#include <Process_Manager.h>
Inheritance diagram for ACE_Process_Manager:

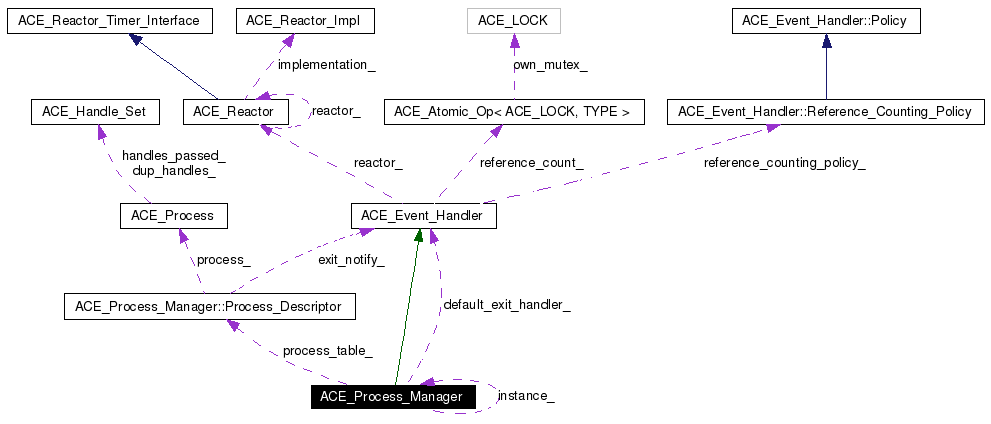
Utility methods | |
| int | register_handler (ACE_Event_Handler *event_handler, pid_t pid=ACE_INVALID_PID) |
| int | remove (pid_t pid) |
| size_t | managed (void) const |
| Return the number of managed processes. | |
| int | set_scheduler (const ACE_Sched_Params ¶ms, pid_t pid) |
| int | set_scheduler_all (const ACE_Sched_Params &) |
| void | dump (void) const |
| Dump the state of an object. | |
| ACE_ALLOC_HOOK_DECLARE | |
| Declare the dynamic allocation hooks. | |
Public Types | |
| enum | { DEFAULT_SIZE = 100 } |
Public Member Functions | |
Initialization and termination methods | |
| ACE_Process_Manager (size_t size=ACE_Process_Manager::DEFAULT_SIZE, ACE_Reactor *reactor=0) | |
| int | open (size_t size=ACE_Process_Manager::DEFAULT_SIZE, ACE_Reactor *r=0) |
| int | close (void) |
| Release all resources. Do not wait for processes to exit. | |
| virtual | ~ACE_Process_Manager (void) |
Process creation methods | |
| pid_t | spawn (ACE_Process *proc, ACE_Process_Options &options, ACE_Event_Handler *event_handler=0) |
| pid_t | spawn (ACE_Process_Options &options, ACE_Event_Handler *event_handler=0) |
| int | spawn_n (size_t n, ACE_Process_Options &options, pid_t *child_pids=0, ACE_Event_Handler *event_Handler=0) |
Process synchronization operations | |
| int | terminate (pid_t pid) |
| int | terminate (pid_t pid, int sig) |
| int | wait (const ACE_Time_Value &timeout=ACE_Time_Value::max_time) |
| pid_t | wait (pid_t pid, const ACE_Time_Value &timeout, ACE_exitcode *status=0) |
| pid_t | wait (pid_t pid, ACE_exitcode *status=0) |
| int | reap (pid_t pid=-1, ACE_exitcode *stat_loc=0, int options=WNOHANG) |
Static Public Member Functions | |
Singleton access and control | |
| ACE_Process_Manager * | instance (void) |
| Get pointer to a process-wide ACE_Process_Manager. | |
| ACE_Process_Manager * | instance (ACE_Process_Manager *) |
| void | close_singleton (void) |
| Delete the dynamically allocated singleton. | |
| void | cleanup (void *instance, void *arg) |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual int | handle_signal (int signum, siginfo_t *=0, ucontext_t *=0) |
Private Member Functions | |
| int | resize (size_t) |
| Resize the pool of Process_Descriptors. | |
| ssize_t | find_proc (pid_t process_id) |
| ssize_t | find_proc (ACE_HANDLE process_handle) |
| int | insert_proc (ACE_Process *process, ACE_Event_Handler *event_handler=0) |
| int | append_proc (ACE_Process *process, ACE_Event_Handler *event_handler=0) |
| int | remove_proc (size_t n) |
| int | notify_proc_handler (size_t n, ACE_exitcode status) |
Private Attributes | |
| Process_Descriptor * | process_table_ |
| Vector that describes process state within the Process_Manager. | |
| size_t | max_process_table_size_ |
| size_t | current_count_ |
| Current number of processes we are managing. | |
| ACE_Event_Handler * | default_exit_handler_ |
| ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex | lock_ |
| This lock protects access/ops on . | |
Static Private Attributes | |
| ACE_Process_Manager * | instance_ = 0 |
| Singleton pointer. | |
| int | delete_instance_ = 0 |
Friends | |
| class | ACE_Process_Control |
This class allows applications to control groups of processes, similar to how the ACE_Thread_Manager controls groups of threads. Naturally, it doesn't work at all on platforms, such as VxWorks or pSoS, that don't support process. There are two main ways of using ACE_Process_Manager, depending on how involved you wish to be with the termination of managed processes. If you want processes to simply go away when they're finished, register the ACE_Process_Manager with an ACE_Reactor that can handle notifications of child process exit:
In this usage scenario, the ACE_Process_Manager will clean up after any processes that it spawns. (On Unix, this means executing a wait(2) to collect the exit status and avoid zombie processes; on Win32, it means closing the process and thread HANDLEs that are created when CreateProcess is called.)
