Create a real-time FIFO
rtf_create creates a real-time fifo (RT-FIFO) of initial size size and assigns it the identifier fifo. It must be used only in kernel space.
- Parameters:
-
minor is a positive integer that identifies the fifo on further operations. It has to be less than RTF_NO. size is the requested size for the fifo.
The RT-FIFO is a character based mechanism to communicate among real-time tasks and ordinary Linux processes. The rtf_* functions are used by the real-time tasks; Linux processes use standard character device access functions such as read, write, and select.
If this function finds an existing fifo of lower size it resizes it to the larger new size. Note that the same condition apply to the standard Linux device open, except that when it does not find any already existing fifo it creates it with a default size of 1K bytes.
It must be remarked that practically any fifo size can be asked for. In fact if size is within the constraint allowed by kmalloc such a function is used, otherwise vmalloc is called, thus allowing any size that can fit into the available core memory.
Multiple calls of this function are allowed, a counter is kept internally to track their number, and avoid destroying/closing a fifo that is still used.
- Return values:
-
0 on success ENODEV if fifo is greater than or equal to RTF_NO ENOMEM if the necessary size could not be allocated for the RT-FIFO.
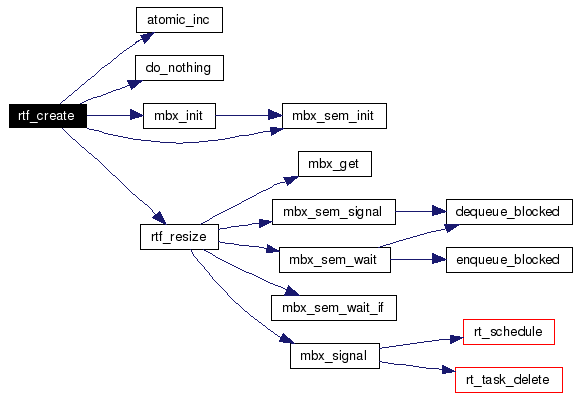
References rt_fifo_struct::asynq, atomic_cmpxchg, atomic_inc(), do_nothing(), fifo, rt_fifo_struct::handler, rt_fifo_struct::malloc_type, MAX_FIFOS, rt_fifo_struct::mbx, mbx_init(), mbx_sem_init(), rt_fifo_struct::opncnt, rt_fifo_struct::pol_asyn_pended, rtf_resize(), lx_mailbox::size, and TRACE_RTAI_FIFO.
Referenced by init_module(), rtf_ioctl(), rtf_named_create(), and rtf_open().
Here is the call graph for this function:
 1.3.8
1.3.8