
|
Collaboration diagram for Inter-process communications.:

|
RTAI fifos maintain full compatibility with those available in NMT_RTLinux while adding many other useful services that avoid the clumsiness of Unix/Linux calls. So if you need portability you should bent yourself to the use of select for timing out IO operations, while if you have not to satisfy such constraints use the available simpler, and more direct, RTAI fifos specific services.
In the table below the standard Unix/Linux services in user space are enclosed in []. See standard Linux man pages if you want to use them, they need not be explained here.
| Called from RT task | Called from Linux process |
| rtf_create | rtf_open_sized [open] |
| rtf_destroy | [close] |
| rtf_reset | rtf_reset |
| rtf_resize | rtf_resize |
| rtf_get | [read] rtf_read_timed rtf_read_all_at_once |
| rtf_put | [write] rtf_write_timed |
| rtf_create_handler | |
| rtf_suspend_timed | |
| rtf_set_async_sig |
In Linux, fifos have to be created by :
$ mknod /dev/rtf<x> c 150 <x>
What is important to remember is that in the user space side you address fifos through the file descriptor you get at fifo device opening while in kernel space you directly address them by their minor number. So you will mate the fd you get in user space by using
open(/dev/rtfxx,...)
xx you will use in kernel space.
Files | |
| file | rtai_fifos.h |
| Interface of the RTAI FIFO module. | |
| file | fifos.c |
| Implementation of the RTAI FIFO module. | |
Functions | |
| static int | rtf_suspend_timed (int fd, int ms_delay) |
| Suspend a process for some time. | |
| static int | rtf_open_sized (const char *dev, int perm, int size) |
| Create a real-time FIFO. | |
| static int | rtf_read_all_at_once (int fd, void *buf, int count) |
| Read data from FIFO in user space, waiting for all of them. | |
| static int | rtf_read_timed (int fd, void *buf, int count, int ms_delay) |
| Read data from FIFO in user space, with timeout. | |
| static int | rtf_write_timed (int fd, void *buf, int count, int ms_delay) |
| Write data to FIFO in user space, with timeout. | |
| static int | rtf_set_async_sig (int fd, int signum) |
| Activate asynchronous notification of data availability. | |
| RTAI_SYSCALL_MODE int | rtf_reset (unsigned int minor) |
| Reset a real-time FIFO. | |
| RTAI_SYSCALL_MODE int | rtf_resize (unsigned int minor, int size) |
| Resize a real-time FIFO. | |
| RTAI_SYSCALL_MODE int | rtf_create (unsigned int minor, int size) |
| Create a real-time FIFO. | |
| RTAI_SYSCALL_MODE int | rtf_destroy (unsigned int minor) |
| Close a real-time FIFO. | |
| int | rtf_create_handler (unsigned int minor, void *handler) |
| Install a FIFO handler function. | |
| RTAI_SYSCALL_MODE int | rtf_put (unsigned int minor, void *buf, int count) |
| Write data to FIFO. | |
| RTAI_SYSCALL_MODE int | rtf_get (unsigned int minor, void *buf, int count) |
| Read data from FIFO. | |
| RTAI_SYSCALL_MODE int rtf_create | ( | unsigned int | minor, | |
| int | size | |||
| ) |
Create a real-time FIFO.
rtf_create creates a real-time fifo (RT-FIFO) of initial size size and assigns it the identifier fifo. It must be used only in kernel space.
| minor | is a positive integer that identifies the fifo on further operations. It has to be less than RTF_NO. | |
| size | is the requested size for the fifo. |
The RT-FIFO is a character based mechanism to communicate among real-time tasks and ordinary Linux processes. The rtf_* functions are used by the real-time tasks; Linux processes use standard character device access functions such as read, write, and select.
If this function finds an existing fifo of lower size it resizes it to the larger new size. Note that the same condition apply to the standard Linux device open, except that when it does not find any already existing fifo it creates it with a default size of 1K bytes.
It must be remarked that practically any fifo size can be asked for. In fact if size is within the constraint allowed by kmalloc such a function is used, otherwise vmalloc is called, thus allowing any size that can fit into the available core memory.
