind (n[0].id,
00207 n[0].kind,
00208 obj,
00209 CosNaming::nobject);
00210 // Check for error conditions.
00211 if (result == -1)
00212 throw CORBA::INTERNAL ();
00213
00214 else if (result == -2)
00215 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::NotFound(
00216 CosNaming::NamingContext::not_object, n);
00217 }
00218 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
This is a version of specifically for naming contexts, so that they can participate in name resolution when compound names are passed. Implements TAO_Naming_Context_Impl. Reimplemented in TAO_Storable_Naming_Context. Definition at line 282 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX, get_context(), CosNaming::Name, TAO_Bindings_Map::rebind(), and TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX.
00284 {
00285 ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX (TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX, ace_mon,
00286 this->lock_,
00287 CORBA::INTERNAL ());
00288
00289 // Check to make sure this object didn't have <destroy> method
00290 // invoked on it.
00291 if (this->destroyed_)
00292 throw CORBA::OBJECT_NOT_EXIST ();
00293
00294 // Get the length of the name.
00295 CORBA::ULong const name_len = n.length ();
00296
00297 // Check for invalid name.
00298 if (name_len == 0)
00299 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::InvalidName();
00300
00301 // If we received compound name, resolve it to get the context in
00302 // which the rebinding should take place, then perform the rebinding
00303 // on target context.
00304 if (name_len > 1)
00305 {
00306 CosNaming::NamingContext_var context =
00307 get_context (n);
00308
00309 CosNaming::Name simple_name;
00310 simple_name.length (1);
00311 simple_name[0] = n[name_len - 1];
00312 try
00313 {
00314 context->rebind_context (simple_name, nc);
00315 }
00316 catch (const CORBA::SystemException&)
00317 {
00318 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::CannotProceed(
00319 context.in (), simple_name);
00320 }
00321 }
00322 else
00323 // If we received a simple name, we need to rebind it in this
00324 // context.
00325 {
00326 int result = this->context_->rebind (n[0].id,
00327 n[0].kind,
00328 nc,
00329 CosNaming::ncontext);
00330 // Check for error conditions.
00331 if (result == -1)
00332 throw CORBA::INTERNAL ();
00333
00334 else if (result == -2)
00335 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::NotFound(
00336 CosNaming::NamingContext::not_context,
00337 n);
00338 }
00339 }
|
|
|
Return object reference that is bound to the name. Compound name resolve is defined as follows: ctx->resolve (<c1; c2; cn>) = ctx->resolve (<c1; c2 cn-1>)->resolve () The naming service does not return the type of the object. Clients are responsible for "narrowing" the object to the appropriate type. Implements TAO_Naming_Context_Impl. Reimplemented in TAO_Storable_Naming_Context. Definition at line 342 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX, TAO_Bindings_Map::find(), CORBA::is_nil(), CosNaming::Name, and TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX. Referenced by get_context().
00343 {
00344 ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX (TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX, ace_mon, this->lock_,
00345 CORBA::INTERNAL ());
00346
00347 // Check to make sure this object didn't have <destroy> method
00348 // invoked on it.
00349 if (this->destroyed_)
00350 throw CORBA::OBJECT_NOT_EXIST ();
00351
00352 // Get the length of the name.
00353 CORBA::ULong const name_len = n.length ();
00354
00355 // Check for invalid name.
00356 if (name_len == 0)
00357 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::InvalidName();
00358
00359 // Resolve the first component of the name.
00360
00361 // Stores the binding type for the first name component.
00362 CosNaming::BindingType type;
00363
00364 // Stores the object reference bound to the first name component.
00365 CORBA::Object_var result;
00366
00367 if (this->context_->find (n[0].id,
00368 n[0].kind,
00369 result.out (),
00370 type) == -1)
00371 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::NotFound(
00372 CosNaming::NamingContext::missing_node,
00373 n);
00374
00375 // If the name we have to resolve is a compound name, we need to
00376 // resolve it recursively.
00377 if (name_len > 1)
00378 {
00379 CosNaming::NamingContext_var context =
00380 CosNaming::NamingContext::_nil ();
00381
00382 if (type == CosNaming::ncontext)
00383 {
00384 // Narrow to NamingContext.
00385 context = CosNaming::NamingContext::_narrow (result.in ());
00386 }
00387 else
00388 // The first name component wasn't bound to a NamingContext.
00389 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::NotFound(
00390 CosNaming::NamingContext::not_context,
00391 n);
00392
00393 // If narrow failed...
00394 if (CORBA::is_nil (context.in ()))
00395 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::NotFound(
00396 CosNaming::NamingContext::not_context,
00397 n);
00398 else
00399 {
00400 // Successfully resolved the first name component, need to
00401 // recursively call resolve on <n> without the first component.
