#include <Timer_Wheel_T.h>
Inheritance diagram for ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >:

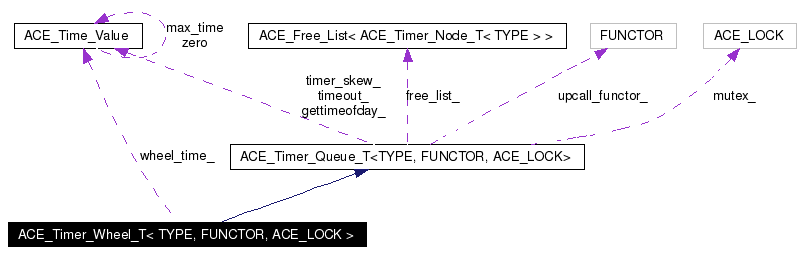
Public Types | |
| typedef ACE_Timer_Wheel_Iterator_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK > | Iterator |
| Type of iterator. | |
| typedef ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE > | Node |
| typedef ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK > | Base |
| Type inherited from. | |
| typedef ACE_Free_List< Node > | FreeList |
Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_Timer_Wheel_T (FUNCTOR *upcall_functor=0, FreeList *freelist=0) | |
| Default constructor. | |
| ACE_Timer_Wheel_T (u_int spoke_count, u_int resolution, size_t prealloc=0, FUNCTOR *upcall_functor=0, FreeList *freelist=0) | |
| Constructor with opportunities to set the wheelsize and resolution. | |
| virtual | ~ACE_Timer_Wheel_T (void) |
| Destructor. | |
| virtual int | is_empty (void) const |
| True if queue is empty, else false. | |
| virtual const ACE_Time_Value & | earliest_time (void) const |
| virtual int | reset_interval (long timer_id, const ACE_Time_Value &interval) |
| virtual int | cancel (const TYPE &type, int dont_call_handle_close=1) |
| virtual int | cancel (long timer_id, const void **act=0, int dont_call_handle_close=1) |
| virtual int | expire (void) |
| int | expire (const ACE_Time_Value &) |
| virtual ACE_Timer_Queue_Iterator_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK > & | iter (void) |
| Returns a pointer to this 's iterator. | |
| virtual ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE > * | remove_first (void) |
| Removes the earliest node from the queue and returns it. | |
| virtual void | dump (void) const |
| Dump the state of an object. | |
| virtual ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE > * | get_first (void) |
| Reads the earliest node from the queue and returns it. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual long | schedule_i (const TYPE &type, const void *act, const ACE_Time_Value &future_time, const ACE_Time_Value &interval) |
| Schedules a timer. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE > * | get_first_i (void) const |
| ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE > * | remove_first_expired (const ACE_Time_Value &now) |
| void | open_i (size_t prealloc, u_int spokes, u_int res) |
| virtual void | reschedule (ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE > *) |
| ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE > * | find_spoke_node (u_int spoke, long timer_id) const |
| Searches for a node by timer_id within one spoke. | |
| ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE > * | find_node (long timer_id) const |
| u_int | calculate_spoke (const ACE_Time_Value &expire) const |
| long | generate_timer_id (u_int spoke) |
| void | schedule_i (ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE > *n, u_int spoke, const ACE_Time_Value &expire) |
| The shared scheduling functionality between schedule() and reschedule(). | |
| void | cancel_i (ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE > *n) |
| Shared subset of the two cancel() methods. | |
| void | unlink (ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE > *n) |
| void | recalc_earliest (const ACE_Time_Value &last) |
| int | power2bits (int n, int min_bits, int max_bits) |
| ACE_Timer_Wheel_T (const ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK > &) | |
| void | operator= (const ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK > &) |
Private Attributes | |
| ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE > ** | spokes_ |
| Timing Wheel. | |
| u_int | spoke_count_ |
| Size of the timing wheel. | |
| int | spoke_bits_ |
| Number of timer_id bits used for the spoke. | |
| u_int | max_per_spoke_ |
| Maximum number of timers per spoke. | |
| int | res_bits_ |
| Resolution (in microsoconds) of the timing wheel. | |
| u_int | earliest_spoke_ |
| Index of the list with the earliest time. | |
| Iterator * | iterator_ |
| Iterator used to expire timers. | |
| ACE_Time_Value | wheel_time_ |
| The total amount of time in one iteration of the wheel. (resolution * spoke_count). | |
| u_int | timer_count_ |
| The total number of timers currently scheduled. | |
Friends | |
| class | ACE_Timer_Wheel_Iterator_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK > |
| Iterator is a friend. | |
This implementation uses a hash table of ordered doubly- linked lists of absolute times. The enhancements over the ACE_Timer_List include adding a free list and the ability to preallocate nodes. Timer Wheel is based on the timing wheel implementation used in Adam M. Costello and George Varghese's paper "Redesigning the BSD Callout and Timer Facilities" (http://dworkin.wustl.edu/~varghese/PAPERS/newbsd.ps.Z)
Definition at line 92 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h.
