#include <Object_Manager.h>
Inheritance diagram for ACE_Object_Manager:

Public Types | |
| ACE_FILECACHE_LOCK | |
| ACE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECTS | |
| ACE_EMPTY_PREALLOCATED_ARRAY | |
| ACE_PREALLOCATED_ARRAYS | |
| Hook for preallocated arrays provided by application. | |
| enum | Preallocated_Object { ACE_FILECACHE_LOCK, ACE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECTS } |
| enum | Preallocated_Array { ACE_EMPTY_PREALLOCATED_ARRAY, ACE_PREALLOCATED_ARRAYS } |
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual int | init (void) |
| virtual int | fini (void) |
| ACE_Object_Manager (void) | |
| ~ACE_Object_Manager (void) | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static int | starting_up (void) |
| static int | shutting_down (void) |
| static int | at_exit (ACE_Cleanup *object, void *param=0) |
| static int | at_exit (void *object, ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC cleanup_hook, void *param) |
| static ACE_Sig_Set & | default_mask (void) |
| static ACE_Object_Manager * | instance (void) |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static void * | preallocated_object [ACE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECTS] = { 0 } |
| Table of preallocated objects. | |
| static void * | preallocated_array [ACE_PREALLOCATED_ARRAYS] = { 0 } |
| Table of preallocated arrays. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| int | at_exit_i (void *object, ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC cleanup_hook, void *param) |
| ACE_Object_Manager (const ACE_Object_Manager &) | |
| ACE_Object_Manager & | operator= (const ACE_Object_Manager &) |
Private Attributes | |
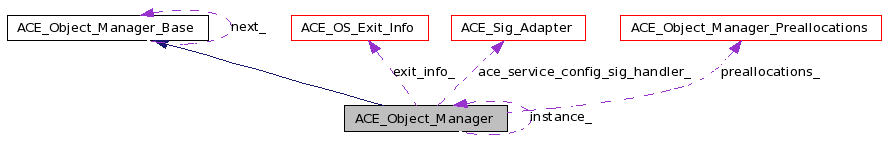
| ACE_OS_Exit_Info | exit_info_ |
| For at_exit support. | |
| ACE_Object_Manager_Preallocations * | preallocations_ |
| Preallocated objects collection. | |
| ACE_Sig_Adapter * | ace_service_config_sig_handler_ |
| ACE_Service_Config signal handler. | |
Static Private Attributes | |
| static ACE_Object_Manager * | instance_ = 0 |
| Singleton pointer. | |
Friends | |
| class | ACE_Object_Manager_Manager |
The ACE_Object_Manager manages cleanup of objects, typically singletons, at program termination. In addition to managing the cleanup of the ACE library, it provides an interface for application to register objects to be cleaned up. This class also shuts down ACE library services, so that they can reclaim their storage, at program termination. It works by creating a static instance whose destructor gets called along with those of all other static objects. Hooks are provided for application code to register objects and arrays for cleanup, e.g., destruction. The order of such cleanup calls is in the reverse order of registration, i.e., that last object/array to register gets cleaned up first. The ACE_Object_Manager API includes ACE_Managed_Object. That class is contained in a separate file because it is a template class, and some compilers require that template and non-template class definitions appear in separate files. Please see ace/Managed_Object.h for a description of that part of the API. In summary, ACE_Managed_Object provides two adapters, the ACE_Cleanup_Adapter and ACE_Managed_Object template classes for adapting objects of any type to be easily managed by the ACE_Object_Manager. There are several mechanisms for adapting objects and arrays for cleanup at program termination, in roughly increasing order of ease-of-use: 1) Derive the object's class from ACE_Cleanup. 2) Allow the ACE_Object_Manager to both dynamically allocate and deallocate the object. 3) Provide an <ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC> cleanup hook for the object or array. 4) Allow the ACE_Object_Manager to both preallocate the object or array, either statically in global data or dynamically on the heap, when its singleton instance is construction.
