Definition at line 642 of file malloc.c.
References printk(), rtai_global_heap, and rtheap_destroy().
Here is the call graph for this function:

Files | |
| file | rtai_nam2num.h |
| Conversion between characters strings and unsigned long identifiers. | |
| file | rtai_scb.h |
| SCB stand for Shared (memory) Circular Buffer. | |
| file | rtai_shm.h |
| Interface of the RTAI SHM module. | |
| file | shm.c |
| Implementation of the RTAI SHM module. | |
| file | malloc.c |
| Dynamic memory allocation services. | |
Defines | |
| #define | GLOBAL_HEAP_ID 0x9ac6d9e5 |
| #define | USE_VMALLOC 0 |
| #define | USE_GFP_KERNEL 1 |
| #define | USE_GFP_ATOMIC 2 |
| #define | USE_GFP_DMA 3 |
| #define | rtai_kmalloc(name, size) rt_shm_alloc(name, size, USE_VMALLOC) |
| Allocate a chunk of memory to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. | |
| #define | rtai_kfree(name) rt_shm_free(name) |
| Free a chunk of shared memory being shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. | |
| #define | RTAI_SHM_DEV "/dev/rtai_shm" |
| #define | rt_shm_alloc(name, size, suprt) _rt_shm_alloc(0, name, size, suprt, 0) |
| #define | rt_heap_open(name, size, suprt) _rt_shm_alloc(0, name, size, suprt, 1) |
| #define | rtai_malloc(name, size) _rt_shm_alloc(0, name, size, USE_VMALLOC, 0) |
| Allocate a chunk of memory to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. | |
| #define | rt_shm_alloc_adr(start_address, name, size, suprt) _rt_shm_alloc(start_address, name, size, suprt, 0) |
| Allocate a chunk of memory to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. | |
| #define | rt_heap_open_adr(start, name, size, suprt) _rt_shm_alloc(start, name, size, suprt, 1) |
| #define | rtai_malloc_adr(start_address, name, size) _rt_shm_alloc(start_address, name, size, USE_VMALLOC, 0) |
| Allocate a chunk of memory to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. | |
| #define | rtai_free(name, adr) rt_shm_free(name) |
| Free a chunk of shared memory being shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. | |
| #define | rt_heap_close(name, adr) rt_shm_free(name) |
| Close a real time group heap being shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. | |
| #define | rt_heap_init rt_heap_open |
| #define | rt_heap_create rt_heap_open |
| #define | rt_heap_acquire rt_heap_open |
| #define | rt_heap_init_adr rt_heap_open_adr |
| #define | rt_heap_create_adr rt_heap_open_adr |
| #define | rt_heap_acquire_adr rt_heap_open_adr |
| #define | rt_heap_delete rt_heap_close |
| #define | rt_heap_destroy rt_heap_close |
| #define | rt_heap_release rt_heap_close |
| #define | rt_global_heap_open() rt_heap_open(GLOBAL_HEAP_ID, 0, 0) |
| Open the global real time heap to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. | |
| #define | rt_global_heap_close() rt_heap_close(GLOBAL_HEAP_ID, 0) |
| Close the global real time heap being shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. | |
| #define | RTAI_SHM_MISC_MINOR 254 |
| #define | ALIGN2PAGE(adr) ((void *)PAGE_ALIGN((unsigned long)adr)) |
| #define | RT_SHM_OP_PERM() (!(_rt_whoami()->is_hard)) |
| #define | GLOBAL 0 |
| #define | SPECIFIC 1 |
| #define | RTAI_TASK(return_instr) |
Functions | |
| void * | _rt_shm_alloc (void *start, unsigned long name, int size, int suprt, int isheap) |
| int | rt_shm_free (unsigned long name) |
| Free a chunk of shared memory being shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. | |
| void * | rt_halloc (int size) |
| Allocate a chunk of a group real time heap in kernel/user space. | |
| void | rt_hfree (void *addr) |
| Free a chunk of a group real time heap. | |
| void * | rt_named_halloc (unsigned long name, int size) |
| Allocate a chunk of a group real time heap in kernel/user space. | |