|
|||||
|
Type inherited from.
Definition at line 101 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h. |
|
|||||
|
Definition at line 102 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h. |
|
|||||
|
Type of iterator.
Definition at line 96 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h. |
|
|||||
|
Definition at line 99 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h. |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Default constructor. Default Constructor that sets defaults for spoke_count_ and resolution_ and doesn't do any preallocation.
Definition at line 46 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_DEFAULT_TIMER_WHEEL_RESOLUTION, ACE_DEFAULT_TIMER_WHEEL_SIZE, and ACE_TRACE.
00049 : Base (upcall_functor, freelist) 00050 , spokes_(0) 00051 , spoke_count_(0) // calculated in open_i 00052 , spoke_bits_(0) 00053 , res_bits_ (0) 00054 , earliest_spoke_ (0) 00055 , iterator_(0) 00056 , timer_count_(0) 00057 { 00058 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::ACE_Timer_Wheel_T"); 00059 this->open_i (0, 00060 ACE_DEFAULT_TIMER_WHEEL_SIZE, 00061 ACE_DEFAULT_TIMER_WHEEL_RESOLUTION); 00062 } |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Constructor with opportunities to set the wheelsize and resolution. Constructor that sets up the timing wheel and also may preallocate some nodes on the free list
Definition at line 76 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_TRACE.
00081 : Base (upcall_functor, freelist) 00082 , spokes_ (0) 00083 , spoke_count_ (0) // calculated in open_i 00084 , spoke_bits_ (0) 00085 , res_bits_ (0) 00086 , earliest_spoke_ (0) 00087 , iterator_ (0) 00088 , timer_count_ (0) 00089 { 00090 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::ACE_Timer_Wheel_T"); 00091 this->open_i (prealloc, spoke_count, resolution); 00092 } |
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
Uses a simple hash to find which spoke to use based on when the timer is due to expire. Hopefully the 64bit int operations avoid any overflow problems. Definition at line 273 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::reschedule(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::schedule_i().
00274 {
00275 return static_cast<u_int> ((t.msec () >> this->res_bits_) & (this->spoke_count_ - 1));
00276 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cancels the single timer that is specified by the timer_id. In this case the timer_id is actually a pointer to the node, so we cast it to the node. This can be dangerous if the timer_id is made up (or deleted twice) so we do a little sanity check. Finally we update the earliest time in case the earliest timer was removed.
Implements ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 592 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::cancel_i(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::find_node(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_act(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::get_first_i(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_timer_value(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_type(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::recalc_earliest(), and ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::upcall_functor().
00595 {
00596 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::cancel");
00597 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_LOCK, ace_mon, this->mutex_, -1));
00598 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* n = this->find_node (timer_id);
00599 if (n != 0)
00600 {
00601 ACE_Time_Value last = n->get_timer_value ();
00602
00603 int recalc = (this->get_first_i () == n);
00604
00605 // Call the close hooks.
00606 int cookie = 0;
00607
00608 // cancel_type() called once per <type>.
00609 this->upcall_functor ().cancel_type (*this,
00610 n->get_type (),
00611 skip_close,
00612 cookie);
00613
00614 // cancel_timer() called once per <timer>.
