Lecture 5 - Visual Binary Systems (1/26/99)
 Mechanics --- | ---
Binaries II
Mechanics --- | ---
Binaries II

Reading:
Chapter 1-5, 12-2 (ZG4)
Prelude P1, P2 (ZG4)
Notes:
pages 16 - 19
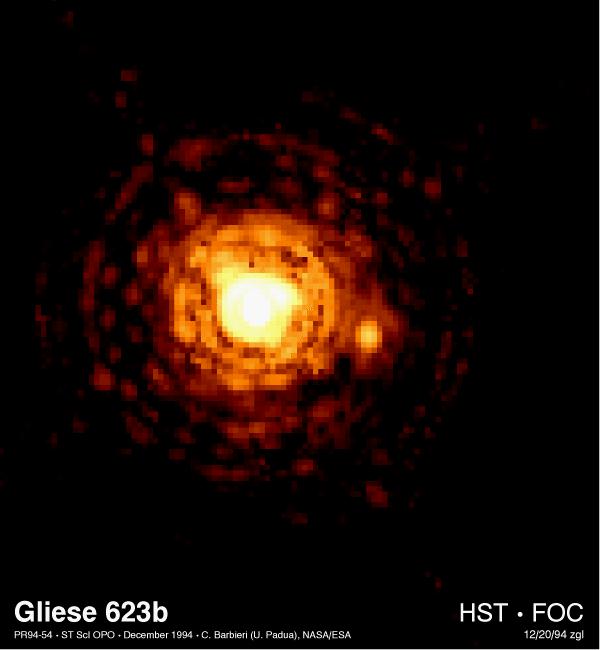
HST FOC image of binary star Gliese 623. The companion
is Gl623b, with a mass of 0.1 Msun, in a 2AU orbit with a 4 year period
around the brighter primary Gl623a. (Courtesy
STSCI)
 |
Key Question: |
What are the conserved integrals
of motion in a two-body system?
|
|---|
 |
Key Principle: |
Kepler's Laws of Motion
|
|---|
 |
Key Problem: |
Determine masses and luminosities
of Sirius A & B.
|
|---|
Investigations:
- Orbital Mechanics continued
- Why are energy and angular momentum integrals of the
motion?
- How do energy and angular momentum generalize to systems with
more than 2 bodies?
- What is the virial theorem?
- How does the total energy determine the semi-major axis of the
orbit?
- How does the total angular momentum determine the eccentricity
and relate to Kepler's 2nd Law?
- What is Kepler's 3rd Law in its final center-of-mass form?
- What two equations give the total mass and mass ratio for
the binary system?
- What are the limitations for using visual binary systems to
determine masses for a large number of stars?
- Visual Binaries - A Primer
- What are periastron and apastron?
- What are the primary and secondary in a binary?
- What is the line of apsides and how does its inclination
affect how the orbit appears on the sky?
- How do you determine the inclination of a visual binary orbit?
- Why must a binary orbit be confined to a plane?
- What input do you need to determine the mass using Kepler's 3rd
Law?
- Example (see homework 1):
Sirius A & B - Masses and Luminosities
- System Data -
| Period: | 49.94 years |
| Parallax: | 0.377" |
| Apparent Magnitudes (bol): |
-1.55, +5.69 |
| Apparent Semi-Major Axis: |
7.62" |
| Ratio of Orbits a_A/a_B: | 0.466 |
| Inclination: | ~0 |
- What is the distance to Sirius in parsecs?
- What are the absolute bolometric magnitudes for Sirius A,B?
- What are the luminosities of Sirius A,B?
- What is the orbital semi-major axis in AU?
- What is the mass ratio m_A/m_B?
- What is the total mass M = m_A + m_B?
- What are the individual masses m_A, m_B?
- What are the mass-to-light ratios M/L of Sirius A,B?
- How do Sirius A, B compare with the Sun?
Binary Stars with HST:
Some binary stars and related objects reported in Hubble Space Telescope
press releases include:
 Prev Lecture ---
Prev Lecture ---
 Next Lecture ---
Next Lecture ---
 Astr12 Index ---
Astr12 Index ---
 Astr12 Home
Astr12 Home
smyers@nrao.edu
Steven T. Myers
 Mechanics --- | ---
Binaries II
Mechanics --- | ---
Binaries II

 Mechanics --- | ---
Binaries II
Mechanics --- | ---
Binaries II





 Prev Lecture ---
Prev Lecture ---
 Next Lecture ---
Next Lecture ---
 Astr12 Index ---
Astr12 Index ---
 Astr12 Home
Astr12 Home