#include <Signal.h>
Inheritance diagram for ACE_Sig_Handler:

Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_Sig_Handler (void) | |
| Default ctor/dtor. | |
| virtual | ~ACE_Sig_Handler (void) |
| virtual int | register_handler (int signum, ACE_Event_Handler *new_sh, ACE_Sig_Action *new_disp=0, ACE_Event_Handler **old_sh=0, ACE_Sig_Action *old_disp=0) |
| virtual int | remove_handler (int signum, ACE_Sig_Action *new_disp=0, ACE_Sig_Action *old_disp=0, int sigkey=-1) |
| virtual ACE_Event_Handler * | handler (int signum) |
| Return the ACE_Sig_Handler associated with . | |
| virtual ACE_Event_Handler * | handler (int signum, ACE_Event_Handler *) |
| void | dump (void) const |
| Dump the state of an object. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| int | sig_pending (void) |
| True if there is a pending signal. | |
| void | sig_pending (int) |
| Reset the value of so that no signal is pending. | |
| void | dispatch (int, siginfo_t *, ucontext_t *) |
Public Attributes | |
| ACE_ALLOC_HOOK_DECLARE | |
| Declare the dynamic allocation hooks. | |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| ACE_Event_Handler * | handler_i (int signum, ACE_Event_Handler *) |
| int | register_handler_i (int signum, ACE_Event_Handler *new_sh, ACE_Sig_Action *new_disp=0, ACE_Event_Handler **old_sh=0, ACE_Sig_Action *old_disp=0) |
| int | in_range (int signum) |
| Check whether the SIGNUM is within the legal range of signals. | |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| sig_atomic_t | sig_pending_ = 0 |
| Keeps track of whether a signal is pending. | |
Static Private Attributes | |
| ACE_Event_Handler * | signal_handlers_ [ACE_NSIG] |
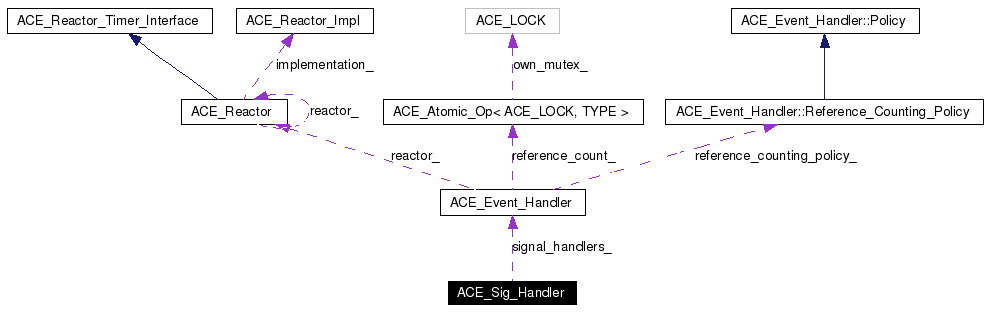
Using this class a program can register an ACE_Event_Handler with the ACE_Sig_Handler in order to handle a designated . When a signal occurs that corresponds to this , the method of the registered ACE_Event_Handler is invoked automatically.
Definition at line 275 of file Signal.h.
|
|
Default ctor/dtor.
Definition at line 262 of file Signal.inl.
00263 {
00264 }
|
|
|
Definition at line 264 of file Signal.cpp.
00265 {
00266 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Callback routine registered with sigaction(2) that dispatches the method of the appropriate pre-registered ACE_Event_Handler. Reimplemented in ACE_Sig_Handlers. Definition at line 441 of file Signal.cpp. References ACE_ASSERT, ACE_SignalHandler, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Event_Handler::handle_close(), ACE_Event_Handler::handle_signal(), in_range(), ACE_Sig_Action::register_action(), register_handler_i(), SIG_DFL, sig_pending_, signal_handlers_, and ucontext_t.
00444 {
00445 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Sig_Handler::dispatch");
00446
00447 // Save/restore errno.
00448 ACE_Errno_Guard error (errno);
00449
00450 // We can't use the <sig_pending> call here because that acquires
00451 // the lock, which is non-portable...
00452 ACE_Sig_Handler::sig_pending_ = 1;
00453
00454 // Darn well better be in range since the OS dispatched this...
00455 ACE_ASSERT (ACE_Sig_Handler::in_range (signum));
00456
00457 ACE_Event_Handler *eh = ACE_Sig_Handler::signal_handlers_[signum];
00458
00459 if (eh != 0)
00460 {
00461 if (eh->handle_signal (signum, siginfo, ucontext) == -1)
00462 {
00463 // Define the default disposition.
