Stores the data payload that is accessed via one or more ACE_Message_Block's. More...
#include <Message_Block.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_Data_Block (void) | |
| Default "do-nothing" constructor. | |
| ACE_Data_Block (size_t size, ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Type msg_type, const char *msg_data, ACE_Allocator *allocator_strategy, ACE_Lock *locking_strategy, ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags flags, ACE_Allocator *data_block_allocator) | |
| Initialize. | |
| virtual | ~ACE_Data_Block (void) |
| Delete all the resources held in the message. | |
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Type | msg_type (void) const |
| Get type of the message. | |
| void | msg_type (ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Type type) |
| Set type of the message. | |
| char * | base (void) const |
| Get message data pointer. | |
| void | base (char *data, size_t size, ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags mflags=ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE) |
| Set message data pointer (doesn't reallocate). | |
| char * | end (void) const |
| Return a pointer to 1 past the end of the allocated data in a message. | |
| char * | mark (void) const |
| size_t | size (void) const |
| int | size (size_t length) |
| size_t | capacity (void) const |
| Get the total amount of allocated space. | |
| virtual ACE_Data_Block * | clone (ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags mask=0) const |
| virtual ACE_Data_Block * | clone_nocopy (ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags mask=0, size_t max_size=0) const |
| ACE_Data_Block * | duplicate (void) |
| Return a "shallow" copy that increments our reference count by 1. | |
| ACE_Data_Block * | release (ACE_Lock *lock=0) |
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | set_flags (ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags more_flags) |
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | clr_flags (ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags less_flags) |
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | flags (void) const |
| Get the current message flags. | |
| ACE_Allocator * | allocator_strategy (void) const |
| Obtain the allocator strategy. | |
| ACE_Lock * | locking_strategy (void) |
| Get the locking strategy. | |
| ACE_Lock * | locking_strategy (ACE_Lock *) |
| Set a new locking strategy and return the hold one. | |
| void | dump (void) const |
| Dump the state of an object. | |
| int | reference_count (void) const |
| Get the current reference count. | |
| ACE_Allocator * | data_block_allocator (void) const |
| Get the allocator used to create this object. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual ACE_Data_Block * | release_i (void) |
| Internal release implementation. | |
| int | reference_count_i (void) const |
| Internal get the current reference count. | |
| ACE_Data_Block * | release_no_delete (ACE_Lock *lock) |
Protected Attributes | |
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Type | type_ |
| Type of message. | |
| size_t | cur_size_ |
| Current size of message block. | |
| size_t | max_size_ |
| Total size of buffer. | |
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | flags_ |
| Misc flags (e.g., DONT_DELETE and USER_FLAGS). | |
| char * | base_ |
| Pointer To beginning of message payload. | |
| ACE_Allocator * | allocator_strategy_ |
| ACE_Lock * | locking_strategy_ |
| int | reference_count_ |
| ACE_Allocator * | data_block_allocator_ |
| The allocator use to destroy ourselves. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| ACE_Data_Block & | operator= (const ACE_Data_Block &) |
| ACE_Data_Block (const ACE_Data_Block &) | |
Friends | |
| class | ACE_Message_Block |
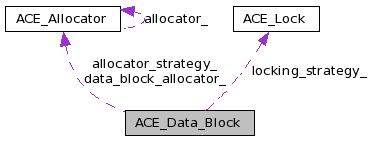
Stores the data payload that is accessed via one or more ACE_Message_Block's.
This data structure is reference counted to maximize sharing. It also contains the <locking_strategy_> (which protects the reference count from race conditions in concurrent programs) and the <allocation_strategy_> (which determines what memory pool is used to allocate the memory).
Definition at line 677 of file Message_Block.h.
| ACE_Data_Block::ACE_Data_Block | ( | void | ) |
Default "do-nothing" constructor.
Definition at line 315 of file Message_Block.cpp.