| void | rt_named_hfree (void *addr) |
| Free a chunk of a group real time heap. | |
| void * | rt_malloc (int size) |
| void | rt_free (void *addr) |
| void * | rt_named_malloc (unsigned long name, int size) |
| Allocate a chunk of the global real time heap in kernel/user space. | |
| void | rt_named_free (void *addr) |
| Free a named chunk of the global real time heap. | |
| MODULE_LICENSE ("GPL") | |
| void * | _rt_shm_alloc (unsigned long name, int size, int suprt) |
| int | _rt_shm_free (unsigned long name, int size) |
| void * | rt_shm_alloc (unsigned long name, int size, int suprt) |
| Allocate a chunk of memory to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. | |
| int | rt_shm_alloc_usp (unsigned long name, int size, int suprt) |
| int | rt_shm_size (unsigned long *arg) |
| void | rtai_shm_vm_open (struct vm_area_struct *vma) |
| void | rtai_shm_vm_close (struct vm_area_struct *vma) |
| void | rt_set_heap (unsigned long, void *) |
| int | rtai_shm_f_ioctl (struct inode *inode, struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) |
| int | rtai_shm_f_mmap (struct file *file, struct vm_area_struct *vma) |
| void * | _rt_halloc (int size, struct rt_heap_t *heap) |
| void | _rt_hfree (void *addr, struct rt_heap_t *heap) |
| void * | rt_halloc_typed (int size, int htype) |
| void | rt_hfree_typed (void *addr, int htype) |
| void * | rt_named_halloc_typed (unsigned long name, int size, int htype) |
| void | rt_named_hfree_typed (void *adr, int htype) |
| void * | rt_malloc_usp (int size) |
| void | rt_free_usp (void *adr) |
| void * | rt_named_malloc_usp (unsigned long name, int size) |
| void | rt_named_free_usp (void *adr) |
| void * | rt_heap_open (unsigned long name, int size, int suprt) |
| Open/create a named group real time heap to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. | |
| int | set_rt_fun_entries (struct rt_native_fun_entry *entry) |
| void | reset_rt_fun_entries (struct rt_native_fun_entry *entry) |
| int | __rtai_shm_init (void) |
| void | __rtai_shm_exit (void) |
| MODULE_PARM (rtai_global_heap_size,"i") | |
| void * | alloc_extent (u_long size) |
| void | free_extent (void *p, u_long size) |
| void | init_extent (rtheap_t *heap, rtextent_t *extent) |
| int | rtheap_init (rtheap_t *heap, void *heapaddr, u_long heapsize, u_long pagesize) |
| Initialize a memory heap. | |
| void | rtheap_destroy (rtheap_t *heap) |
| Destroys a memory heap. | |
| caddr_t | get_free_range (rtheap_t *heap, u_long bsize, int log2size, int mode) |
| void * | rtheap_alloc (rtheap_t *heap, u_long size, int mode) |
| Allocate a memory block from a memory heap. | |
| int | rtheap_free (rtheap_t *heap, void *block) |
| Release a memory block to a memory heap. | |
| int | __rtai_heap_init (void) |
| void | __rtai_heap_exit (void) |
Variables | |
| int | SUPRT [] = { 0, GFP_KERNEL, GFP_ATOMIC, GFP_DMA } |
| vm_operations_struct | rtai_shm_vm_ops |
| file_operations | rtai_shm_fops |
| miscdevice | rtai_shm_dev |
| rtheap_t | rtai_global_heap |
| void * | rtai_global_heap_adr |
| int | rtai_global_heap_size |
| rt_native_fun_entry | rt_shm_entries [] |
| int | rtai_global_heap_size = RTHEAP_GLOBALSZ |
| void * | rtai_global_heap_adr = NULL |
| rtheap_t | rtai_global_heap |
|
|
Definition at line 48 of file shm.c. Referenced by _rt_shm_alloc(), rt_set_heap(), and rtai_shm_f_mmap(). |
|
|
Definition at line 265 of file shm.c. Referenced by __rtai_shm_init(), rt_free_usp(), rt_malloc_usp(), rt_named_free_usp(), rt_named_malloc_usp(), and rt_set_heap(). |
|
|
Definition at line 38 of file rtai_shm.h. Referenced by __rtai_shm_exit(), __rtai_shm_init(), _rt_shm_free(), and rt_set_heap(). |
|
|
Close the global real time heap being shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes.