00464 ACE_Sig_Action sa ((ACE_SignalHandler) SIG_DFL, (sigset_t *) 0);
00465
00466 ACE_Sig_Handler::signal_handlers_[signum] = 0;
00467
00468 // Remove the current disposition by registering the default
00469 // disposition.
00470 sa.register_action (signum);
00471
00472 // Allow the event handler to close down if necessary.
00473 eh->handle_close (ACE_INVALID_HANDLE,
00474 ACE_Event_Handler::SIGNAL_MASK);
00475 }
00476 #if defined (ACE_WIN32)
00477 else
00478 // Win32 is weird in the sense that it resets the signal
00479 // disposition to SIG_DFL after a signal handler is
00480 // dispatched. Therefore, to workaround this "feature" we
00481 // must re-register the <ACE_Event_Handler> with <signum>
00482 // explicitly.
00483 ACE_Sig_Handler::register_handler_i (signum,
00484 eh);
00485 #endif /* ACE_WIN32*/
00486 }
00487 }
|
|
|
Dump the state of an object.
Reimplemented in ACE_Sig_Handlers. Definition at line 269 of file Signal.cpp. References ACE_TRACE. Referenced by ACE_WFMO_Reactor::dump(), and ACE_Select_Reactor_T< ACE_SELECT_REACTOR_TOKEN >::dump().
00270 {
00271 #if defined (ACE_HAS_DUMP)
00272 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Sig_Handler::dump");
00273 #endif /* ACE_HAS_DUMP */
00274 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Set a new ACE_Event_Handler that is associated with . Return the existing handler. Reimplemented in ACE_Sig_Handlers. Definition at line 332 of file Signal.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, and handler_i().
00334 {
00335 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Sig_Handler::handler");
00336 ACE_MT (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex *lock =
00337 ACE_Managed_Object<ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex>::get_preallocated_object
00338 (ACE_Object_Manager::ACE_SIG_HANDLER_LOCK);
00339 ACE_Guard<ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex> m (*lock));
00340
00341 return ACE_Sig_Handler::handler_i (signum, new_sh);
00342 }
|
|
|
Return the ACE_Sig_Handler associated with .
Reimplemented in ACE_Sig_Handlers. Definition at line 300 of file Signal.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, in_range(), and signal_handlers_. Referenced by ACE_WFMO_Reactor::handler(), ACE_Dev_Poll_Reactor::handler(), and ACE_Select_Reactor_T< ACE_SELECT_REACTOR_TOKEN >::handler_i().
00301 {
00302 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Sig_Handler::handler");
00303 ACE_MT (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex *lock =
00304 ACE_Managed_Object<ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex>::get_preallocated_object
00305 (ACE_Object_Manager::ACE_SIG_HANDLER_LOCK);
00306 ACE_Guard<ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex> m (*lock));
00307
00308 if (ACE_Sig_Handler::in_range (signum))
00309 return ACE_Sig_Handler::signal_handlers_[signum];
00310 else
00311 return 0;
00312 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Set a new ACE_Event_Handler that is associated with . Return the existing handler. Does not acquire any locks so that it can be called from a signal handler, such as . Definition at line 315 of file Signal.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, in_range(), and signal_handlers_. Referenced by handler(), and register_handler_i().
00317 {
00318 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Sig_Handler::handler_i");
00319
00320 if (ACE_Sig_Handler::in_range (signum))
00321 {
00322 ACE_Event_Handler *sh = ACE_Sig_Handler::signal_handlers_[signum];
00323
00324 ACE_Sig_Handler::signal_handlers_[signum] = new_sh;
00325 return sh;
00326 }
00327 else
00328 return 0;
00329 }
|
|
|
Check whether the SIGNUM is within the legal range of signals.
Definition at line 267 of file Signal.inl. References ACE_NSIG, and ACE_TRACE. Referenced by dispatch(), handler(), handler_i(), ACE_Sig_Handlers::register_handler(), register_handler_i(), ACE_Sig_Handlers::remove_handler(), and remove_handler().
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This implementation method is called by and . It doesn't do any locking so that it can be called within a signal handler, such as . It adds a new ACE_Event_Handler and a new sigaction associated with . Passes back the existing ACE_Event_Handler and its sigaction if pointers are non-zero. Returns -1 on failure and >= 0 on success. Definition at line 349 of file Signal.cpp. References ace_signal_handler_dispatcher, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Sig_Action::flags(), ACE_Sig_Action::handler(), handler_i(), in_range(), ACE_Sig_Action::register_action(), and SA_SIGINFO. Referenced by dispatch(), and register_handler().