00615 this->upcall_functor ().cancel_timer (*this,
00616 n->get_type (),
00617 skip_close,
00618 cookie);
00619 if (act != 0)
00620 *act = n->get_act ();
00621
00622 this->cancel_i (n);
00623
00624 if (recalc)
00625 this->recalc_earliest (last);
00626
00627 return 1;
00628 }
00629 return 0;
00630 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Cancel all timer associated with . If is 0 then the will be invoked. Returns number of timers cancelled. Implements ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 510 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::cancel_i(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::get_first(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_next(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_timer_value(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_type(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::is_empty(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::recalc_earliest(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::spoke_count_, ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::spokes_, and ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::upcall_functor().
00511 {
00512 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::cancel");
00513 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_LOCK, ace_mon, this->mutex_, -1));
00514
00515 int num_canceled = 0; // Note : Technically this can overflow.
00516
00517 if (!this->is_empty ())
00518 {
00519 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* first = this->get_first ();
00520 ACE_Time_Value last = first->get_timer_value ();
00521 int recalc = 0;
00522
00523 for (u_int i = 0; i < this->spoke_count_; ++i)
00524 {
00525 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* root = this->spokes_[i];
00526 for (ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* n = root->get_next (); n != root; )
00527 {
00528 if (n->get_type () == type)
00529 {
00530 ++num_canceled;
00531 if (n == first)
00532 recalc = 1;
00533
00534 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* tmp = n;
00535 n = n->get_next ();
00536
00537 this->cancel_i (tmp);
00538 }
00539 else
00540 {
00541 n = n->get_next ();
00542 }
00543 }
00544 }
00545
00546 if (recalc)
00547 this->recalc_earliest (last);
00548 }
00549
00550 // Call the close hooks.
00551 int cookie = 0;
00552
00553 // cancel_type() called once per <type>.
00554 this->upcall_functor ().cancel_type (*this,
00555 type,
00556 skip_close,
00557 cookie);
00558
00559 for (int i = 0;
00560 i < num_canceled;
00561 ++i)
00562 {
00563 // cancel_timer() called once per <timer>.
00564 this->upcall_functor ().cancel_timer (*this,
00565 type,
00566 skip_close,
00567 cookie);
00568 }
00569
00570 return num_canceled;
00571 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Shared subset of the two cancel() methods.
Definition at line 634 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::free_node(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::unlink(). Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::cancel().
|
|
||||||||||
|
Dump the state of an object. Dumps out the size of the wheel, the resolution, and the contents of the wheel. Reimplemented from ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 690 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_BEGIN_DUMP, ACE_DEBUG, ACE_END_DUMP, ACE_LIB_TEXT, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::dump(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_next(), LM_DEBUG, ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::spoke_count_, and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::spokes_.
00691 {
00692 #if defined (ACE_HAS_DUMP)
00693 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::dump");
00694 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_BEGIN_DUMP, this));
00695
00696 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG,
00697 ACE_LIB_TEXT ("\nspoke_count_ = %d"), this->spoke_count_));
00698 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG,
00699 ACE_LIB_TEXT ("\nresolution_ = %d"), 1 << this->res_bits_));
00700 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG,
00701 ACE_LIB_TEXT ("\nwheel_ = \n")));
00702
00703 for (u_int i = 0; i < this->spoke_count_; ++i)
00704 {
00705 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_LIB_TEXT ("%d\n"), i));
00706 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* root = this->spokes_[i];
00707 for (ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* n = root->get_next ();
00708 n != root;
00709 n = n->get_next ())
00710 {
00711 n->dump ();
00712 }
00713 }
00714
00715 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_END_DUMP));
00716 #endif /* ACE_HAS_DUMP */
00717 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Returns the time of the earlier node in the . Must be called on a non-empty queue. Implements ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 259 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::get_first_i(), and ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_timer_value().
00260 {
00261 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::earliest_time");
00262 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* n = this->get_first_i ();
00263 if (n != 0)
00264 return n->get_timer_value ();
00265 return ACE_Time_Value::zero;
00266 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
This is a specialized version of expire that is more suited for the internal data representation.
Reimplemented from ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 811 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::free_node(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_dispatch_info(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_interval(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_timer_value(), ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::postinvoke(), ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::preinvoke(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::remove_first_expired(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::reschedule(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::set_timer_value(), and ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::upcall().