: type_ (ACE_Message_Block::MB_DATA), cur_size_ (0), max_size_ (0), flags_ (ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE), base_ (0), allocator_strategy_ (0), locking_strategy_ (0), reference_count_ (1), data_block_allocator_ (0) { ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::ACE_Data_Block"); ACE_FUNCTION_TIMEPROBE (ACE_DATA_BLOCK_CTOR1_ENTER); ACE_ALLOCATOR (this->allocator_strategy_, ACE_Allocator::instance ()); ACE_ALLOCATOR (this->data_block_allocator_, ACE_Allocator::instance ()); }
| ACE_Data_Block::ACE_Data_Block | ( | size_t | size, | |
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Type | msg_type, | |||
| const char * | msg_data, | |||
| ACE_Allocator * | allocator_strategy, | |||
| ACE_Lock * | locking_strategy, | |||
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | flags, | |||
| ACE_Allocator * | data_block_allocator | |||
| ) |
Initialize.
Definition at line 336 of file Message_Block.cpp.
: type_ (msg_type), cur_size_ (0), // Reset later if memory alloc'd ok max_size_ (0), flags_ (flags), base_ (const_cast <char *> (msg_data)), allocator_strategy_ (allocator_strategy), locking_strategy_ (locking_strategy), reference_count_ (1), data_block_allocator_ (data_block_allocator) { ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::ACE_Data_Block"); ACE_FUNCTION_TIMEPROBE (ACE_DATA_BLOCK_CTOR2_ENTER); // If the user didn't pass one in, let's use the // <ACE_Allocator::instance>. if (this->allocator_strategy_ == 0) ACE_ALLOCATOR (this->allocator_strategy_, ACE_Allocator::instance ()); if (this->data_block_allocator_ == 0) ACE_ALLOCATOR (this->data_block_allocator_, ACE_Allocator::instance ()); if (msg_data == 0) { ACE_ALLOCATOR (this->base_, (char *) this->allocator_strategy_->malloc (size)); #if defined (ACE_INITIALIZE_MEMORY_BEFORE_USE) (void) ACE_OS::memset (this->base_, '\0', size); #endif /* ACE_INITIALIZE_MEMORY_BEFORE_USE */ } // ACE_ALLOCATOR returns on alloc failure but we cant throw, so setting // the size to 0 (i.e. "bad bit") ... if (this->base_ == 0) { size = 0; } // The memory is legit, whether passed in or allocated, so set // the size. this->cur_size_ = this->max_size_ = size; }
| ACE_Data_Block::~ACE_Data_Block | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Delete all the resources held in the message.
Definition at line 758 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
// Sanity check...
ACE_ASSERT (this->reference_count_ <= 1);
// Just to be safe...
this->reference_count_ = 0;
if (ACE_BIT_DISABLED (this->flags_,
ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE))
{
this->allocator_strategy_->free ((void *) this->base_);
this->base_ = 0;
}
}
| ACE_Data_Block::ACE_Data_Block | ( | const ACE_Data_Block & | ) | [private] |
| ACE_Allocator * ACE_Data_Block::allocator_strategy | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Obtain the allocator strategy.
Definition at line 469 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::allocator_strategy");
return this->allocator_strategy_;
}
| char * ACE_Data_Block::base | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get message data pointer.
Definition at line 52 of file Message_Block.inl.
| void ACE_Data_Block::base | ( | char * | data, | |
| size_t | size, | |||
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | mflags = ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE | |||
| ) |
Set message data pointer (doesn't reallocate).
Definition at line 1264 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
if (ACE_BIT_DISABLED (this->flags_,
ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE))
this->allocator_strategy_->free (this->base_);
this->max_size_ = msg_length;
this->cur_size_ = msg_length;
this->base_ = msg_data;
this->flags_ = msg_flags;
}
| size_t ACE_Data_Block::capacity | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the total amount of allocated space.
Definition at line 66 of file Message_Block.inl.
| ACE_Data_Block * ACE_Data_Block::clone | ( | ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | mask = 0 |
) | const [virtual] |
Return an exact "deep copy" of the message, i.e., create fresh new copies of all the Data_Blocks and continuations. Notice that Data_Blocks can act as "Prototypes", i.e. derived classes can override this method and create instances of themselves.