Multiple calls of this function are allowed, a counter is kept internally to track their number, and avoid destroying/closing a fifo that is still used.
| 0 | on success | |
| ENODEV | if fifo is greater than or equal to RTF_NO | |
| ENOMEM | if the necessary size could not be allocated for the RT-FIFO. |
Definition at line 971 of file fifos.c.
References rt_fifo_struct::asynq, atomic_cmpxchg(), atomic_inc, buf, do_nothing(), fifo, rt_fifo_struct::handler, rt_fifo_struct::malloc_type, MAX_FIFOS, mbx_init(), mbx_sem_init(), rt_fifo_struct::opncnt, rt_fifo_struct::pol_asyn_pended, rtf_resize(), and TRACE_RTAI_FIFO.
Here is the call graph for this function:
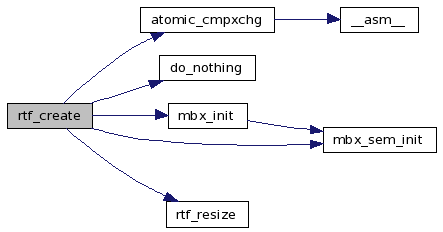
| int rtf_create_handler | ( | unsigned int | minor, | |
| void * | handler | |||
| ) |
Install a FIFO handler function.
rtf_create_handler installs a handler which is executed when data is written to or read from a real-time fifo.
| minor | is an RT-FIFO that must have previously been created with a call to rtf_create(). | |
| handler | is a pointer on a function wich will be called whenever a Linux process accesses that fifo. |
| 0 | on success. | |
| EINVAL | if fifo is greater than or equal to RTF_NO, or handler is NULL. |
Definition at line 1077 of file fifos.c.
References fifo, rt_fifo_struct::handler, MAX_FIFOS, and TRACE_RTAI_FIFO.
| RTAI_SYSCALL_MODE int rtf_destroy | ( | unsigned int | minor | ) |
Close a real-time FIFO.
rtf_destroy closes, in kernel space, a real-time fifo previously created or reopened with rtf_create() or rtf_open_sized(). An internal mechanism counts how many times a fifo was opened. Opens and closes must be in pair. rtf_destroy should be called as many times as rtf_create was. After the last close the fifo is really destroyed.
No need for any particular function for the same service in user space, simply use the standard Unix close.
a a negative value is returned as described below.
| ENODEV | if fifo is greater than or equal to RTF_NO. | |
| EINVAL | if fifo refers to a not opened fifo. |
Definition at line 1030 of file fifos.c.
References rt_fifo_struct::asynq, atomic_dec_and_test, do_nothing(), fifo, rt_fifo_struct::handler, mbx_delete(), rt_fifo_struct::name, rt_fifo_struct::opncnt, rt_fifo_struct::pol_asyn_pended, TRACE_RTAI_FIFO, and VALID_FIFO.
Here is the call graph for this function:
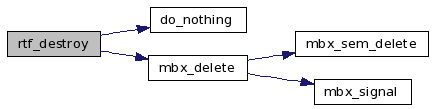
| RTAI_SYSCALL_MODE int rtf_get | ( | unsigned int | minor, | |
| void * | buf, | |||
| int | count | |||
| ) |
Read data from FIFO.
rtf_get tries to read a block of data from a real-time fifo previously created with a call to rtf_create().
| minor | is the ID with which the RT-FIFO was created. | |
| buf | points a buffer provided by the caller. | |
| count | is the size of buf in bytes. |
rtf_get is often used in conjunction with rtf_create_handler() to process data received asynchronously from a Linux process. A handler is installed via rtf_create_handler(); this handler calls rtf_get to receive any data present in the RT-FIFO as it becomes available. In this way, polling is not necessary; the handler is called only when data is present in the fifo.
| ENODEV | if fifo is greater than or equal to RTF_NO. | |
| EINVAL | if fifo refers to a not opened fifo. |
Definition at line 1184 of file fifos.c.