For internal use only. rt_global_heap_close is used to close the global real time heap. Closing a global heap in user space has just the effect of deregistering its use and unmapping the related memory from a process address space. In kernel tasks just the deregistration is performed. The global real time heap is destroyed just a the rmmoding of the shared memory module. Definition at line 489 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Open the global real time heap to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes.
For internal use only. rt_global_heap_open is used to open the global real time heap. The global heap is created by the shared memory module and its opening is needed in user space to map it to the process address space. In kernel space opening the global heap in a task is not required but should be done anyhow, both for symmetry and to register its usage. Definition at line 471 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 445 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 448 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Close a real time group heap being shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes.
For internal use only. rt_heap_close is used to close a previously opened real time group heap.
|
|
|
Definition at line 444 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 447 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 450 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 451 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 443 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 446 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 226 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 296 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 452 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 223 of file rtai_shm.h. Referenced by rt_heap_open(), and rt_scb_init(). |
|
|
Allocate a chunk of memory to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. rt_shm_alloc_adr is used to allocate in user space.
name can be a clumsy identifier, services are provided to convert 6 characters identifiers to unsigned long, and vice versa.It must be remarked that only the very first call does a real allocation, any subsequent call to allocate with the same name from anywhere will just increase the usage count and map the area to user space, or return the related pointer to the already allocated space in kernel space. The function returns a pointer to the allocated memory, appropriately mapped to the memory space in use. So if one is really sure that the named shared memory has been allocated already parameters size and suprt are not used and can be assigned any value.
|
|
|
Definition at line 49 of file shm.c. Referenced by _rt_shm_alloc(), and _rt_shm_free(). |
|
|
Free a chunk of shared memory being shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. rtai_free is used to free a shared memory chunk from user space.
|
|
|
Free a chunk of shared memory being shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes. rtai_kfree is used to free a shared memory chunk from kernel space.
|
|
|
Allocate a chunk of memory to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes.