Definition at line 1107 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::clone");
ACE_Data_Block *nb = this->clone_nocopy (mask);
// Copy all of the payload memory into the new object. The new block
// was allocated with max_size_ (and, thus, it's cur_size_ is the same
// as max_size_). Maintain the same "has been written" boundary in the
// new block by only copying cur_size_ bytes.
if (nb != 0)
{
ACE_OS::memcpy (nb->base_,
this->base_,
this->cur_size_);
}
return nb;
}
| ACE_Data_Block * ACE_Data_Block::clone_nocopy | ( | ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | mask = 0, |
|
| size_t | max_size = 0 | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
As clone above, but it does not copy the contents of the buffer, i.e., create a new Data_Block of the same dynamic type, with the same allocator, locking_strategy, and with the same amount of storage available (if max_size is zero) but the buffer is unitialized. If max_size is specified other than zero, it will be used when creating the new data block.
Reimplemented in ACE_Locked_Data_Block< ACE_LOCK >.
Definition at line 1128 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_FUNCTION_TIMEPROBE(ACE_DATA_BLOCK_CLONE_ENTER);
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::clone_nocopy");
// You always want to clear this one to prevent memory leaks but you
// might add some others later.
const ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags always_clear =
ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE;
const size_t newsize =
max_size == 0 ? this->max_size_ : max_size;
ACE_Data_Block *nb = 0;
ACE_NEW_MALLOC_RETURN (nb,
static_cast<ACE_Data_Block*> (
this->data_block_allocator_->malloc (sizeof (ACE_Data_Block))),
ACE_Data_Block (newsize, // size
this->type_, // type
0, // data
this->allocator_strategy_, // allocator
this->locking_strategy_, // locking strategy
this->flags_, // flags
this->data_block_allocator_),
0);
// Message block initialization may fail while the construction
// succeds. Since as a matter of policy, ACE may throw no
// exceptions, we have to do a separate check like this.
if (nb != 0 && nb->size () < newsize)
{
nb->ACE_Data_Block::~ACE_Data_Block(); // placement destructor ...
this->data_block_allocator_->free (nb); // free ...
errno = ENOMEM;
return 0;
}
// Set new flags minus the mask...
nb->clr_flags (mask | always_clear);
return nb;
}
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags ACE_Data_Block::clr_flags | ( | ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | less_flags | ) | [inline] |
Clear the message flag bits specified in <less_flags> and return the new value.
Definition at line 82 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::clr_flags");
// Later we might mask more_flags so that user can't change internal
// ones: less_flags &= ~(USER_FLAGS -1).
return ACE_CLR_BITS (this->flags_, less_flags);
}
| ACE_Allocator * ACE_Data_Block::data_block_allocator | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the allocator used to create this object.
Definition at line 98 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::data_block_allocator");
return this->data_block_allocator_;
}
| void ACE_Data_Block::dump | ( | void | ) | const |
Dump the state of an object.
Definition at line 146 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
#if defined (ACE_HAS_DUMP)
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::dump");
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_BEGIN_DUMP, this));
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG,
ACE_TEXT ("-----( Data Block )-----\n")
ACE_TEXT ("type_ = %d\n")
ACE_TEXT ("cur_size_ = %u\n")
ACE_TEXT ("max_size_ = %u\n")
ACE_TEXT ("flags_ = %u\n")
ACE_TEXT ("base_ = %@\n")
ACE_TEXT ("locking_strategy_ = %u\n")
ACE_TEXT ("reference_count_ = %u\n")
ACE_TEXT ("---------------------------\n"),
this->type_,
this->cur_size_,
this->max_size_,
this->flags_,
this->base_,
this->locking_strategy_,
this->reference_count_));
this->allocator_strategy_->dump ();
ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_END_DUMP));
#endif /* ACE_HAS_DUMP */
}
| ACE_Data_Block * ACE_Data_Block::duplicate | ( | void | ) |
Return a "shallow" copy that increments our reference count by 1.