There are also several mechanisms for registering objects and arrays for cleanup. In decreasing order of flexibility and complexity (with the exception of the last mechanism):
1) ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit (void *object, ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC cleanup_hook, void *param); can be used to register any object or array for any cleanup activity at program termination. 2) ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit (ACE_Cleanup *object, void *param = 0); can be used to register an ACE_Cleanup object for any cleanup activity at program termination. The final mechanism is not general purpose, but can only be used to allocate objects and arrays at program startup: 3) ACE_Managed_Object::get_preallocated_object (ACE_Object_Manager::Preallocated_Object id); and ACE_Managed_Object::get_preallocated_array (ACE_Object_Manager::Preallocated_Array id); can only be used to allocate objects at program startup, either in global data or on the heap (selected at compile time). These are intended to replace static locks, etc. Instead of creating a static ACE_Object_Manager instance, one can alternatively be created on the stack of the main program thread. It is created just after entry to main (int, char *[]), and before any existing code in that function is executed. To enable this alternative, add define ACE_HAS_NONSTATIC_OBJECT_MANAGER before including the platform specific config-* file in ace/config.h prior to building the ACE library and your applications. This define is enabled in some config files that are supplied with ACE.
To ensure a static object manager is used, undef ACE_HAS_NONSTATIC_OBJECT_MANAGER *after* including the platform specific config-* file. Note that the ACE_Object_Manager _must_ be created before any threads are spawned by the program. If ACE_HAS_NONSTATIC_OBJECT_MANAGER is not defined, the ACE library creates a static, singleton ACE_Object_Manager instance. The instance is placed in global program data, and constructed via a static object constructor. If ACE_HAS_NONSTATIC_OBJECT_MANAGER is defined, the ACE_Object_Manager instance is created on the stack of the main program thread, as noted above.
With ACE_HAS_NONSTATIC_OBJECT_MANAGER enabled, the ACE library has no static objects that require destruction. However, there are two drawbacks to using it: 1) main (int, char *[]) must be declared with arguments, even if they're not used. All of ACE is converted to this, so just applications have to be concerned with it. 2) If there any static objects that depend on those that are cleaned up by the Object_Manager, they'll get cleaned up too late. The ACE tests do not violate this requirement. However, applications may have trouble with it. NOTE on the use of <exit> -- <exit> does not destroy automatic objects. Therefore, if ACE_HAS_NONSTATIC_OBJECT_MANAGER is enabled, the ACE_Object_Manager instance will *not* be destroyed if <exit> is called! However, <ACE_OS::exit> will properly destroy the ACE_Object_Manager. It is highly recommended that <ACE_OS::exit> be used instead of <exit>.
However, <exit> and <ACE_OS::exit> are tricky to use properly, especially in multithread programs. It is much safer to throw an exception (or simulate that effect) that will be caught by <main> instead of calling exit. Then, <main> can perform any necessary application-specific cleanup and return the status value. In addition, it's usually best to avoid calling <exit> and <ACE_OS::exit> from threads other than the main thread. Thanks to Jeff Greif <jmg@trivida.com> for pointing out that <exit> doesn't destroy automatic objects, and for developing the recommendations in this paragraph.
Instead of creating a static ACE_Object_Manager, or letting ACE create it on the stack of <main> for you, another alternative is to define ACE_DOESNT_INSTANTIATE_NONSTATIC_OBJECT_MANAGER. With that define, the application must create the ACE_Object_Manager. The recommended way is to call <ACE::init> at the start of the program, and call <ACE::fini> at the end. Alternatively, the application could explicity construct an ACE_Object_Manager.
Definition at line 198 of file Object_Manager.h.
Unique identifiers for preallocated arrays. Please see ace/Managed_Object.h for information on accessing preallocated arrays.
| ACE_EMPTY_PREALLOCATED_ARRAY | There currently are no preallocated arrays in the ACE library. If the application doesn't have any, make sure the the preallocated_array size is at least one by declaring this dummy . . . |
| ACE_PREALLOCATED_ARRAYS | Hook for preallocated arrays provided by application. |
Definition at line 311 of file Object_Manager.h.
00312 { 00313 /// There currently are no preallocated arrays in the ACE 00314 /// library. If the application doesn't have any, make sure 00315 /// the the preallocated_array size is at least one by declaring 00316 /// this dummy . . . 00317 ACE_EMPTY_PREALLOCATED_ARRAY, 00318 00319 /// Hook for preallocated arrays provided by application. 00320 ACE_APPLICATION_PREALLOCATED_ARRAY_DECLARATIONS 00321 00322 ACE_PREALLOCATED_ARRAYS // This enum value must be last! 00323 };
Unique identifiers for preallocated objects. Please see ace/Managed_Object.h for information on accessing preallocated objects.
Definition at line 282 of file Object_Manager.h.