References fifo, mbx_receive_wp(), TRACE_RTAI_FIFO, and VALID_FIFO.
Here is the call graph for this function:
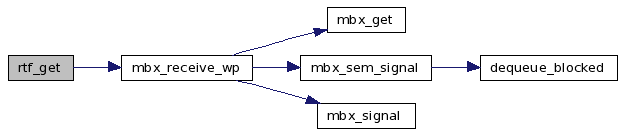
| static int rtf_open_sized | ( | const char * | dev, | |
| int | perm, | |||
| int | size | |||
| ) | [inline, static] |
Create a real-time FIFO.
rtf_open_sized is the equivalent of rtf_create() in user space; it creates a real-time fifo (RT-FIFO) of initial size size.
| size | is the requested size for the fifo. |
If this function finds an existing fifo of lower size it resizes it to the larger new size. Note that the same condition apply to the standard Linux device open, except that when it does not find any already existing fifo it creates it with a default size of 1K bytes.
It must be remarked that practically any fifo size can be asked for. In fact if size is within the constraint allowed by kmalloc such a function is used, otherwise vmalloc is called, thus allowing any size that can fit into the available core memory.
Multiple calls of this function are allowed, a counter is kept internally to track their number, and avoid destroying/closing a fifo that is still used.
| -ENOMEM | if the necessary size could not be allocated for the RT-FIFO. |
Definition at line 525 of file rtai_fifos.h.
| RTAI_SYSCALL_MODE int rtf_put | ( | unsigned int | minor, | |
| void * | buf, | |||
| int | count | |||
| ) |
Write data to FIFO.
rtf_put tries to write a block of data to a real-time fifo previously created with rtf_create().
| minor | is the ID with which the RT-FIFO was created. | |
| buf | points the block of data to be written. | |
| count | is the size of the block in bytes. |
| ENODEV | if fifo is greater than or equal to RTF_NO. | |
| EINVAL | if fifo refers to a not opened fifo. |
Definition at line 1116 of file fifos.c.
References fifo, mbx_send_wp(), TRACE_RTAI_FIFO, and VALID_FIFO.
Here is the call graph for this function:
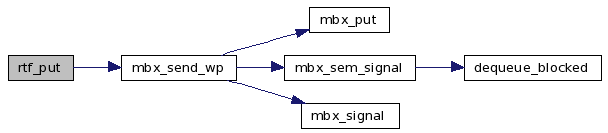
| static int rtf_read_all_at_once | ( | int | fd, | |
| void * | buf, | |||
| int | count | |||
| ) | [inline, static] |
Read data from FIFO in user space, waiting for all of them.
rtf_read_all_at_once reads a block of data from a real-time fifo identified by the file descriptor fd blocking till all waiting at most count bytes are available, whichever option was used at the related device opening.
| fd | is the file descriptor returned at fifo open. | |
| buf | points the block of data to be written. | |
| count | is the size in bytes of the buffer. |
| -EINVAL | if fd refers to a not opened fifo. |
Definition at line 562 of file rtai_fifos.h.
References args, errno, and READ_ALL_AT_ONCE.
| static int rtf_read_timed | ( | int | fd, | |
| void * | buf, | |||
| int | count, | |||
| int | ms_delay | |||
| ) | [inline, static] |
Read data from FIFO in user space, with timeout.
rtf_read_timed reads a block of data from a real-time fifo identified by the file descriptor fd waiting at most delay milliseconds to complete the operation.
| fd | is the file descriptor returned at fifo open. | |
| buf | points the block of data to be written. | |
| count | is the size of the block in bytes. | |
| ms_delay | is the timeout time in milliseconds. |
| -EINVAL | if fd refers to a not opened fifo. |
Definition at line 590 of file rtai_fifos.h.