Definition at line 991 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::duplicate");
// Create a new <ACE_Message_Block>, but share the <base_> pointer
// data (i.e., don't copy that).
if (this->locking_strategy_)
{
// We need to acquire the lock before incrementing the count.
ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Lock, ace_mon, *this->locking_strategy_, 0);
++this->reference_count_;
}
else
++this->reference_count_;
return this;
}
| char * ACE_Data_Block::end | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Return a pointer to 1 past the end of the allocated data in a message.
Definition at line 333 of file Message_Block.inl.
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags ACE_Data_Block::flags | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the current message flags.
Definition at line 91 of file Message_Block.inl.
| ACE_Lock * ACE_Data_Block::locking_strategy | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
Get the locking strategy.
Definition at line 476 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::locking_strategy");
return this->locking_strategy_;
}
Set a new locking strategy and return the hold one.
Definition at line 483 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::locking_strategy");
ACE_Lock *ols = this->locking_strategy_;
this->locking_strategy_ = nls;
return ols;
}
| char * ACE_Data_Block::mark | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Return a pointer to 1 past the end of the allotted data in a message. The allotted data may be less than allocated data if <size()> is passed an argument less than <capacity()>.
Definition at line 319 of file Message_Block.inl.
| void ACE_Data_Block::msg_type | ( | ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Type | type | ) | [inline] |
Set type of the message.
Definition at line 168 of file Message_Block.inl.
| ACE_Message_Block::ACE_Message_Type ACE_Data_Block::msg_type | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get type of the message.
Definition at line 161 of file Message_Block.inl.
| ACE_Data_Block& ACE_Data_Block::operator= | ( | const ACE_Data_Block & | ) | [private] |
| int ACE_Data_Block::reference_count | ( | void | ) | const |
Get the current reference count.
Definition at line 200 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
if (this->locking_strategy_)
{
// We need to acquire the lock before retrieving the count
ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Lock, ace_mon, *this->locking_strategy_, 0);
return this->reference_count_i ();
}
return this->reference_count_i ();
}
| int ACE_Data_Block::reference_count_i | ( | void | ) | const [inline, protected] |
Internal get the current reference count.
Definition at line 40 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
return reference_count_;
}
| ACE_Data_Block * ACE_Data_Block::release | ( | ACE_Lock * | lock = 0 |
) |
Decrease the shared reference count by 1. If the reference count is > 0 then return this; else if reference count == 0 then delete this and mb and return 0. Behavior is undefined if reference count < 0.
Definition at line 840 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::release");
ACE_Allocator *allocator = this->data_block_allocator_;
ACE_Data_Block *result = this->release_no_delete (lock);
// We must delete this outside the scope of the locking_strategy_
// since otherwise we'd be trying to "release" through a deleted
// pointer!
if (result == 0)
ACE_DES_FREE (this,
allocator->free,
ACE_Data_Block);
return result;
}
| ACE_Data_Block * ACE_Data_Block::release_i | ( | void | ) | [protected, virtual] |
Internal release implementation.
Definition at line 775 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::release_i");
ACE_ASSERT (this->reference_count_ > 0);
ACE_Data_Block *result = 0;
// decrement reference count
--this->reference_count_;
if (this->reference_count_ == 0)
// this will cause deletion of this
result = 0;
else
result = this;
return result;
}
| ACE_Data_Block * ACE_Data_Block::release_no_delete | ( | ACE_Lock * | lock | ) | [protected] |
Definition at line 796 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::release_no_delete");
ACE_Data_Block *result = 0;
ACE_Lock *lock_to_be_used = 0;
// Check if we were passed in a lock
if (lock != 0)
{
// Make sure that the lock passed in and our lock are the same
if (lock == this->locking_strategy_)
// In this case no locking is required.