00283 { 00284 ACE_FILECACHE_LOCK, 00285 #if defined (ACE_HAS_THREADS) 00286 ACE_STATIC_OBJECT_LOCK, 00287 #endif /* ACE_HAS_THREADS */ 00288 #if defined (ACE_MT_SAFE) && (ACE_MT_SAFE != 0) 00289 ACE_MT_CORBA_HANDLER_LOCK, 00290 ACE_DUMP_LOCK, 00291 ACE_SIG_HANDLER_LOCK, 00292 ACE_SINGLETON_NULL_LOCK, 00293 ACE_SINGLETON_RECURSIVE_THREAD_LOCK, 00294 ACE_THREAD_EXIT_LOCK, 00295 #if !defined (ACE_LACKS_ACE_TOKEN) 00296 ACE_TOKEN_MANAGER_CREATION_LOCK, 00297 ACE_TOKEN_INVARIANTS_CREATION_LOCK, 00298 #endif /* ! ACE_LACKS_ACE_TOKEN */ 00299 ACE_PROACTOR_EVENT_LOOP_LOCK, 00300 #endif /* ACE_MT_SAFE */ 00301 00302 // Hook for preallocated objects provided by application. 00303 ACE_APPLICATION_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT_DECLARATIONS 00304 00305 ACE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECTS // This enum value must be last! 00306 };
| ACE_Object_Manager::ACE_Object_Manager | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 314 of file Object_Manager.cpp.
References ACE_NEW, init(), and instance_.
00317 : exit_info_ () 00318 #if !defined (ACE_LACKS_ACE_SVCCONF) 00319 , preallocations_ (0) 00320 , ace_service_config_sig_handler_ (0) 00321 #endif /* ! ACE_LACKS_ACE_SVCCONF */ 00322 #if defined (ACE_MT_SAFE) && (ACE_MT_SAFE != 0) 00323 , singleton_null_lock_ (0) 00324 , singleton_recursive_lock_ (0) 00325 #endif /* ACE_MT_SAFE */ 00326 #if defined (ACE_HAS_TSS_EMULATION) 00327 , ts_storage_initialized_ (false) 00328 #endif 00329 { 00330 #if defined (ACE_MT_SAFE) && (ACE_MT_SAFE != 0) 00331 ACE_NEW (internal_lock_, ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex); 00332 # endif /* ACE_MT_SAFE */ 00333 00334 // If instance_ was not 0, then another ACE_Object_Manager has 00335 // already been instantiated (it is likely to be one initialized by way 00336 // of library/DLL loading). Let this one go through construction in 00337 // case there really is a good reason for it (like, ACE is a static/archive 00338 // library, and this one is the non-static instance (with 00339 // ACE_HAS_NONSTATIC_OBJECT_MANAGER, or the user has a good reason for 00340 // creating a separate one) but the original one will be the one retrieved 00341 // from calls to ACE_Object_Manager::instance(). 00342 00343 // Be sure that no further instances are created via instance (). 00344 if (instance_ == 0) 00345 instance_ = this; 00346 00347 init (); 00348 }
| ACE_Object_Manager::~ACE_Object_Manager | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 350 of file Object_Manager.cpp.
References ACE_Object_Manager_Base::dynamically_allocated_, and fini().
00351 { 00352 dynamically_allocated_ = false; // Don't delete this again in fini() 00353 fini (); 00354 }
| ACE_Object_Manager::ACE_Object_Manager | ( | const ACE_Object_Manager & | ) | [private] |
| ACE_INLINE int ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit | ( | void * | object, | |
| ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC | cleanup_hook, | |||
| void * | param | |||
| ) | [static] |
Register an object (or array) for cleanup at process termination. "cleanup_hook" points to a (global, or static member) function that is called for the object or array when it to be destroyed. It may perform any necessary cleanup specific for that object or its class. "param" is passed as the second parameter to the "cleanup_hook" function; the first parameter is the object (or array) to be destroyed. "cleanup_hook", for example, may delete the object (or array). For OS's that do not have processes, this function is the same as <at_thread_exit>. Returns 0 on success. On failure, returns -1 and sets errno to: EAGAIN if shutting down, ENOMEM if insufficient virtual memory, or EEXIST if the object (or array) had already been registered.
Definition at line 20 of file Object_Manager.inl.
References at_exit_i(), and instance().