For internal use only. rtai_kalloc is used to allocate shared memory from kernel space.
|
|
|
Allocate a chunk of memory to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes.
For internal use only. rtai_malloc is used to allocate shared memory from user space.
|
|
|
Allocate a chunk of memory to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes.
For internal use only. rtai_malloc_adr is used to allocate shared memory from user space.
|
|
|
Definition at line 184 of file rtai_shm.h. Referenced by _rt_shm_alloc(), and rt_shm_free(). |
|
|
Definition at line 32 of file shm.c. Referenced by __rtai_shm_init(). |
|
|
Value: Definition at line 373 of file shm.c. Referenced by rt_halloc_typed(), rt_hfree_typed(), rt_named_halloc_typed(), rt_named_hfree_typed(), and rt_set_heap(). |
|
|
Definition at line 266 of file shm.c. Referenced by rt_set_heap(). |
|
|
Definition at line 42 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 43 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 41 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 40 of file rtai_shm.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 642 of file malloc.c. References printk(), rtai_global_heap, and rtheap_destroy(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
Definition at line 630 of file malloc.c. References printk(), rtai_global_heap, rtai_global_heap_adr, rtai_global_heap_size, and rtheap_init(). Here is the call graph for this function: 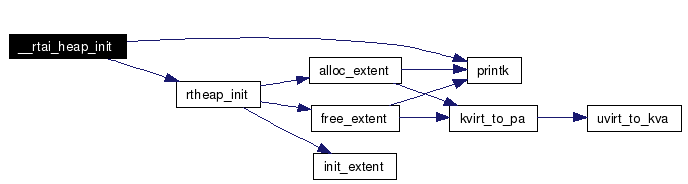 |
|
|
Definition at line 664 of file shm.c. References _rt_shm_free(), GLOBAL_HEAP_ID, max_slots, rt_registry_entry::name, num2nam(), reset_rt_fun_entries(), rt_drg_on_name_cnt(), rt_get_registry_slot(), rt_printk(), rt_shm_entries, rtai_shm_dev, and rt_registry_entry::type. Here is the call graph for this function: 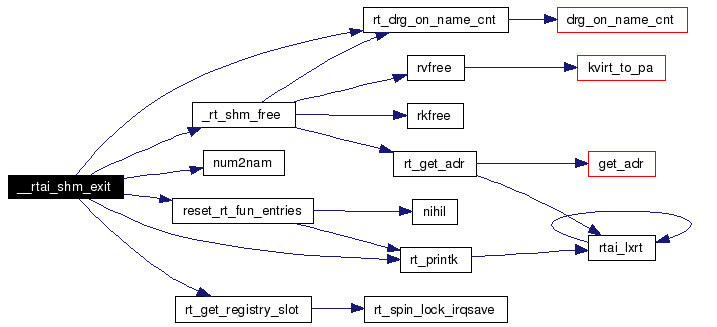 |
|
|
Definition at line 647 of file shm.c. References GLOBAL, GLOBAL_HEAP_ID, printk(), rt_register(), rt_shm_entries, rt_smp_linux_task, rtai_global_heap, rtai_global_heap_adr, rtai_global_heap_size, rtai_shm_dev, RTAI_SHM_MISC_MINOR, and set_rt_fun_entries(). Here is the call graph for this function: 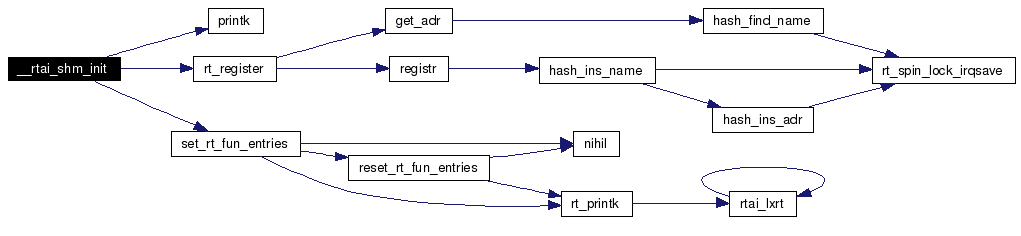 |
|
||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 250 of file shm.c. References rtheap_alloc(). Referenced by rt_halloc_typed(), and rt_named_halloc_typed(). Here is the call graph for this function: 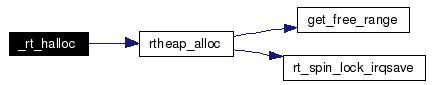 |
|
||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 260 of file shm.c. References rtheap_free(). Referenced by rt_hfree_typed(), rt_named_halloc_typed(), and rt_named_hfree_typed(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 53 of file shm.c. References ALIGN2PAGE, rkfree(), rkmalloc(), rt_get_adr_cnt(), rt_register(), RT_SHM_OP_PERM, rvfree(), rvmalloc(), and SUPRT. Referenced by rt_shm_alloc(), and rt_shm_alloc_usp(). Here is the call graph for this function: 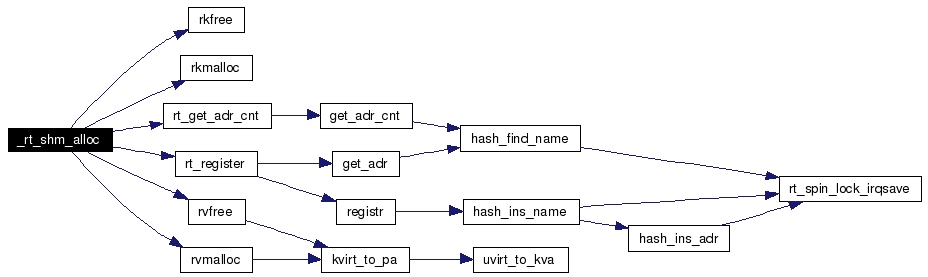 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 186 of file rtai_shm.h. References BIDX, HEAP_SET, rtai_lxrt_t::i, LOW, rtai_lxrt(), RTAI_SHM_DEV, SHM_ALLOC, SHM_FREE, and SIZARG. Here is the call graph for this function: 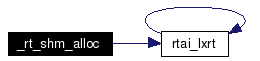 |