lock_to_be_used = 0;
// The lock passed in does not match our lock
else
// Lock to be used is our lock
lock_to_be_used = this->locking_strategy_;
}
// This is the case when no lock was passed in
else
{
// Lock to be used is our lock
lock_to_be_used = this->locking_strategy_;
}
// If there's a locking strategy then we need to acquire the lock
// before decrementing the count.
if (lock_to_be_used != 0)
{
ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Lock, ace_mon, *lock_to_be_used, 0);
result = this->release_i ();
}
else
{
result = this->release_i ();
}
return result;
}
| ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags ACE_Data_Block::set_flags | ( | ACE_Message_Block::Message_Flags | more_flags | ) | [inline] |
Bitwise-or the <more_flags> into the existing message flags and return the new value.
Definition at line 73 of file Message_Block.inl.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::set_flags");
// Later we might mask more_glags so that user can't change internal
// ones: more_flags &= ~(USER_FLAGS -1).
return ACE_SET_BITS (this->flags_, more_flags);
}
| size_t ACE_Data_Block::size | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Get the total amount of allotted space in the message. The amount of allotted space may be less than allocated space.
Definition at line 59 of file Message_Block.inl.
| int ACE_Data_Block::size | ( | size_t | length | ) |
Set the total amount of space in the message. Returns 0 if successful, else -1.
Definition at line 214 of file Message_Block.cpp.
{
ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Data_Block::size");
if (length <= this->max_size_)
this->cur_size_ = length;
else
{
// We need to resize!
char *buf = 0;
ACE_ALLOCATOR_RETURN (buf,
(char *) this->allocator_strategy_->malloc (length),
-1);
ACE_OS::memcpy (buf,
this->base_,
this->cur_size_);
if (ACE_BIT_DISABLED (this->flags_,
ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE))
this->allocator_strategy_->free ((void *) this->base_);
else
// We now assume ownership.
ACE_CLR_BITS (this->flags_,
ACE_Message_Block::DONT_DELETE);
this->max_size_ = length;
this->cur_size_ = length;
this->base_ = buf;
}
return 0;
}
friend class ACE_Message_Block [friend] |
Decrease the reference count, but don't delete the object. Returns 0 if the object should be removed. If lock is equal to the locking strategy then we assume that the lock is beign held by the current thread; this is used to release all the data blocks in a chain while holding a single lock.
Definition at line 810 of file Message_Block.h.
ACE_Allocator* ACE_Data_Block::allocator_strategy_ [protected] |
Pointer to the allocator defined for this ACE_Data_Block. Note that this pointer is shared by all owners of this ACE_Data_Block.
Definition at line 834 of file Message_Block.h.
char* ACE_Data_Block::base_ [protected] |
Pointer To beginning of message payload.
Definition at line 826 of file Message_Block.h.
size_t ACE_Data_Block::cur_size_ [protected] |
Current size of message block.
Definition at line 817 of file Message_Block.h.
ACE_Allocator* ACE_Data_Block::data_block_allocator_ [protected] |
The allocator use to destroy ourselves.
Definition at line 853 of file Message_Block.h.
Misc flags (e.g., DONT_DELETE and USER_FLAGS).
Definition at line 823 of file Message_Block.h.
ACE_Lock* ACE_Data_Block::locking_strategy_ [protected] |
Pointer to the locking strategy defined for this ACE_Data_Block. This is used to protect regions of code that access shared ACE_Data_Block state. Note that this lock is shared by all owners of the ACE_Data_Block's data.
Definition at line 842 of file Message_Block.h.
size_t ACE_Data_Block::max_size_ [protected] |
Total size of buffer.
Definition at line 820 of file Message_Block.h.
int ACE_Data_Block::reference_count_ [protected] |
Reference count for this ACE_Data_Block, which is used to avoid deep copies (i.e., <clone>). Note that this pointer value is shared by all owners of the <Data_Block>'s data, i.e., all the ACE_Message_Blocks.
Definition at line 850 of file Message_Block.h.
Type of message.
Definition at line 814 of file Message_Block.h.
 1.7.0
1.7.0