00023 { 00024 return ACE_Object_Manager::instance ()->at_exit_i ( 00025 object, 00026 cleanup_hook, 00027 param); 00028 }
| ACE_BEGIN_VERSIONED_NAMESPACE_DECL ACE_INLINE int ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit | ( | ACE_Cleanup * | object, | |
| void * | param = 0 | |||
| ) | [static] |
Register an ACE_Cleanup object for cleanup at process termination. The object is deleted via the <ace_cleanup_destroyer>. If you need more flexiblity, see the <other at_exit>=""> method below. For OS's that do not have processes, cleanup takes place at the end of <main>. Returns 0 on success. On failure, returns -1 and sets errno to: EAGAIN if shutting down, ENOMEM if insufficient virtual memory, or EEXIST if the object (or array) had already been registered.
Definition at line 9 of file Object_Manager.inl.
References ACE_CLEANUP_DESTROYER_NAME, at_exit_i(), and instance().
Referenced by ACE_TSS_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), ACE_Process_Manager::instance(), and ACE_Log_Msg::instance().
00011 { 00012 return ACE_Object_Manager::instance ()->at_exit_i ( 00013 object, 00014 (ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC) ACE_CLEANUP_DESTROYER_NAME, 00015 param); 00016 }
| int ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit_i | ( | void * | object, | |
| ACE_CLEANUP_FUNC | cleanup_hook, | |||
| void * | param | |||
| ) | [private] |
Register an object or array for deletion at program termination. See description of static version above for return values.
Definition at line 381 of file Object_Manager.cpp.
References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_OS_Exit_Info::at_exit_i(), exit_info_, ACE_OS_Exit_Info::find(), instance_, and ACE_Object_Manager_Base::shutting_down_i().
Referenced by at_exit().
00384 { 00385 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, 00386 *instance_->internal_lock_, -1)); 00387 00388 if (shutting_down_i ()) 00389 { 00390 errno = EAGAIN; 00391 return -1; 00392 } 00393 00394 if (exit_info_.find (object)) 00395 { 00396 // The object has already been registered. 00397 errno = EEXIST; 00398 return -1; 00399 } 00400 00401 return exit_info_.at_exit_i (object, cleanup_hook, param); 00402 }
| ACE_INLINE ACE_Sig_Set & ACE_Object_Manager::default_mask | ( | void | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 32 of file Object_Manager.inl.
References ACE_OS_Object_Manager::default_mask().
00033 { 00034 // A safe cast, but this static method shouldn't be used anyways. 00035 // Use ACE_Object_Manager::default_mask () instead. 00036 return 00037 *reinterpret_cast<ACE_Sig_Set *> (ACE_OS_Object_Manager::default_mask ()); 00038 }
| int ACE_Object_Manager::fini | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Explicitly destroy the singleton instance of the ACE_Object_Manager. Returns 0 on success, -1 on failure, and 1 if it had already been called.
Implements ACE_Object_Manager_Base.
Definition at line 628 of file Object_Manager.cpp.
References ACE_APPLICATION_PREALLOCATED_ARRAY_DELETIONS, ACE_APPLICATION_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT_DELETIONS, ACE_DELETE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT, ACE_FILECACHE_LOCK, ace_service_config_sig_handler_, ACE_SYNCH_RW_MUTEX, ACE_OS_Exit_Info::call_hooks(), ACE_OS::cleanup_tss(), ACE_Service_Config::close(), ACE_Allocator::close_singleton(), ACE_Thread_Manager::close_singleton(), ACE_DLL_Manager::close_singleton(), ACE_Framework_Repository::close_singleton(), ACE_Object_Manager_Base::dynamically_allocated_, exit_info_, ACE_OS_Object_Manager::fini(), ACE_Service_Config::fini_svcs(), ACE_OS_Object_Manager::instance_, instance_, ACE_Object_Manager_Base::OBJ_MAN_SHUT_DOWN, ACE_Object_Manager_Base::OBJ_MAN_SHUTTING_DOWN, ACE_Object_Manager_Base::object_manager_state_, preallocations_, ACE_Object_Manager_Base::shutting_down_i(), and ACE_Trace::stop_tracing().
Referenced by ACE::fini(), and ~ACE_Object_Manager().