|
||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 75 of file shm.c. References GLOBAL_HEAP_ID, rkfree(), rt_drg_on_name_cnt(), rt_get_adr(), RT_SHM_OP_PERM, and rvfree(). Referenced by __rtai_shm_exit(), rtai_shm_f_ioctl(), and rtai_shm_vm_close(). Here is the call graph for this function: 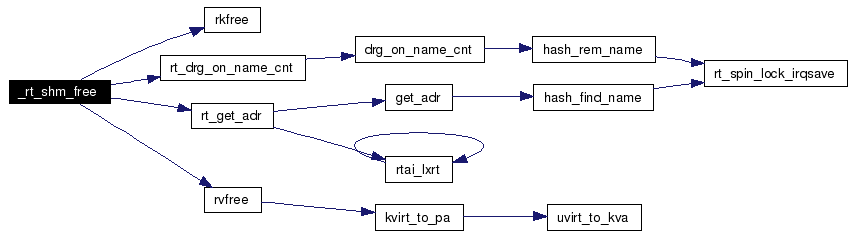 |
|
|
Definition at line 56 of file malloc.c. References kvirt_to_pa(), and printk(). Referenced by rtheap_init(). Here is the call graph for this function: 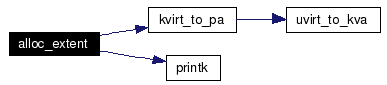 |
|
||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 79 of file malloc.c. References kvirt_to_pa(), and printk(). Referenced by rtheap_destroy(), and rtheap_init(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 296 of file malloc.c. Referenced by rtheap_alloc(). |
|
||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 95 of file malloc.c. Referenced by rtheap_init(). |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Definition at line 399 of file rtai_shm.h. References BIDX, FREE, rtai_lxrt(), and SIZARG. Referenced by __rt_proxy_attach(), __task_delete(), __task_init(), _receive(), _rt_named_msgq_init(), _rt_named_rwl_init(), _rt_named_spl_init(), _rt_typed_named_mbx_init(), _rt_typed_named_sem_init(), delete_queue(), free_bad_task(), handle_lxrt_request(), linux_process_termination(), lxrt_resume(), rt_bits_delete_u(), rt_bits_init_u(), rt_msgq_delete(), rt_named_bits_delete(), rt_named_bits_init(), rt_named_mbx_delete(), rt_named_msgq_delete(), rt_named_rwl_delete(), rt_named_sem_delete(), rt_named_spl_delete(), rt_named_task_delete(), rt_named_task_init(), rt_named_task_init_cpuid(), rt_Proxy_detach(), and rt_proxy_detach(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
Definition at line 539 of file shm.c. References GLOBAL, rt_hfree_typed(), and rtai_global_heap_adr. Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
Allocate a chunk of a group real time heap in kernel/user space. Since it is not named there is no chance to retrieve and share it elsewhere. For internal use only. rt_halloc is used to allocate a non sharable piece of a group real time heap.
References BIDX, HEAP_ALLOC, LOW, rtai_lxrt(), SIZARG, and rtai_lxrt_t::v. Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 382 of file shm.c. References _rt_halloc(), RT_TASK, RTAI_TASK, and task. Referenced by rt_malloc_usp(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Open/create a named group real time heap to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes.
For internal use only. rt_heap_open is used to allocate open/create a shared real time heap.
It must be remarked that only the very first open does a real allocation, any subsequent one with the same name from anywhere will just map the area to the user space, or return the related pointer to the already allocated memory in kernel space. In any case the functions return a pointer to the allocated memory, appropriately mapped to the memory space in use. Be careful and avoid opening more than one group heap per process/task, if more than one is opened then just the last will used.