00812 {
00813 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::expire");
00814 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_LOCK, ace_mon, this->mutex_, -1));
00815
00816 int expcount = 0;
00817 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* n = this->remove_first_expired (cur_time);
00818
00819 while (n != 0)
00820 {
00821 ++expcount;
00822
00823 //ACE_ERROR((LM_ERROR, "Expiring %x\n", (long) n));
00824
00825 ACE_Timer_Node_Dispatch_Info_T<TYPE> info;
00826
00827 // Get the dispatch info
00828 n->get_dispatch_info (info);
00829
00830 if (n->get_interval () > ACE_Time_Value::zero)
00831 {
00832 // Make sure that we skip past values that have already
00833 // "expired".
00834 do
00835 n->set_timer_value (n->get_timer_value () +
00836 n->get_interval ());
00837 while (n->get_timer_value () <= cur_time);
00838
00839 this->reschedule (n);
00840 }
00841 else
00842 {
00843 this->free_node (n);
00844 }
00845
00846 const void *upcall_act = 0;
00847
00848 this->preinvoke (info, cur_time, upcall_act);
00849
00850 this->upcall (info, cur_time);
00851
00852 this->postinvoke (info, cur_time, upcall_act);
00853
00854 n = this->remove_first_expired (cur_time);
00855 }
00856
00857 return expcount;
00858 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Run the for all timers whose values are <= <ACE_OS::gettimeofday>. Also accounts for . Returns the number of timers canceled. Reimplemented from ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 797 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::expire().
00798 {
00799 return ACE_Timer_Queue_T<TYPE,FUNCTOR,ACE_LOCK>::expire ();
00800 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Searches all spokes for a node matching the specified timer_id Uses the spoke encoded in the timer_id as a starting place. Definition at line 213 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::find_spoke_node(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::spoke_count_. Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::cancel(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::reset_interval().
00214 {
00215 if (timer_id == -1)
00216 return 0;
00217
00218 // Search the spoke where timer_id was originally scheduled
00219 u_int spoke_mask = this->spoke_count_ - 1;
00220 u_int start = timer_id & spoke_mask;
00221 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* n = this->find_spoke_node (start, timer_id);
00222 if (n != 0)
00223 return n;
00224
00225 //ACE_ERROR((LM_ERROR, "Node not found in original spoke.\n"));
00226
00227 // Search the rest of the spokes
00228 for (u_int i = 0; i < this->spoke_count_; ++i)
00229 {
00230 if (i != start)
00231 { // already searched this one
00232 n = this->find_spoke_node (i, timer_id);
00233 if (n != 0)
00234 return n;
00235 }
00236 }
00237
00238 //ACE_ERROR((LM_ERROR, "Node not found.\n"));
00239 return 0;
00240 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Searches for a node by timer_id within one spoke.
Definition at line 196 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_next(), and ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_timer_id(). Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::find_node(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::generate_timer_id().
00197 {
00198 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* root = this->spokes_[spoke];
00199 for (ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* n = root->get_next ();
00200 n != root;
00201 n = n->get_next ())
00202 {
00203 if (n->get_timer_id () == timer_id)
00204 return n;
00205 }
00206 return 0;
00207 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Generates a unique timer_id for the given spoke. It should be pretty fast until the point where the counter overflows. At that time you have to do exhaustive searches within the spoke to ensure that a particular timer id is not already in use. Some optimizations are in place so that this hopefully doesn't have to happen often. Definition at line 284 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::find_spoke_node(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_act(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_next(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_timer_id(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::set_act(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::spoke_bits_, ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::spoke_count_, and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::spokes_. Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::schedule_i().
00285 {
00286
00287 int cnt_bits = sizeof (long) * 8 - this->spoke_bits_;
00288 long max_cnt = ((long)1 << cnt_bits) - 1;
00289 if (spoke == this->spoke_count_)
00290 --max_cnt; // Because -1 is used as a special invalid timer_id.
00291
00292 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* root = this->spokes_[spoke];
00293
00294 if (root == root->get_next ())
00295 root->set_act(0);
00296
00297 // We use this field to keep track of the next counter value that
00298 // may be in use. Of course it may have expired, so we just use
00299 // this field so that we know when we don't have to check for duplicates
00300 #if defined (ACE_WIN64)
00301 // The cast below is legit... we know that long is shorter than a
00302 // pointer, but are only using it as a 'long' storage area.