00629 { 00630 if (shutting_down_i ()) 00631 // Too late. Or, maybe too early. Either fini () has already 00632 // been called, or init () was never called. 00633 return object_manager_state_ == OBJ_MAN_SHUT_DOWN ? 1 : -1; 00634 00635 // No mutex here. Only the main thread should destroy the singleton 00636 // ACE_Object_Manager instance. 00637 00638 // Indicate that this ACE_Object_Manager instance is being 00639 // shut down. 00640 object_manager_state_ = OBJ_MAN_SHUTTING_DOWN; 00641 00642 // Call all registered cleanup hooks, in reverse order of 00643 // registration. 00644 exit_info_.call_hooks (); 00645 00646 if (this == instance_) 00647 { 00648 #if !defined (ACE_LACKS_ACE_SVCCONF) 00649 delete preallocations_; 00650 preallocations_ = 0; 00651 #endif /* ! ACE_LACKS_ACE_SVCCONF */ 00652 00653 #if defined (ACE_HAS_TRACE) 00654 ACE_Trace::stop_tracing (); 00655 #endif /* ACE_HAS_TRACE */ 00656 00657 #if !defined (ACE_LACKS_ACE_SVCCONF) 00658 // Close and possibly delete all service instances in the Service 00659 // Repository. 00660 ACE_Service_Config::fini_svcs (); 00661 00662 // Unlink all services in the Service Repository and close/delete 00663 // all ACE library services and singletons. 00664 ACE_Service_Config::close (); 00665 #endif /* ! ACE_LACKS_ACE_SVCCONF */ 00666 00667 // This must come after closing ACE_Service_Config, since it will 00668 // close down it's dlls--it manages ACE_DLL_Manager. 00669 ACE_Framework_Repository::close_singleton (); 00670 ACE_DLL_Manager::close_singleton (); 00671 00672 # if ! defined (ACE_THREAD_MANAGER_LACKS_STATICS) 00673 ACE_Thread_Manager::close_singleton (); 00674 # endif /* ! ACE_THREAD_MANAGER_LACKS_STATICS */ 00675 00676 // Close the main thread's TSS, including its Log_Msg instance. 00677 ACE_OS::cleanup_tss (1 /* main thread */); 00678 00679 // 00680 // Note: Do not access Log Msg after this since it is gone 00681 // 00682 00683 // Close the ACE_Allocator. 00684 ACE_Allocator::close_singleton (); 00685 00686 #if ! defined (ACE_HAS_STATIC_PREALLOCATION) 00687 // Hooks for deletion of preallocated objects and arrays provided by 00688 // application. 00689 ACE_APPLICATION_PREALLOCATED_ARRAY_DELETIONS 00690 ACE_APPLICATION_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT_DELETIONS 00691 00692 // Cleanup the dynamically preallocated arrays. 00693 // (none) 00694 00695 // Cleanup the dynamically preallocated objects. 00696 ACE_DELETE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT (ACE_SYNCH_RW_MUTEX, ACE_FILECACHE_LOCK) 00697 #if defined (ACE_HAS_THREADS) 00698 ACE_DELETE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, 00699 ACE_STATIC_OBJECT_LOCK) 00700 #endif /* ACE_HAS_THREADS */ 00701 # if defined (ACE_MT_SAFE) && (ACE_MT_SAFE != 0) 00702 ACE_DELETE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT (ACE_Thread_Mutex, 00703 ACE_MT_CORBA_HANDLER_LOCK) 00704 ACE_DELETE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT (ACE_Thread_Mutex, ACE_DUMP_LOCK) 00705 ACE_DELETE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, 00706 ACE_SIG_HANDLER_LOCK) 00707 ACE_DELETE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT (ACE_Null_Mutex, 00708 ACE_SINGLETON_NULL_LOCK) 00709 ACE_DELETE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, 00710 ACE_SINGLETON_RECURSIVE_THREAD_LOCK) 00711 ACE_DELETE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT (ACE_Thread_Mutex, ACE_THREAD_EXIT_LOCK) 00712 #if !defined (ACE_LACKS_ACE_TOKEN) && defined (ACE_HAS_TOKENS_LIBRARY) 00713 ACE_DELETE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT (ACE_TOKEN_CONST::MUTEX, 00714 ACE_TOKEN_MANAGER_CREATION_LOCK) 00715 