Lecture 10 - Radiative Transfer (2/16/99)
 Stat Mech --- | ---
Stellar Structure I
Stat Mech --- | ---
Stellar Structure I

 Reading:
Reading:
Chapter 8-7, 10-2, 13-1 (ZG4)
Notes:
pages 38 - 42
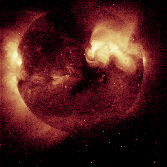
This is an X-ray image of the Sun obtained on February 21,
1994. The brighter regions are sources of increased X-ray emissions. (Courtesy
Calvin J. Hamilton, and Yohkoh)
 |
Key Question: |
How does an atmosphere attenuate
a beam of light?
|
|---|
 |
Key Principle: |
Radiative Transfer
|
|---|
 |
Key Problem: |
Construct a Model Photosphere
|
|---|
Investigations:
- Radiative Transfer II - Opacity and Optical Depth
- How does the absorption depend upon the gas density?
- How does the absorption depend upon the incident intensity?
- How does the absorption depend upon the layer thickness?
- What is the opacity of a gas?
- What is the optical depth of an absorbing medium?
- How do you solve the differential equation for pure absorption?
- Why is the solution to the radiative transfer equation an
exponential in the optical depth?
- What are the implications of this for the case of observed photons
from the solar photosphere?
- How deep is the tau=1 layer in the solar photosphere?
- The Plane-Parallel Atmosphere
- How does the radiative transfer equation scale with inclination angle?
- What is the airmass?
- In what limit can observations through the Earth's atmosphere be
approximated as absorption in a plane-parallel medium?
- How can observations at different angles be used to solve for
the zenith optical depth and the incident intensity?
- Why is this important for observational astronomy?
- Radiative Transfer III - Emission + Absorption
- How does the emission depend upon the density and thickness?
- What is the source function?
- What is the radiative transfer equation?
- Where in the radiative transfer equation is all the physics
contained?
- How does the source function "drag" the intensity toward its
value?
- What is the solution to the radiative transfer equation for
a uniform intensity medium?
- What is the source function for a medium in thermodynamic
equilibrium?
- What is the solution for a constant source function?
- How fast is the incident intensity replaced by the thermal emission
of the medium?
- Opacity in the Solar Photosphere
- How do we know that the solar photosphere is opaque at optical
wavelengths?
- How can the photosphere be opaque at the low densities and
temperatures prevalent there?
- What is the primary opacity agent in the solar photosphere?
- What is the H- ion?
- What is the ionization potential of H- compared with that
of H?
- What is meant by a bound-free transition?
- What is a bound-bound transition?
- What is free-free absorption and emission?
- What is electron scattering?
- Upon what things do the opacity and source function in a stellar
atmosphere depend?
- Interlude - Iterative Solution of Equations
- How do you find the maximum of the blackbody function (Wien's Law)?
- How do you solve the Saha equation for the temperature at a fixed
ionization fraction?
- How can you iteratively solve an equation x=f(x)?
- How is this related to root-finding?
- What determines whether this procedure converges?
Iterative Solution of Numerical Problems
I mentioned in class that a wide range of numerical problems can be solved
iteratively, often with just your calculator. These problems are of the
type that can be put in the form
x = f(x)
and that starting with a guess x_1 you can iterate
xi+1 = f( xi )
to arrive at a stable solution. Note that there are often 2 or more
ways to set up the equation, since by taking the inverse
x = f-1(x) should work also (that isnt an exponent, but a
functional inverse).
 Prev Lecture ---
Prev Lecture ---
 Next Lecture ---
Next Lecture ---
 Astr12 Index ---
Astr12 Index ---
 Astr12 Home
Astr12 Home
smyers@nrao.edu
Steven T. Myers
 Stat Mech --- | ---
Stellar Structure I
Stat Mech --- | ---
Stellar Structure I

 Stat Mech --- | ---
Stellar Structure I
Stat Mech --- | ---
Stellar Structure I

 Reading:
Reading: 


 Prev Lecture ---
Prev Lecture ---
 Next Lecture ---
Next Lecture ---
 Astr12 Index ---
Astr12 Index ---
 Astr12 Home
Astr12 Home