Note that in either case, ACE_Process_Manager allows you to register an ACE_Event_Handler to be called when a specific spawned process exits, or when any process without a specific ACE_Event_Handler exits. When a process exits, the appropriate ACE_Event_Handler's handle_input() method is called; the ACE_HANDLE passed is either the process's HANDLE (on Win32), or its pid cast to an ACE_HANDLE (on POSIX). It is also possible to call the wait() functions even when the ACE_Process_Manager is registered with a reactor.
Definition at line 98 of file Process_Manager.h.
|
|
Definition at line 103 of file Process_Manager.h.
00104 {
00105 DEFAULT_SIZE = 100
00106 };
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Initialize an ACE_Process_Manager with a table containing up to size processes. This table resizes itself automatically as needed. If a reactor is provided, this ACE_Process_Manager uses it to notify an application when a process it controls exits. By default, however, we don't use an ACE_Reactor. Definition at line 246 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_ERROR, ACE_TEXT, ACE_TRACE, LM_ERROR, and open().
00248 : ACE_Event_Handler (), 00249 process_table_ (0), 00250 max_process_table_size_ (0), 00251 current_count_ (0), 00252 default_exit_handler_ (0) 00253 #if defined (ACE_HAS_THREADS) 00254 , lock_ () 00255 #endif /* ACE_HAS_THREADS */ 00256 { 00257 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::ACE_Process_Manager"); 00258 00259 if (this->open (size, 00260 r) == -1) 00261 ACE_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, 00262 ACE_TEXT ("%p\n"), 00263 ACE_TEXT ("ACE_Process_Manager"))); 00264 } |
|
|
Destructor releases all resources and does not wait for processes to exit. Definition at line 301 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, and close().
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Append information about a process, i.e., its in the . Each entry is added at the end, growing the table if necessary. Register event_handler to be called back when the process exits. Definition at line 497 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, current_count_, DEFAULT_SIZE, ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::exit_notify_, ACE_Process::gethandle(), max_process_table_size_, ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::process_, process_table_, ACE_Event_Handler::reactor(), ACE_Reactor::register_handler(), and resize(). Referenced by insert_proc(), and spawn().
00499 {
00500 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::append_proc");
00501
00502 // Try to resize the array to twice its existing size (or the DEFAULT_SIZE,
00503 // if there are no array entries) if we run out of space...
00504 if (this->current_count_ >= this->max_process_table_size_)
00505 {
00506 size_t new_size = this->max_process_table_size_ * 2;
00507 if (new_size == 0)
00508 new_size = ACE_Process_Manager::DEFAULT_SIZE;
00509 if (this->resize (new_size) == -1)
00510 return -1;
00511 }
00512
00513 Process_Descriptor &proc_desc =
00514 this->process_table_[this->current_count_];
00515
00516 proc_desc.process_ = proc;
00517 proc_desc.exit_notify_ = event_handler;
00518
00519 #if defined (ACE_WIN32)
00520 // If we have a Reactor, then we're supposed to reap Processes
00521 // automagically. Get a handle to this new Process and tell the
00522 // Reactor we're interested in <handling_input> on it.