ACE_DELETE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT (ACE_TOKEN_CONST::MUTEX, 00716 ACE_TOKEN_INVARIANTS_CREATION_LOCK) 00717 #endif /* ! ACE_LACKS_ACE_TOKEN && ACE_HAS_TOKENS_LIBRARY */ 00718 ACE_DELETE_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT (ACE_Thread_Mutex, 00719 ACE_PROACTOR_EVENT_LOOP_LOCK) 00720 # endif /* ACE_MT_SAFE */ 00721 #endif /* ! ACE_HAS_STATIC_PREALLOCATION */ 00722 00723 #if defined (ACE_HAS_THREADS) 00724 ACE_Static_Object_Lock::cleanup_lock (); 00725 #endif /* ACE_HAS_THREADS */ 00726 } 00727 00728 #if !defined (ACE_LACKS_ACE_SVCCONF) 00729 delete ace_service_config_sig_handler_; 00730 ace_service_config_sig_handler_ = 0; 00731 #endif /* ! ACE_LACKS_ACE_SVCCONF */ 00732 00733 #if defined (ACE_MT_SAFE) && (ACE_MT_SAFE != 0) 00734 delete internal_lock_; 00735 internal_lock_ = 0; 00736 00737 delete singleton_null_lock_; 00738 singleton_null_lock_ = 0; 00739 00740 delete singleton_recursive_lock_; 00741 singleton_recursive_lock_ = 0; 00742 #endif /* ACE_MT_SAFE */ 00743 00744 // Indicate that this ACE_Object_Manager instance has been shut down. 00745 object_manager_state_ = OBJ_MAN_SHUT_DOWN; 00746 00747 // Then, ensure that the ACE_OS_Object_Manager gets shut down. 00748 if (this == instance_ && ACE_OS_Object_Manager::instance_) 00749 ACE_OS_Object_Manager::instance_->fini (); 00750 00751 if (dynamically_allocated_) 00752 { 00753 delete this; 00754 } 00755 00756 if (this == instance_) 00757 instance_ = 0; 00758 00759 return 0; 00760 }
| int ACE_Object_Manager::init | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Explicitly initialize (construct the singleton instance of) the ACE_Object_Manager. Returns 0 on success, -1 on failure, and 1 if it had already been called.
Implements ACE_Object_Manager_Base.
Definition at line 176 of file Object_Manager.cpp.
References ACE_APPLICATION_PREALLOCATED_ARRAY_DEFINITIONS, ACE_APPLICATION_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT_DEFINITIONS, ACE_FILECACHE_LOCK, ACE_LOG_MSG, ACE_NEW_RETURN, ACE_PREALLOCATE_OBJECT, ace_service_config_sig_handler_, ACE_SYNCH_RW_MUTEX, ACE_Service_Config::handle_signal(), ACE_OS_Object_Manager::instance(), instance_, ACE_Object_Manager_Base::next_, ACE_Object_Manager_Base::OBJ_MAN_INITIALIZED, ACE_Object_Manager_Base::OBJ_MAN_INITIALIZING, ACE_Object_Manager_Base::object_manager_state_, preallocations_, ACE_Service_Config::signal_handler(), ACE_Trace::start_tracing(), and ACE_Object_Manager_Base::starting_up_i().
Referenced by ACE_Object_Manager(), and ACE::init().
00177 { 00178 if (starting_up_i ()) 00179 { 00180 // First, indicate that the ACE_Object_Manager instance is being 00181 // initialized. 00182 object_manager_state_ = OBJ_MAN_INITIALIZING; 00183 00184 // Only The Instance sets up with ACE_OS_Object_Manager and initializes 00185 // the preallocated objects. 00186 if (this == instance_) 00187 { 00188 // Make sure that the ACE_OS_Object_Manager has been created, 00189 // and register with it for chained fini (). 00190 ACE_OS_Object_Manager::instance ()->next_ = this; 00191 00192 # if defined (ACE_HAS_BUILTIN_ATOMIC_OP) 00193 ACE_Atomic_Op<ACE_Thread_Mutex, long>::init_functions (); 00194 ACE_Atomic_Op<ACE_Thread_Mutex, unsigned long>::init_functions (); 00195 # endif /* ACE_HAS_BUILTIN_ATOMIC_OP */ 00196 00197 # if !defined (ACE_LACKS_ACE_SVCCONF) 00198 // Construct the ACE_Service_Config's signal handler. 00199 ACE_NEW_RETURN (ace_service_config_sig_handler_, 00200 ACE_Sig_Adapter (&ACE_Service_Config::handle_signal), -1); 00201 ACE_Service_Config::signal_handler (ace_service_config_sig_handler_); 00202 # endif /* ! ACE_LACKS_ACE_SVCCONF */ 00203 00204 // Allocate the preallocated (hard-coded) object instances. 