References rt_set_heap(), and rt_shm_alloc. Here is the call graph for this function: 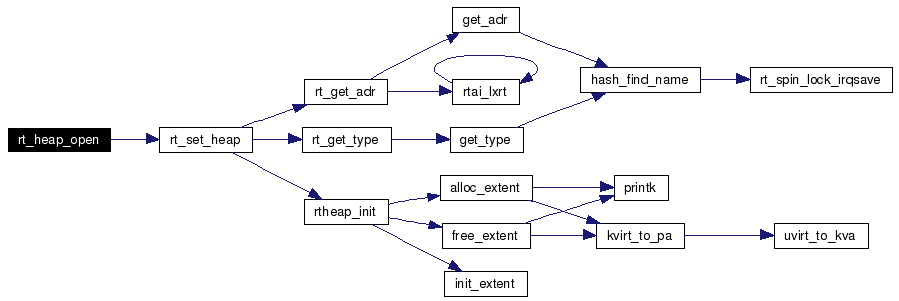 |
|
|
Free a chunk of a group real time heap.
For internal use only. rt_hfree is used to free a previously allocated chunck of a group real time heap.
References BIDX, HEAP_FREE, rtai_lxrt(), and SIZARG. Here is the call graph for this function: 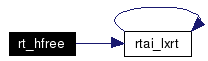 |
|
||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 390 of file shm.c. References _rt_hfree(), RT_TASK, RTAI_TASK, and task. Referenced by rt_free_usp(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
Definition at line 393 of file rtai_shm.h. References BIDX, LOW, MALLOC, rtai_lxrt(), SIZARG, and rtai_lxrt_t::v. Referenced by __rt_proxy_attach(), __task_init(), _broadcast(), _rt_named_msgq_init(), _rt_named_rwl_init(), _rt_named_spl_init(), _rt_typed_named_mbx_init(), _rt_typed_named_sem_init(), _send(), handle_lxrt_request(), lxrt_resume(), mq_open(), new_bad_task(), rt_alloc_dynamic_task(), rt_bits_init_u(), rt_msgq_init(), rt_named_bits_init(), rt_named_task_init(), rt_named_task_init_cpuid(), rt_request_signal(), and rt_request_signal_(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
Definition at line 534 of file shm.c. References GLOBAL, rt_halloc_typed(), and rtai_global_heap_adr. Here is the call graph for this function: 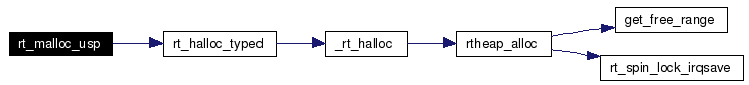 |
|
|
Free a named chunk of the global real time heap.
For internal use only. rt_named_free is used to free a previously allocated chunk of the global real time heap.
References BIDX, NAMED_FREE, rtai_lxrt(), and SIZARG. Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
Definition at line 551 of file shm.c. References GLOBAL, rt_named_hfree_typed(), and rtai_global_heap_adr. Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||
|
Allocate a chunk of a group real time heap in kernel/user space. Since it is named it can be retrieved and shared everywhere among the group peers, i.e all processes/tasks that have opened the same group heap. For internal use only. rt_named_halloc is used to allocate a sharable piece of a group real time heap.
A process/task must have opened the real time group heap to use and can use just one real time group heap. Be careful and avoid opening more than one group real time heap per process/task. If more than one is opened then just the last will used. It must be remarked that only the very first call does a real allocation, any subsequent call with the same name will just increase the usage count and receive the appropriate pointer to the already allocated memory having the same name.
References BIDX, HEAP_NAMED_ALLOC, LOW, rtai_lxrt(), SIZARG, and rtai_lxrt_t::v. Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 398 of file shm.c. References _rt_halloc(), _rt_hfree(), IS_HPCK, rt_get_adr_cnt(), rt_register(), RT_TASK, RTAI_TASK, and task. Referenced by rt_named_malloc_usp(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
Free a chunk of a group real time heap.
For internal use only. rt_named_hfree is used to free a previously allocated chunk of the global real time heap.