00523
00524 ACE_Reactor * const r = this->reactor ();
00525 if (r != 0)
00526 r->register_handler (this, proc->gethandle ());
00527 #endif /* ACE_WIN32 */
00528
00529 ++this->current_count_;
00530 return 0;
00531 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Cleanup method, used by the ACE_Object_Manager to destroy the singleton. Definition at line 38 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References close_singleton(). Referenced by instance().
00039 {
00040 ACE_Process_Manager::close_singleton ();
00041 }
|
|
|
Release all resources. Do not wait for processes to exit.
Definition at line 269 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, current_count_, default_exit_handler_, ACE_Event_Handler::handle_close(), max_process_table_size_, process_table_, ACE_Event_Handler::reactor(), ACE_Reactor::remove_handler(), remove_proc(), and SIGCHLD. Referenced by ~ACE_Process_Manager().
00270 {
00271 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::close");
00272
00273 if (this->reactor () != 0)
00274 {
00275 #if !defined (ACE_WIN32) && !defined (ACE_LACKS_UNIX_SIGNALS)
00276 this->reactor ()->remove_handler (SIGCHLD, (ACE_Sig_Action *) 0);
00277 #endif /* !ACE_WIN32 */
00278 this->reactor (0);
00279 }
00280
00281 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, this->lock_, -1));
00282
00283 if (this->process_table_ != 0)
00284 {
00285 while (this->current_count_ > 0)
00286 this->remove_proc (0);
00287
00288 delete [] this->process_table_;
00289 this->process_table_ = 0;
00290 this->max_process_table_size_ = 0;
00291 this->current_count_ = 0;
00292 }
00293
00294 if (this->default_exit_handler_ != 0)
00295 this->default_exit_handler_->handle_close (ACE_INVALID_HANDLE,0);
00296 this->default_exit_handler_ = 0;
00297
00298 return 0;
00299 }
|
|
|
Delete the dynamically allocated singleton.
Definition at line 176 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_GUARD, ACE_TRACE, delete_instance_, and instance_. Referenced by cleanup().
00177 {
00178 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::close_singleton");
00179
00180 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon,
00181 *ACE_Static_Object_Lock::instance ()));
00182
00183 if (ACE_Process_Manager::delete_instance_)
00184 {
00185 delete ACE_Process_Manager::instance_;
00186 ACE_Process_Manager::instance_ = 0;
00187 ACE_Process_Manager::delete_instance_ = 0;
00188 }
00189 }
|
|
|
Dump the state of an object.
Definition at line 84 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_BEGIN_DUMP, ACE_DEBUG, ACE_END_DUMP, ACE_TEXT, ACE_TRACE, current_count_, ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::dump(), LM_DEBUG, and process_table_.
00085 {
00086 #if defined (ACE_HAS_DUMP)
00087 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::dump");
00088
00089 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_BEGIN_DUMP, this));
00090
00091 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\nmax_process_table_size_ = %d"), this->max_process_table_size_));
00092 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("\ncurrent_count_ = %d"), this->current_count_));
00093
00094 for (size_t i = 0; i < this->current_count_; i++)
00095 this->process_table_[i].dump ();
00096
00097 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_END_DUMP));
00098 #endif /* ACE_HAS_DUMP */
00099 }
|
|
|
Locate the index of the table slot occupied by process_handle. Returns ~0 if process_handle is not in the Definition at line 704 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, current_count_, ACE_Process::gethandle(), ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::process_, and process_table_.
00705 {
00706 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::find_proc");
00707
00708 for (size_t i = 0; i < this->current_count_; ++i)
00709 if (h == this->process_table_[i].process_->gethandle ())
00710 return i;
00711
00712 return -1;
00713 }
|
|
|
Locate the index of the table slot occupied by . Returns -1 if is not in the Definition at line 688 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, current_count_, ACE_Process::getpid(), pid_t, ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::process_, and process_table_. Referenced by handle_signal(), insert_proc(), register_handler(), remove(), set_scheduler(), terminate(), and wait().
00689 {
00690 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::find_proc");
00691
00692 for (size_t i = 0; i < this->current_count_; ++i)
00693 if (pid == this->process_table_[i].process_->getpid ())
00694 return i;
00695
00696 return -1;
00697 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
On Unix, this routine is called asynchronously when a SIGCHLD is received. We just tweak the reactor so that it'll call back our function, which allows us to handle Process exits synchronously. On Win32, this routine is called synchronously, and is passed the HANDLE of the Process that exited, so we can do all our work here Reimplemented from ACE_Event_Handler. Definition at line 341 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_ERROR_RETURN, ACE_exitcode, ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_INVALID_PID, ACE_TEXT, find_proc(), ACE_Process::getpid(), LM_ERROR, ACE_Reactor::notify(), notify_proc_handler(), pid_t, ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::process_, process_table_, ACE_Event_Handler::reactor(), remove_proc(), siginfo_t::si_handle_, ssize_t, and ucontext_t.