00205 ACE_PREALLOCATE_OBJECT (ACE_SYNCH_RW_MUTEX, ACE_FILECACHE_LOCK) 00206 # if defined (ACE_HAS_THREADS) 00207 ACE_PREALLOCATE_OBJECT (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, 00208 ACE_STATIC_OBJECT_LOCK) 00209 # endif /* ACE_HAS_THREADS */ 00210 # if defined (ACE_MT_SAFE) && (ACE_MT_SAFE != 0) 00211 ACE_PREALLOCATE_OBJECT (ACE_Thread_Mutex, 00212 ACE_MT_CORBA_HANDLER_LOCK) 00213 ACE_PREALLOCATE_OBJECT (ACE_Thread_Mutex, ACE_DUMP_LOCK) 00214 ACE_PREALLOCATE_OBJECT (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, 00215 ACE_SIG_HANDLER_LOCK) 00216 ACE_PREALLOCATE_OBJECT (ACE_Null_Mutex, ACE_SINGLETON_NULL_LOCK) 00217 ACE_PREALLOCATE_OBJECT (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, 00218 ACE_SINGLETON_RECURSIVE_THREAD_LOCK) 00219 ACE_PREALLOCATE_OBJECT (ACE_Thread_Mutex, ACE_THREAD_EXIT_LOCK) 00220 #if !defined (ACE_LACKS_ACE_TOKEN) && defined (ACE_HAS_TOKENS_LIBRARY) 00221 ACE_PREALLOCATE_OBJECT (ACE_TOKEN_CONST::MUTEX, 00222 ACE_TOKEN_MANAGER_CREATION_LOCK) 00223 ACE_PREALLOCATE_OBJECT (ACE_TOKEN_CONST::MUTEX, 00224 ACE_TOKEN_INVARIANTS_CREATION_LOCK) 00225 #endif /* ! ACE_LACKS_ACE_TOKEN && ACE_HAS_TOKENS_LIBRARY */ 00226 ACE_PREALLOCATE_OBJECT (ACE_Thread_Mutex, 00227 ACE_PROACTOR_EVENT_LOOP_LOCK) 00228 # endif /* ACE_MT_SAFE */ 00229 } 00230 00231 if (this == instance_) 00232 { 00233 // Hooks for preallocated objects and arrays provided by application. 00234 ACE_APPLICATION_PREALLOCATED_OBJECT_DEFINITIONS 00235 ACE_APPLICATION_PREALLOCATED_ARRAY_DEFINITIONS 00236 00237 # if defined (ACE_HAS_TSS_EMULATION) 00238 // Initialize the main thread's TS storage. 00239 if (!ts_storage_initialized_) 00240 { 00241 ACE_TSS_Emulation::tss_open (ts_storage_); 00242 ts_storage_initialized_ = true; 00243 } 00244 # endif /* ACE_HAS_TSS_EMULATION */ 00245 00246 #if defined (ACE_DISABLE_WIN32_ERROR_WINDOWS) && \ 00247 defined (ACE_WIN32) && !defined (ACE_HAS_WINCE) 00248 #if defined (_DEBUG) && (defined (_MSC_VER) || defined (__INTEL_COMPILER)) 00249 _CrtSetReportMode( _CRT_ERROR, _CRTDBG_MODE_FILE ); 00250 _CrtSetReportFile( _CRT_ERROR, _CRTDBG_FILE_STDERR ); 00251 _CrtSetReportMode( _CRT_ASSERT, _CRTDBG_MODE_FILE ); 00252 _CrtSetReportFile( _CRT_ASSERT, _CRTDBG_FILE_STDERR ); 00253 #endif /* _DEBUG && _MSC_VER || __INTEL_COMPILER */ 00254 00255 // The system does not display the critical-error-handler message box 00256 SetErrorMode(SEM_FAILCRITICALERRORS); 00257 00258 // And this will catch all unhandled exceptions. 00259 SetUnhandledExceptionFilter (&ACE_UnhandledExceptionFilter); 00260 #endif /* ACE_DISABLE_WIN32_ERROR_WINDOWS && ACE_WIN32 && !ACE_HAS_WINCE */ 00261 00262 00263 # if !defined (ACE_LACKS_ACE_SVCCONF) 00264 ACE_NEW_RETURN (preallocations_, 00265 ACE_Object_Manager_Preallocations, 00266 -1); 00267 # endif /* ! ACE_LACKS_ACE_SVCCONF */ 00268 00269 // Open the main thread's ACE_Log_Msg. 00270 if (0 == ACE_LOG_MSG) 00271 return -1; 00272 } 00273 00274 // Finally, indicate that the ACE_Object_Manager instance has 00275 // been initialized. 00276 object_manager_state_ = OBJ_MAN_INITIALIZED; 00277 00278 #if defined (ACE_HAS_TRACE) 00279 // Allow tracing again (useful if user does init/fini/init) 00280 ACE_Trace::start_tracing (); 00281 #endif /* ACE_HAS_TRACE */ 00282 00283 return 0; 00284 } else { 00285 // Had already initialized. 00286 return 1; 00287 } 00288 }
| ACE_Object_Manager * ACE_Object_Manager::instance | ( | void | ) | [static] |
Accessor to singleton instance. Because static member functions are provided in the interface, this should not be public. However, it is public so that ACE_Managed_Object<TYPE> can access it.
