#include <Singleton.h>
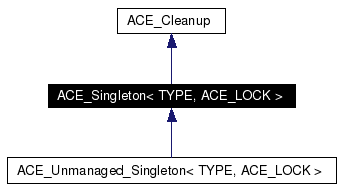
Inheritance diagram for ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >:

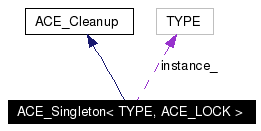
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual void | cleanup (void *param=0) |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| TYPE * | instance (void) |
| Global access point to the Singleton. | |
| void | dump (void) |
| Dump the state of the object. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| ACE_Singleton (void) | |
| Default constructor. | |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK > *& | instance_i (void) |
| Get pointer to the Singleton instance. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| TYPE | instance_ |
| Contained instance. | |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK > * | singleton_ = 0 |
| Pointer to the Singleton (ACE_Cleanup) instance. | |
This implementation is a slight variation on the GoF Singleton pattern. In particular, a single <ACE_Singleton<TYPE, ACE_LOCK> > instance is allocated here, not a instance. The reason for this is to allow registration with the ACE_Object_Manager, so that the Singleton can be cleaned up when the process exits. For this scheme to work, a (static) cleanup() function must be provided. ACE_Singleton provides one so that TYPE doesn't need to. If you want to make sure that only the singleton instance of is created, and that users cannot create their own instances of , do the following to class : (a) Make the constructor of private (or protected) (b) Make Singleton a friend of Here is an example:
* class foo * { * friend class ACE_Singleton<foo, ACE_Null_Mutex>; * private: * foo () { cout << "foo constructed" << endl; } * ~foo () { cout << "foo destroyed" << endl; } * }; * typedef ACE_Singleton<foo, ACE_Null_Mutex> FOO; *
Definition at line 79 of file Singleton.h.
|
||||||||||
|
Default constructor.
Definition at line 13 of file Singleton.inl.
00014 {
00015 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Cleanup method, used by to destroy the ACE_Singleton. Reimplemented from ACE_Cleanup. Definition at line 109 of file Singleton.cpp. References ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance_i(). Referenced by ACE_Unmanaged_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::close().
00110 {
00111 delete this;
00112 ACE_Singleton<TYPE, ACE_LOCK>::instance_i () = 0;
00113 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Dump the state of the object.
Reimplemented in ACE_Unmanaged_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 29 of file Singleton.cpp. References ACE_DEBUG, ACE_END_DUMP, ACE_LIB_TEXT, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance_i(), and LM_DEBUG.
00030 {
00031 #if defined (ACE_HAS_DUMP)
00032 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Singleton<TYPE, ACE_LOCK>::dump");
00033
00034 #if !defined (ACE_LACKS_STATIC_DATA_MEMBER_TEMPLATES)
00035 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_LIB_TEXT ("instance_ = %x"),
00036 ACE_Singleton<TYPE, ACE_LOCK>::instance_i ()));
00037 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_END_DUMP));
00038 #endif /* ACE_LACKS_STATIC_DATA_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
00039 #endif /* ACE_HAS_DUMP */
00040 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Global access point to the Singleton.
Reimplemented in ACE_Unmanaged_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 57 of file Singleton.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_NEW_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit(), ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance_, ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance_i(), ACE_Object_Manager::shutting_down(), and ACE_Object_Manager::starting_up(). Referenced by ACE_Timeprobe_Ex< ACE_LOCK, ALLOCATOR >::allocator(), ACE_Metrics_Cache< ACE_LOCK, ALLOCATOR >::allocator(), and ACE_Service_Config::global().
00058 {
00059 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Singleton<TYPE, ACE_LOCK>::instance");
00060
00061 ACE_Singleton<TYPE, ACE_LOCK> *&singleton =
00062 ACE_Singleton<TYPE, ACE_LOCK>::instance_i ();
00063
00064 // Perform the Double-Check pattern...
00065 if (singleton == 0)
00066 {
00067 if (ACE_Object_Manager::starting_up () ||
00068 ACE_Object_Manager::shutting_down ())
00069 {
00070 // The program is still starting up, and therefore assumed
00071 // to be single threaded. There's no need to double-check.
00072 // Or, the ACE_Object_Manager instance has been destroyed,
00073 // so the preallocated lock is not available. Either way,
00074 // don't register for destruction with the
00075 // ACE_Object_Manager: we'll have to leak this instance.
00076
00077 ACE_NEW_RETURN (singleton, (ACE_Singleton<TYPE, ACE_LOCK>), 0);
00078 }
00079 else
00080 {
00081 #if defined (ACE_MT_SAFE) && (ACE_MT_SAFE != 0)
00082 // Obtain a lock from the ACE_Object_Manager. The pointer
00083 // is static, so we only obtain one per ACE_Singleton
00084 // instantiation.
00085 static ACE_LOCK *lock = 0;
00086 if (ACE_Object_Manager::get_singleton_lock (lock) != 0)
00087 // Failed to acquire the lock!
00088 return 0;
00089
00090 ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_LOCK, ace_mon, *lock, 0);
00091
00092 if (singleton == 0)
00093 {
00094 #endif /* ACE_MT_SAFE */
00095 ACE_NEW_RETURN (singleton, (ACE_Singleton<TYPE, ACE_LOCK>), 0);
00096
00097 // Register for destruction with ACE_Object_Manager.
00098 ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit (singleton);
00099 #if defined (ACE_MT_SAFE) && (ACE_MT_SAFE != 0)
00100 }
00101 #endif /* ACE_MT_SAFE */
00102 }
00103 }
00104
00105 return &singleton->instance_;
00106 }
|
|
||||||||||
|
Get pointer to the Singleton instance.
Reimplemented in ACE_Unmanaged_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 43 of file Singleton.cpp. References ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::singleton_. Referenced by ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::cleanup(), ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::dump(), and ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance().
00044 {
00045 #if defined (ACE_LACKS_STATIC_DATA_MEMBER_TEMPLATES)
00046 // Pointer to the Singleton instance. This works around a bug with
00047 // G++ and it's (mis-)handling of templates and statics...
00048 static ACE_Singleton<TYPE, ACE_LOCK> *singleton_ = 0;
00049
00050 return singleton_;
00051 #else
00052 return ACE_Singleton<TYPE, ACE_LOCK>::singleton_;
00053 #endif /* ACE_LACKS_STATIC_DATA_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
00054 }
|
|
|||||
|
Contained instance.
Definition at line 97 of file Singleton.h. Referenced by ACE_Unmanaged_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), and ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(). |
|
|||||
|
Pointer to the Singleton (ACE_Cleanup) instance.
Reimplemented in ACE_Unmanaged_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >. Definition at line 118 of file Singleton.cpp. Referenced by ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance_i(). |
 1.3.6
1.3.6