00344 {
00345 #if defined (ACE_WIN32)
00346 ACE_HANDLE proc = si->si_handle_;
00347 ACE_exitcode status = 0;
00348 BOOL result = ::GetExitCodeProcess (proc,
00349 &status);
00350 if (result)
00351 {
00352 if (status != STILL_ACTIVE)
00353 {
00354 {
00355 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, lock_, -1));
00356
00357 ssize_t const i = this->find_proc (proc);
00358 if (i == -1)
00359 return -1;
00360 #if 0
00361 pid_t pid = i != -1
00362 ? process_table_[i].process_->getpid ()
00363 : ACE_INVALID_PID;
00364 #endif
00365 this->notify_proc_handler (i, status);
00366 this->remove_proc (i);
00367 }
00368 return -1; // remove this HANDLE/Event_Handler combination
00369 }
00370 else
00371 ACE_ERROR_RETURN ((LM_ERROR,
00372 ACE_TEXT ("Process still active")
00373 ACE_TEXT (" -- shouldn't have been called yet!\n")),
00374 0); // return 0 : stay registered
00375 }
00376 else
00377 {
00378 // <GetExitCodeProcess> failed.
00379 ACE_ERROR_RETURN ((LM_ERROR,
00380 ACE_TEXT ("GetExitCodeProcess failed")),
00381 -1); // return -1: unregister
00382 }
00383 #else /* !ACE_WIN32 */
00384 ACE_UNUSED_ARG (si);
00385 return reactor ()->notify (this, ACE_Event_Handler::READ_MASK);
00386 #endif /* !ACE_WIN32 */
00387 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Insert a process in the table (checks for duplicates). Omitting the process handle won't work on Win32... Register event_handler to be called back when the process exits. Definition at line 537 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, append_proc(), find_proc(), and ACE_Process::getpid().
00539 {
00540 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::insert_proc");
00541
00542 // Check for duplicates and bail out if they're already
00543 // registered...
00544 if (this->find_proc (proc->getpid ()) != -1)
00545 return -1;
00546
00547 return this->append_proc (proc, event_handler);
00548 }
|
|
|
Set pointer to a process-wide ACE_Process_Manager and return existing pointer. Definition at line 147 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit(), cleanup(), delete_instance_, and instance_.
00148 {
00149 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::instance");
00150 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon,
00151 *ACE_Static_Object_Lock::instance (), 0));
00152
00153 ACE_Process_Manager *t = ACE_Process_Manager::instance_;
00154 // We can't safely delete it since we don't know who created it!
00155 ACE_Process_Manager::delete_instance_ = 0;
00156
00157 // Register with the Object_Manager so that the wrapper to
00158 // delete the proactor will be called when Object_Manager is
00159 // being terminated.
00160
00161 #if defined ACE_HAS_SIG_C_FUNC
00162 ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit (ACE_Process_Manager::instance_,
00163 ACE_Process_Manager_cleanup,
00164 0);
00165 #else
00166 ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit (ACE_Process_Manager::instance_,
00167 ACE_Process_Manager::cleanup,
00168 0);
00169 #endif /* ACE_HAS_SIG_C_FUNC */
00170
00171 ACE_Process_Manager::instance_ = tm;
00172 return t;
00173 }
|
|
|
Get pointer to a process-wide ACE_Process_Manager.
Definition at line 109 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_NEW_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit(), cleanup(), delete_instance_, and instance_.
00110 {
00111 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::instance");
00112
00113 if (ACE_Process_Manager::instance_ == 0)
00114 {
00115 // Perform Double-Checked Locking Optimization.
00116 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon,
00117 *ACE_Static_Object_Lock::instance (), 0));
00118
00119 if (ACE_Process_Manager::instance_ == 0)
00120 {
00121 ACE_NEW_RETURN (ACE_Process_Manager::instance_,
00122 ACE_Process_Manager,
00123 0);
00124 ACE_Process_Manager::delete_instance_ = 1;
00125
00126 // Register with the Object_Manager so that the wrapper to
00127 // delete the proactor will be called when Object_Manager is
00128 // being terminated.