References BIDX, HEAP_NAMED_FREE, rtai_lxrt(), and SIZARG. Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 416 of file shm.c. References _rt_hfree(), rt_drg_on_name_cnt(), rt_get_name(), RT_TASK, RTAI_TASK, and task. Referenced by rt_named_free_usp(). Here is the call graph for this function: 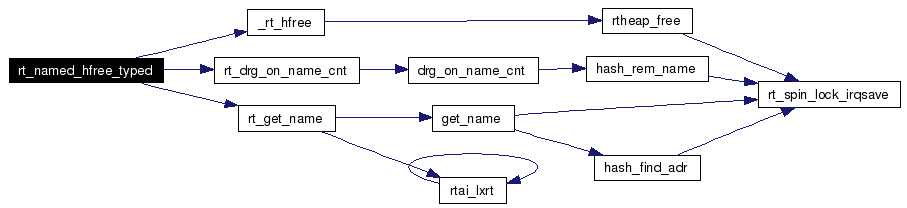 |
|
||||||||||||
|
Allocate a chunk of the global real time heap in kernel/user space. Since it is named it can be retrieved and shared everywhere. For internal use only. rt_named_malloc is used to allocate a sharable piece of the global real time heap.
It must be remarked that only the very first call does a real allocation, any subsequent call to allocate with the same name will just increase the usage count and return the appropriate pointer to the already allocated memory having the same name. So if one is really sure that the named chunk has been allocated already the size parameter is not used and can be assigned any value.
References BIDX, LOW, NAMED_MALLOC, rtai_lxrt(), SIZARG, and rtai_lxrt_t::v. Here is the call graph for this function: 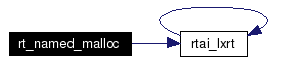 |
|
||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 546 of file shm.c. References GLOBAL, rt_named_halloc_typed(), and rtai_global_heap_adr. Here is the call graph for this function: 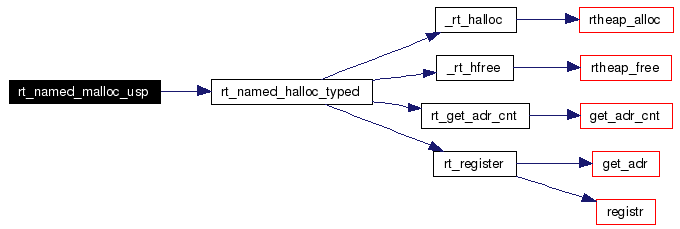 |
|
||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 558 of file shm.c. References ALIGN2PAGE, atomic_cmpxchg, GLOBAL, GLOBAL_HEAP_ID, rt_get_adr(), rt_get_type(), RT_TASK, rtai_global_heap, rtai_global_heap_adr, RTAI_TASK, rtheap_init(), SPECIFIC, and task. Referenced by rt_heap_open(), and rtai_shm_f_ioctl(). Here is the call graph for this function: 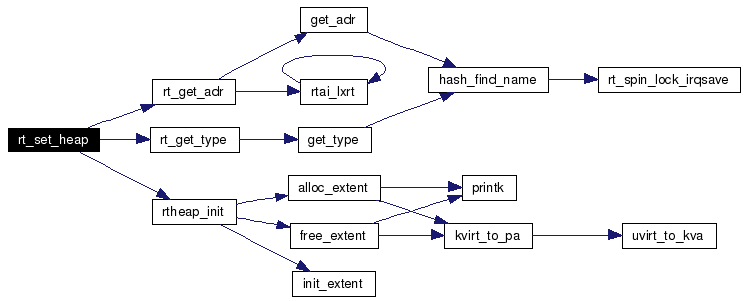 |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Allocate a chunk of memory to be shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes.
For internal use only. rt_shm_alloc is used to allocate shared memory.
It must be remarked that only the very first call does a real allocation, any following call to allocate with the same name from anywhere will just increase the usage count and maps the area to the user space, or return the related pointer to the already allocated space in kernel space. In any case the functions return a pointer to the allocated memory, appropriately mapped to the memory space in use. So if one is really sure that the named shared memory has been allocated already parameters size and suprt are not used and can be assigned any value.
References _rt_shm_alloc(), and TRACE_RTAI_SHM. Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 136 of file shm.c. References _rt_shm_alloc(), rt_get_type(), and TRACE_RTAI_SHM. Referenced by rtai_shm_f_ioctl(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
Free a chunk of shared memory being shared inter-intra kernel modules and Linux processes.
For internal use only. rt_shm_free is used to free a previously allocated shared memory.