00303 # pragma warning(push)
00304 # pragma warning(disable : 4311)
00305 #endif /* ACE_WIN64 */
00306 long next_cnt = reinterpret_cast<long> (root->get_act ());
00307 #if defined (ACE_WIN64)
00308 # pragma warning(pop)
00309 #endif /* ACE_WIN64 */
00310
00311 // This field is used as a counter instead of a timer_id.
00312 long cnt = root->get_timer_id ();
00313
00314 if (cnt >= max_cnt && root == root->get_next ())
00315 {
00316 // Special case when we overflow on an empty spoke. We can just
00317 // wrap the count around without searching for duplicates. We only
00318 // want to do this when the counter overflows, so that we return
00319 // unique timer_id values as often as possible.
00320 root->set_timer_id (1);
00321 return spoke;
00322 }
00323 else if (cnt >= max_cnt)
00324 { // overflow
00325 cnt = 0; // try again starting at zero
00326 }
00327 else if (next_cnt == 0 || cnt < next_cnt)
00328 {
00329 root->set_timer_id (cnt + 1);
00330 return (cnt << this->spoke_bits_) | spoke;
00331 }
00332
00333 //ACE_ERROR((LM_ERROR, "Timer id overflow. We have to search now.\n"));
00334
00335 // We've run out of consecutive id numbers so now we have to search
00336 // for a unique id.
00337 // We'll try increasing numbers until we find one that is not in use,
00338 // and we'll record the next highest number so that we can avoid this
00339 // search as often as possible.
00340 for (; cnt < max_cnt - 1; ++cnt)
00341 {
00342 long id = (cnt << this->spoke_bits_) | spoke;
00343 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* n = this->find_spoke_node (spoke, id);
00344 if (n == 0)
00345 {
00346 root->set_timer_id (cnt + 1);
00347 // Now we need to find the next highest cnt in use
00348 next_cnt = 0;
00349 for (; n != root; n = n->get_next ())
00350 {
00351 long tmp = n->get_timer_id () >> this->spoke_bits_;
00352 if (tmp > cnt && (tmp < next_cnt || next_cnt == 0))
00353 next_cnt = tmp;
00354 }
00355 #if defined (ACE_WIN64)
00356 // The cast below is legit... we know we're storing a long in
00357 // a pointer, but are only using it as a 'long' storage area.
00358 # pragma warning(push)
00359 # pragma warning(disable : 4312)
00360 #endif /* ACE_WIN64 */
00361 root->set_act (reinterpret_cast<void*> (next_cnt));
00362 #if defined (ACE_WIN64)
00363 # pragma warning(pop)
00364 #endif /* ACE_WIN64 */
00365 return id;
00366 }
00367 }
00368
00369 return -1; // We did our best, but the spoke is full.
00370 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Reads the earliest node from the queue and returns it. Returns the earliest node without removing it
Implements ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 763 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::get_first_i(). Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::cancel(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::remove_first_expired().
00764 {
00765 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::get_first");
00766 return this->get_first_i ();
00767 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Definition at line 771 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::earliest_spoke_, ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_next(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::spokes_. Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::cancel(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::earliest_time(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::get_first().
00772 {
00773 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* root = this->spokes_[this->earliest_spoke_];
00774 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* first = root->get_next ();
00775 if (first != root)
00776 return first;
00777 return 0;
00778 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
True if queue is empty, else false. Check to see if the wheel is empty
Implements ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 248 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::timer_count_. Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::cancel().
00249 {
00250 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::is_empty");
00251 return timer_count_ == 0;
00252 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Returns a pointer to this 's iterator.
Implements ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 786 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Initialize the queue. Uses the established members for all needed information. Definition at line 132 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_NEW, ACE_TRACE, and ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::set().
00133 {
00134 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::open_i");
00135
00136 this->gettimeofday (ACE_OS::gettimeofday);
00137
00138 // Rather than waste bits in our timer id, we might as well round up
00139 // the spoke count to the next power of two - 1 . (i.e 1,3,7,15,...127,etc.)