Definition at line 357 of file Object_Manager.cpp.
References ACE_ASSERT, ACE_NEW_RETURN, ACE_Object_Manager_Base::dynamically_allocated_, and instance_.
Referenced by at_exit(), ACE::fini(), and ACE::init().
00358 { 00359 // This function should be called during construction of static 00360 // instances, or before any other threads have been created in 00361 // the process. So, it's not thread safe. 00362 00363 if (instance_ == 0) 00364 { 00365 ACE_Object_Manager *instance_pointer = 0; 00366 00367 ACE_NEW_RETURN (instance_pointer, 00368 ACE_Object_Manager, 00369 0); 00370 ACE_ASSERT (instance_pointer == instance_); 00371 00372 instance_pointer->dynamically_allocated_ = true; 00373 00374 return instance_pointer; 00375 } 00376 else 00377 return instance_; 00378 }
| ACE_Object_Manager& ACE_Object_Manager::operator= | ( | const ACE_Object_Manager & | ) | [private] |
| int ACE_Object_Manager::shutting_down | ( | void | ) | [static] |
Returns 1 after the ACE_Object_Manager has been destroyed. This flag can be used to determine if the program is in the midst of destroying static objects. (Note that the program might destroy some static objects before this flag can return 1, if ACE_HAS_NONSTATIC_OBJECT_MANAGER is not defined.)
Definition at line 150 of file Object_Manager.cpp.
References instance_, and ACE_Object_Manager_Base::shutting_down_i().
Referenced by ACE_DLL_Singleton_T< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), ACE_Unmanaged_TSS_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), ACE_TSS_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), ACE_Unmanaged_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), ACE_Service_Repository::instance(), ACE_Framework_Repository::instance(), and ACE_Thread_Manager::wait().
00151 { 00152 return ACE_Object_Manager::instance_ ? instance_->shutting_down_i () : 1; 00153 }
| int ACE_Object_Manager::starting_up | ( | void | ) | [static] |
Returns 1 before the ACE_Object_Manager has been constructed. This flag can be used to determine if the program is constructing static objects. If no static object spawns any threads, the program will be single-threaded when this flag returns 1. (Note that the program still might construct some static objects when this flag returns 0, if ACE_HAS_NONSTATIC_OBJECT_MANAGER is not defined.)
Definition at line 144 of file Object_Manager.cpp.
References instance_, and ACE_Object_Manager_Base::starting_up_i().
Referenced by ACE_DLL_Singleton_T< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), ACE_Unmanaged_TSS_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), ACE_TSS_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), ACE_Unmanaged_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), ACE_Singleton< TYPE, ACE_LOCK >::instance(), ACE_Service_Repository::instance(), and ACE_Framework_Repository::instance().
00145 { 00146 return ACE_Object_Manager::instance_ ? instance_->starting_up_i () : 1; 00147 }
friend class ACE_Object_Manager_Manager [friend] |
Definition at line 436 of file Object_Manager.h.
For at_exit support.
Definition at line 334 of file Object_Manager.h.
Referenced by at_exit_i(), and fini().
ACE_BEGIN_VERSIONED_NAMESPACE_DECL ACE_Object_Manager * ACE_Object_Manager::instance_ = 0 [static, private] |
Singleton pointer.
Definition at line 415 of file Object_Manager.h.
Referenced by ACE_Object_Manager(), at_exit_i(), fini(), init(), instance(), shutting_down(), and starting_up().
void * ACE_Object_Manager::preallocated_array = { 0 } [static] |
Table of preallocated arrays.
Definition at line 403 of file Object_Manager.h.
Referenced by ACE_Managed_Object< TYPE >::get_preallocated_array().
void * ACE_Object_Manager::preallocated_object = { 0 } [static] |
Table of preallocated objects.
Definition at line 400 of file Object_Manager.h.
Referenced by ACE_Managed_Object< TYPE >::get_preallocated_object().
 1.4.7
1.4.7