References args, errno, and READ_TIMED.
| RTAI_SYSCALL_MODE int rtf_reset | ( | unsigned int | minor | ) |
Reset a real-time FIFO.
rtf_reset resets RT-FIFO fd_fifo by setting its buffer pointers to zero, so that any existing data is discarded and the fifo started anew like at its creations. It can be used both in kernel and user space.
| minor | is a file descriptor returned by standard UNIX open in user space while it is directly the chosen fifo number in kernel space. |
| 0 | on succes. | |
| ENODEV | if fd_fifo is greater than or equal to RTF_NO. | |
| EINVAL | if fd_fifo refers to a not opened fifo. | |
| EFAULT | if the operation was unsuccessful. |
Definition at line 821 of file fifos.c.
References lx_mailbox::avbs, current, lx_mailbox::fbyte, fifo, lx_mailbox::frbs, lx_mailbox::lbyte, rt_fifo_struct::mbx, mbx_sem_signal(), mbx_sem_wait(), mbx_sem_wait_if(), mbx_signal(), lx_mailbox::rcvsem, lx_mailbox::size, lx_mailbox::sndsem, TRACE_RTAI_FIFO, VALID_FIFO, and lx_mailbox::waiting_task.
Here is the call graph for this function:
| RTAI_SYSCALL_MODE int rtf_resize | ( | unsigned int | minor, | |
| int | size | |||
| ) |
Resize a real-time FIFO.
rtf_resize modifies the real-time fifo fifo, previously created with, rtf_create(), to have a new size of size. Any data in the fifo is discarded.
| minor | is a file descriptor returned by standard UNIX open in user space while it is directly the chosen fifo number in kernel space. | |
| size | is the requested new size. |
| size | on success. | |
| -ENODEV | if fifo is greater than or equal to RTF_NO. | |
| -EINVAL | if fifo refers to a not opened fifo. | |
| -ENOMEM | if size bytes could not be allocated for the RT-FIFO. Fifo | |
| -EBUSY | if size is smaller than actual content size is unchanged. |
Definition at line 871 of file fifos.c.
References lx_mailbox::avbs, lx_mailbox::bufadr, current, lx_mailbox::fbyte, fifo, lx_mailbox::frbs, lx_mailbox::lbyte, rt_fifo_struct::malloc_type, rt_fifo_struct::mbx, mbx_get(), mbx_sem_signal(), mbx_sem_wait(), mbx_sem_wait_if(), mbx_signal(), lx_mailbox::rcvsem, lx_mailbox::size, lx_mailbox::sndsem, TRACE_RTAI_FIFO, VALID_FIFO, and lx_mailbox::waiting_task.
Here is the call graph for this function:
| static int rtf_set_async_sig | ( | int | fd, | |
| int | signum | |||
| ) | [inline, static] |
Activate asynchronous notification of data availability.
rtf_set_async_sig activate an asynchronous signals to notify data availability by catching a user set signal signum.
| signum | is a user chosen signal number to be used, default is SIGIO. |
| -EINVAL | if fd refers to a not opened fifo. |
Definition at line 741 of file rtai_fifos.h.
References errno, and SET_ASYNC_SIG.
| static int rtf_suspend_timed | ( | int | fd, | |
| int | ms_delay | |||
| ) | [inline, static] |
Suspend a process for some time.
rtf_suspend_timed suspends a Linux process according to delay.
| fd | is the file descriptor returned at fifo open, rtf_suspend_timed needs a fifo support. | |
| ms_delay | is the timeout time in milliseconds. |
Definition at line 485 of file rtai_fifos.h.
References errno, and RTF_SUSPEND_TIMED.
| static int rtf_write_timed | ( | int | fd, | |
| void * | buf, | |||
| int | count, | |||
| int | ms_delay | |||
| ) | [inline, static] |
Write data to FIFO in user space, with timeout.
rtf_write_timed writes a block of data to a real-time fifo identified by the file descriptor fd waiting at most @æ delay milliseconds to complete the operation.
| fd | is the file descriptor returned at fifo open. | |
| buf | points the block of data to be written. | |
| count | is the size of the block in bytes. | |
| ms_delay | is the timeout time in milliseconds. |
| -EINVAL | if fd refers to a not opened fifo. |
Definition at line 625 of file rtai_fifos.h.
References args, errno, and WRITE_TIMED.
 1.4.7
1.4.7