00140 const int MIN_SPOKE_BITS = 3; // Allow between 8 and 4096 spokes
00141 const int MAX_SPOKE_BITS = 12;
00142 const int MAX_RES_BITS = 20; // 20 is plenty, even on 64 bit platforms.
00143
00144 this->spoke_bits_ = power2bits (spokes, MIN_SPOKE_BITS, MAX_SPOKE_BITS);
00145 this->res_bits_ = power2bits (res, 1, MAX_RES_BITS);
00146
00147 this->spoke_count_ = 1 << this->spoke_bits_;
00148
00149 this->free_list_->resize (prealloc + this->spoke_count_);
00150
00151 this->wheel_time_.msec (1 << (this->res_bits_ + this->spoke_bits_));
00152
00153 ACE_NEW (this->spokes_, ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* [this->spoke_count_]);
00154
00155 // Create the root nodes. These will be treated specially
00156 for (u_int i = 0; i < this->spoke_count_; ++i)
00157 {
00158 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* root = this->alloc_node ();
00159 root->set (0, 0, ACE_Time_Value::zero, ACE_Time_Value::zero, root, root, 0);
00160 this->spokes_[i] = root;
00161 }
00162
00163 ACE_NEW (iterator_, Iterator (*this));
00164 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 95 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp.
00098 {
00099 int max = (1 << max_bits) - 1;
00100 if (n > max)
00101 return max_bits;
00102
00103 // count the bits in n.
00104 int i = 0;
00105 int tmp = n;
00106 do
00107 {
00108 tmp >>= 1;
00109 ++i;
00110 }
00111 while (tmp != 0);
00112
00113 if (i <= min_bits)
00114 return min_bits;
00115
00116 // Which is nearest?
00117 int a = (1 << i) - n;
00118 int b = (1 << (i - 1)) - n;
00119 if (b < 0)
00120 b = -b;
00121 if (b < a)
00122 return i - 1;
00123 return i;
00124 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
There are a few places where we have to figure out which timer will expire next. This method makes the assumption that spokes are always sorted, and that timers are always in the correct spoke determined from their expiration time. The last time is always passed in, even though you can often calculate it as get_first()->get_timer_value(). Definition at line 648 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_next(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_timer_value(), and is_empty(). Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::cancel(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::remove_first_expired().
00649 {
00650 // This is possible because we use a count for is_empty()
00651 if (this->is_empty ())
00652 return;
00653
00654 ACE_Time_Value et = ACE_Time_Value::zero;
00655 u_int es = 0;
00656 u_int spoke = this->earliest_spoke_;
00657
00658 // We will have to go around the wheel at most one time.
00659 for (u_int i = 0; i < this->spoke_count_; ++i)
00660 {
00661 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* root = this->spokes_[spoke];
00662 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* n = root->get_next ();
00663 if (n != root)
00664 {
00665 ACE_Time_Value t = n->get_timer_value ();
00666 if (t < last + this->wheel_time_)
00667 {
00668 this->earliest_spoke_ = spoke;
00669 return;
00670 }
00671 else if (et == ACE_Time_Value::zero || t < et)
00672 {
00673 et = t;
00674 es = spoke;
00675 }
00676 }
00677 if (++spoke >= this->spoke_count_)
00678 spoke = 0;
00679 }
00680
00681 this->earliest_spoke_ = es;
00682 //ACE_ERROR((LM_ERROR, "We had to search the whole wheel.\n"));
00683 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Removes the earliest node from the queue and returns it. Removes the earliest node and then find the new
Implements ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 726 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::remove_first_expired().
00727 {
00728 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::remove_first");
00729 return remove_first_expired (ACE_Time_Value::max_time);
00730 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Definition at line 744 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::get_first(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_timer_value(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::recalc_earliest(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::unlink(). Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::expire(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::remove_first().
00745 {
00746 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* n = this->get_first ();
00747 if (n != 0 && n->get_timer_value() <= now)
00748 {
00749 this->unlink (n);
00750 this->recalc_earliest (n->get_timer_value ());
00751 return n;
00752 }
00753 return 0;
00754 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Takes an ACE_Timer_Node and inserts it into the correct position in the correct list. Also makes sure to update the earliest time.