00354 {
00355 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Sig_Handler::register_handler_i");
00356
00357 if (ACE_Sig_Handler::in_range (signum))
00358 {
00359 ACE_Sig_Action sa; // Define a "null" action.
00360 ACE_Event_Handler *sh = ACE_Sig_Handler::handler_i (signum,
00361 new_sh);
00362
00363 // Return a pointer to the old <ACE_Sig_Handler> if the user
00364 // asks for this.
00365 if (old_sh != 0)
00366 *old_sh = sh;
00367
00368 // Make sure that <new_disp> points to a valid location if the
00369 // user doesn't care...
00370 if (new_disp == 0)
00371 new_disp = &sa;
00372
00373 new_disp->handler (ace_signal_handler_dispatcher);
00374 #if !defined (ACE_HAS_LYNXOS_SIGNALS)
00375 new_disp->flags (new_disp->flags () | SA_SIGINFO);
00376 #endif /* ACE_HAS_LYNXOS_SIGNALS */
00377 return new_disp->register_action (signum, old_disp);
00378 }
00379 else
00380 return -1;
00381 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Remove the ACE_Event_Handler currently associated with . is ignored in this implementation since there is only one instance of a signal handler. Install the new disposition (if given) and return the previous disposition (if desired by the caller). Returns 0 on success and -1 if is invalid. Reimplemented in ACE_Sig_Handlers. Definition at line 410 of file Signal.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, in_range(), ACE_Sig_Action::register_action(), SIG_DFL, and signal_handlers_. Referenced by ACE_MMAP_Memory_Pool::handle_signal(), ACE_WFMO_Reactor::remove_handler(), ACE_Select_Reactor_T< ACE_SELECT_REACTOR_TOKEN >::remove_handler(), and ACE_Dev_Poll_Reactor::remove_handler().
00414 {
00415 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Sig_Handler::remove_handler");
00416 ACE_MT (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex *lock =
00417 ACE_Managed_Object<ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex>::get_preallocated_object
00418 (ACE_Object_Manager::ACE_SIG_HANDLER_LOCK);
00419 ACE_Guard<ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex> m (*lock));
00420
00421 if (ACE_Sig_Handler::in_range (signum))
00422 {
00423 ACE_Sig_Action sa (SIG_DFL, (sigset_t *) 0); // Define the default disposition.
00424
00425 if (new_disp == 0)
00426 new_disp = &sa;
00427
00428 ACE_Sig_Handler::signal_handlers_[signum] = 0;
00429
00430 // Register either the new disposition or restore the default.
00431 return new_disp->register_action (signum, old_disp);
00432 }
00433
00434 return -1;
00435 }
|
|
|
Reset the value of so that no signal is pending.
Definition at line 288 of file Signal.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, and sig_pending_.
00289 {
00290 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Sig_Handler::sig_pending");
00291
00292 ACE_MT (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex *lock =
00293 ACE_Managed_Object<ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex>::get_preallocated_object
00294 (ACE_Object_Manager::ACE_SIG_HANDLER_LOCK);
00295 ACE_Guard<ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex> m (*lock));
00296 ACE_Sig_Handler::sig_pending_ = pending;
00297 }
|
|
|
True if there is a pending signal.
Definition at line 277 of file Signal.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, and sig_pending_. Referenced by ACE_Select_Reactor_T< ACE_SELECT_REACTOR_TOKEN >::dispatch(), ACE_Dev_Poll_Reactor::handle_events_i(), and ACE_TP_Reactor::handle_signals().
00278 {
00279 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Sig_Handler::sig_pending");
00280 ACE_MT (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex *lock =
00281 ACE_Managed_Object<ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex>::get_preallocated_object
00282 (ACE_Object_Manager::ACE_SIG_HANDLER_LOCK);
00283 ACE_Guard<ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex> m (*lock));
00284 return ACE_Sig_Handler::sig_pending_ != 0;
00285 }
|
|
|
Declare the dynamic allocation hooks.
Reimplemented in ACE_Sig_Handlers. |
|
|
Keeps track of whether a signal is pending.
Definition at line 54 of file Signal.cpp. Referenced by dispatch(), and sig_pending(). |
|
|
Array used to store one user-defined Event_Handler for every signal. Definition at line 51 of file Signal.cpp. Referenced by dispatch(), handler(), handler_i(), and remove_handler(). |
 1.3.6
1.3.6