00402
00403 // We need a name just like <n> but without the first
00404 // component. Instead of copying data we can reuse <n>'s
00405 // buffer since we will only be using it for 'in' parameters
00406 // (no modifications).
00407 CosNaming::Name rest_of_name
00408 (n.maximum () - 1,
00409 n.length () - 1,
00410 const_cast<CosNaming::NameComponent*> (n.get_buffer ())
00411 + 1);
00412
00413 // If there are any exceptions, they will propagate up.
00414 try
00415 {
00416 CORBA::Object_ptr resolved_ref;
00417 resolved_ref = context->resolve (rest_of_name);
00418 return resolved_ref;
00419 }
00420 catch (const CORBA::SystemException&)
00421 {
00422 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::CannotProceed(
00423 context.in (), rest_of_name);
00424 }
00425 }
00426 }
00427 // If the name we had to resolve was simple, we just need to return
00428 // the result.
00429 return result._retn ();
00430 }
|
|
|
Returns true if this Naming Context is a root Naming Context for the server, and false otherwise. Definition at line 588 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. References ACE_OS::strcmp(), and TAO_ROOT_NAMING_CONTEXT. Referenced by TAO_Storable_Naming_Context::destroy(), and destroy().
00589 {
00590 return (ACE_OS::strcmp (this->poa_id_.fast_rep (),
00591 TAO_ROOT_NAMING_CONTEXT) == 0);
00592 }
|
|
|
Remove the name binding from the context. When compound names are used, unbind is defined as follows: ctx->unbind (<c1; c2; cn>) = (ctx->resolve (<c1; c2; cn-1>))->unbind () Implements TAO_Naming_Context_Impl. Reimplemented in TAO_Storable_Naming_Context. Definition at line 433 of file Hash_Naming_Context.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX, get_context(), CosNaming::Name, TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX, and TAO_Bindings_Map::unbind().
00434 {
00435 ACE_GUARD_THROW_EX (TAO_SYNCH_RECURSIVE_MUTEX, ace_mon,
00436 this->lock_,
00437 CORBA::INTERNAL ());
00438
00439 // Check to make sure this object didn't have <destroy> method
00440 // invoked on it.
00441 if (this->destroyed_)
00442 throw CORBA::OBJECT_NOT_EXIST ();
00443
00444 // Get the length of the name.
00445 CORBA::ULong const name_len = n.length ();
00446
00447 // Check for invalid name.
00448 if (name_len == 0)
00449 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::InvalidName();
00450
00451 // If we received compound name, resolve it to get the context in
00452 // which the unbinding should take place, then perform the unbinding
00453 // on target context.
00454 if (name_len > 1)
00455 {
00456 CosNaming::NamingContext_var context =
00457 get_context (n);
00458
00459 CosNaming::Name simple_name;
00460 simple_name.length (1);
00461 simple_name[0] = n[name_len - 1];
00462 try
00463 {
00464 context->unbind (simple_name);
00465 }
00466 catch (const CORBA::SystemException&)
00467 {
00468 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::CannotProceed(
00469 context.in (), simple_name);
00470 }
00471 }
00472 // If we received a simple name, we need to unbind it in this
00473 // context.
00474 else
00475 if (this->context_->unbind (n[0].id,
00476 n[0].kind) == -1)
00477 throw CosNaming::NamingContext::NotFound(
00478 CosNaming::NamingContext::missing_node, n);
00479 }
|
|
|
Pointer to the data structure used to store this Naming Context's bindings. is initialized with a concrete data structure by subclasses, which know which data structure to use. Definition at line 236 of file Hash_Naming_Context.h. Referenced by TAO_Storable_Naming_Context::new_context(), and TAO_Storable_Naming_Context::recreate_all(). |
|
|
Flag indicating whether this Naming Context is no longer valid. This flag is necessary because immediate destruction might not be possible if there are pending requests on this servant in the POA. Definition at line 255 of file Hash_Naming_Context.h. |
|
|
Pointer to the object for which we serve as a , i.e., the object that delegates to us all client CosNaming::NamingContext CORBA calls. We need this pointer for reference counting. Definition at line 244 of file Hash_Naming_Context.h. Referenced by interface(). |
|
|
Lock used to serialize access to the underlying data structure.
Definition at line 247 of file Hash_Naming_Context.h. |
|
|
POA we are registered with.
Reimplemented in TAO_Storable_Naming_Context. Definition at line 258 of file Hash_Naming_Context.h. |
|
|
ID with which we are registered with . Note, if is equivalent to TAO_ROOT_NAMING_CONTEXT, then this Naming Context is the root Naming Context for the server, i.e., it is un<destroy>able. Definition at line 265 of file Hash_Naming_Context.h. Referenced by destroy(), and TAO_Persistent_Naming_Context::make_new_context(). |
 1.3.6
1.3.6