Implements ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 422 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::calculate_spoke(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_timer_value(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::schedule_i(). Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::expire().
00423 {
00424 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::reschedule");
00425 const ACE_Time_Value& expire = n->get_timer_value ();
00426 u_int spoke = calculate_spoke (expire);
00427 this->schedule_i (n, spoke, expire);
00428 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Changes the interval of a timer (and can make it periodic or non periodic by setting it to ACE_Time_Value::zero or not). Implements ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 480 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::find_node(), and ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::set_interval().
00483 {
00484 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::reset_interval");
00485 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_LOCK, ace_mon, this->mutex_, -1));
00486 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* n = this->find_node (timer_id);
00487 if (n != 0)
00488 {
00489 // The interval will take effect the next time this node is expired.
00490 n->set_interval (interval);
00491 return 0;
00492 }
00493 return -1;
00494 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
The shared scheduling functionality between schedule() and reschedule().
Definition at line 433 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_next(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_prev(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::get_timer_value(), is_empty(), ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::set_next(), and ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::set_prev().
00436 {
00437 // See if we need to update the earliest time
00438 if (this->is_empty() || expire < this->earliest_time ())
00439 this->earliest_spoke_ = spoke;
00440
00441 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* root = this->spokes_[spoke];
00442 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* last = root->get_prev ();
00443
00444 ++timer_count_;
00445
00446 // If the spoke is empty
00447 if (last == root) {
00448 n->set_prev (root);
00449 n->set_next (root);
00450 root->set_prev (n);
00451 root->set_next (n);
00452 return;
00453 }
00454
00455 // We always want to search backwards from the tail of the list, because
00456 // this minimizes the search in the extreme case when lots of timers are
00457 // scheduled for exactly the same time
00458 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* p = root->get_prev ();
00459 while (p != root && p->get_timer_value () > expire)
00460 p = p->get_prev ();
00461
00462 // insert after
00463 n->set_prev (p);
00464 n->set_next (p->get_next ());
00465 p->get_next ()->set_prev (n);
00466 p->set_next (n);
00467 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Schedules a timer. Creates a ACE_Timer_Node_T based on the input parameters. Then inserts the node into the wheel using reschedule (). Then returns a timer_id.
Implements ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 386 of file Timer_Wheel_T.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, ACE_Timer_Queue_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::alloc_node(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::calculate_spoke(), ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::generate_timer_id(), and ACE_Timer_Node_T< TYPE >::set(). Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::reschedule().
00390 {
00391 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Timer_Wheel_T::schedule_i");
00392
00393 ACE_Timer_Node_T<TYPE>* n = this->alloc_node ();
00394
00395 if (n != 0)
00396 {
00397 u_int spoke = calculate_spoke (future_time);
00398 long id = generate_timer_id (spoke);
00399
00400 //ACE_ERROR((LM_ERROR, "Scheduling %x spoke:%d id:%d\n", (long) n, spoke, id));
00401
00402 if (id != -1)
00403 {
00404 n->set (type, act, future_time, interval, 0, 0, id);
00405 this->schedule_i (n, spoke, future_time);
00406 }
00407 return id;
00408 }
00409
00410 // Failure return
00411 errno = ENOMEM;
00412 return -1;
00413 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
|||||
|
Iterator is a friend.
Definition at line 98 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h. |
|
|||||
|
Index of the list with the earliest time.
Definition at line 201 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h. Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::get_first_i(). |
|
|||||
|
Iterator used to expire timers.
Definition at line 203 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h. |
|
|||||
|
Maximum number of timers per spoke.
Definition at line 197 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h. |
|
|||||
|
Resolution (in microsoconds) of the timing wheel.
Definition at line 199 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h. |
|
|||||
|
Number of timer_id bits used for the spoke.
Definition at line 195 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h. Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::generate_timer_id(). |
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
The total number of timers currently scheduled.
Definition at line 207 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h. Referenced by ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::is_empty(), and ACE_Timer_Wheel_T< TYPE, FUNCTOR, ACE_LOCK >::unlink(). |
|
|||||
|
The total amount of time in one iteration of the wheel. (resolution * spoke_count).
Definition at line 205 of file Timer_Wheel_T.h. |
 1.3.6
1.3.6