References BIDX, rtai_lxrt_t::i, LOW, rtai_lxrt(), RTAI_SHM_DEV, SHM_SIZE, and SIZARG. Referenced by rt_scb_delete(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
Definition at line 173 of file shm.c. References rt_get_type(). Referenced by rtai_shm_f_ioctl(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 205 of file shm.c. References _rt_shm_free(), HEAP_SET, rt_get_type(), rt_set_heap(), rt_shm_alloc_usp(), rt_shm_size(), SHM_ALLOC, SHM_FREE, SHM_SIZE, and TRACE_RTAI_SHM. Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 228 of file shm.c. References ALIGN2PAGE, rkmmap(), rt_get_adr(), rt_get_type(), rtai_shm_vm_ops, and rvmmap(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
Definition at line 193 of file shm.c. References _rt_shm_free(), and rt_get_type(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
Definition at line 188 of file shm.c. References rt_get_adr_cnt(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Allocate a memory block from a memory heap. Allocates a contiguous region of memory from an active memory heap. Such allocation is guaranteed to be time-bounded if the heap is non-extendable (see rtheap_init()). Otherwise, it might trigger a dynamic extension of the storage area through an internal request to the Linux allocation service (kmalloc/vmalloc).
Context: This routine can always be called on behalf of a thread context. It can also be called on behalf of an IST context if the heap storage area has been statically-defined at initialization time (see rtheap_init()). Definition at line 427 of file malloc.c. References flags, get_free_range(), rt_spin_lock_irqsave(), and rt_spin_unlock_irqrestore. Referenced by _rt_halloc(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
Destroys a memory heap. Destroys a memory heap. Dynamically allocated extents are returned to Linux.
Context: This routine must be called on behalf of a thread context. Definition at line 280 of file malloc.c. References free_extent(). Referenced by __rtai_heap_exit(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||
|
Release a memory block to a memory heap. Releases a memory region to the memory heap it was previously allocated from.
Context: This routine can be called on behalf of a thread or IST context Definition at line 527 of file malloc.c. References flags, rt_spin_lock_irqsave(), and rt_spin_unlock_irqrestore. Referenced by _rt_hfree(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Initialize a memory heap. Initializes a memory heap suitable for dynamic memory allocation requests. The heap manager can operate in two modes, whether time-bounded if the heap storage area and size are statically defined at initialization time, or dynamically extendable at the expense of a less deterministic behaviour.
Context: This routine must be called on behalf of a thread context. Definition at line 178 of file malloc.c. References alloc_extent(), free_extent(), and init_extent(). Referenced by __rtai_heap_init(), and rt_set_heap(). Here is the call graph for this function:  |
|
|
|
Initial value: Definition at line 628 of file shm.c. Referenced by __rtai_shm_exit(), and __rtai_shm_init(). |
|
|
Definition at line 54 of file malloc.c. Referenced by __rtai_heap_exit(), __rtai_heap_init(), __rtai_shm_init(), and rt_set_heap(). |
|
|
Definition at line 54 of file malloc.c. Referenced by __rtai_heap_exit(), __rtai_heap_init(), __rtai_shm_init(), and rt_set_heap(). |
|
|
Definition at line 52 of file malloc.c. Referenced by __rtai_heap_init(), __rtai_shm_init(), rt_free_usp(), rt_malloc_usp(), rt_named_free_usp(), rt_named_malloc_usp(), and rt_set_heap(). |
|
|
Definition at line 52 of file malloc.c. Referenced by __rtai_heap_init(), __rtai_shm_init(), rt_free_usp(), rt_malloc_usp(), rt_named_free_usp(), rt_named_malloc_usp(), and rt_set_heap(). |
|
|
Definition at line 50 of file malloc.c. Referenced by __rtai_heap_init(), and __rtai_shm_init(). |
|
|
Definition at line 50 of file malloc.c. Referenced by __rtai_heap_init(), and __rtai_shm_init(). |
|
|
Initial value: Definition at line 247 of file shm.c. Referenced by __rtai_shm_exit(), and __rtai_shm_init(). |
|
|
Initial value: Definition at line 242 of file shm.c. |
|
|
Initial value: Definition at line 198 of file shm.c. Referenced by rtai_shm_f_mmap(). |
|
|
Definition at line 51 of file shm.c. Referenced by _rt_shm_alloc(). |
 1.3.8
1.3.8