00129
00130 #if defined ACE_HAS_SIG_C_FUNC
00131 ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit (ACE_Process_Manager::instance_,
00132 ACE_Process_Manager_cleanup,
00133 0);
00134 #else
00135 ACE_Object_Manager::at_exit (ACE_Process_Manager::instance_,
00136 ACE_Process_Manager::cleanup,
00137 0);
00138 #endif /* ACE_HAS_SIG_C_FUNC */
00139
00140 }
00141 }
00142
00143 return ACE_Process_Manager::instance_;
00144 }
|
|
|
Return the number of managed processes.
Definition at line 8 of file Process_Manager.inl. References current_count_.
00009 {
00010 return current_count_;
00011 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
If there's a specific handler for the Process at index n in the table, or there's a default handler, call it. Definition at line 990 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_DEBUG, ACE_exitcode, ACE_TEXT, current_count_, default_exit_handler_, ACE_Process::exit_code(), ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::exit_notify_, ACE_Event_Handler::handle_close(), ACE_Event_Handler::handle_exit(), LM_DEBUG, ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::process_, and process_table_. Referenced by handle_signal(), and wait().
00992 {
00993 if (i < this->current_count_)
00994 {
00995 Process_Descriptor &proc_desc =
00996 this->process_table_[i];
00997
00998 proc_desc.process_->exit_code (exit_code);
00999
01000 if (proc_desc.exit_notify_ != 0)
01001 proc_desc.exit_notify_->handle_exit (proc_desc.process_);
01002 else if (this->default_exit_handler_ != 0
01003 && this->default_exit_handler_->handle_exit (proc_desc.process_) < 0)
01004 {
01005 this->default_exit_handler_->handle_close
01006 (ACE_INVALID_HANDLE,
01007 0);
01008 this->default_exit_handler_ = 0;
01009 }
01010 return 1;
01011 }
01012 else
01013 {
01014 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG,
01015 ACE_TEXT ("(%P:%t|%T) ACE_Process_Manager::notify_proc_handler:")
01016 ACE_TEXT (" unknown/unmanaged process reaped\n")));
01017 return 0;
01018 }
01019 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Initialize an ACE_Process_Manager with a table containing up to size processes. This table resizes itself automatically as needed. If a reactor is provided, this ACE_Process_Manager uses it to notify an application when a process it controls exits. By default, however, we don't use an ACE_Reactor. Definition at line 222 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, max_process_table_size_, ACE_Event_Handler::reactor(), ACE_Reactor::register_handler(), resize(), and SIGCHLD. Referenced by ACE_Process_Manager().
00224 {
00225 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::open");
00226
00227 if (r)
00228 {
00229 this->reactor (r);
00230 #if !defined (ACE_WIN32) && !defined (ACE_LACKS_UNIX_SIGNALS)
00231 // Register signal handler object.
00232 if (r->register_handler (SIGCHLD, this) == -1)
00233 return -1;
00234 #endif /* !defined(ACE_WIN32) */
00235 }
00236
00237 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, this->lock_, -1));
00238
00239 if (this->max_process_table_size_ < size)
00240 this->resize (size);
00241 return 0;
00242 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 972 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_BIT_ENABLED, ACE_exitcode, ACE_TRACE, pid_t, wait(), and WNOHANG.
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Register an event handler to be called back when the specified process exits. If pid == ACE_INVALID_PID this handler is called when any process with no specific handler exits.
Definition at line 390 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_INVALID_PID, default_exit_handler_, ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::exit_notify_, find_proc(), ACE_Event_Handler::handle_close(), pid_t, process_table_, and ssize_t.
00392 {
00393 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, this->lock_, -1));
00394
00395 if (pid == ACE_INVALID_PID)
00396 {
00397 if (this->default_exit_handler_ != 0)
00398 this->default_exit_handler_->handle_close (ACE_INVALID_HANDLE, 0);
00399 this->default_exit_handler_ = eh;
00400 return 0;
00401 }
00402
00403 ssize_t const i = this->find_proc (pid);
00404
00405 if (i == -1)
00406 {
00407 errno = EINVAL;
00408 return -1;
00409 }
00410
00411 Process_Descriptor &proc_desc = this->process_table_[i];
00412
00413 if (proc_desc.exit_notify_ != 0)
00414 proc_desc.exit_notify_->handle_close (ACE_INVALID_HANDLE, 0);
00415 proc_desc.exit_notify_ = eh;
00416 return 0;
00417 }
|
|
|
Remove process pid from the ACE_Process_Manager's internal records. This is called automatically by the reap() method after it successfully reaps a process. It's also possible to call this method directly from a signal handler, but don't call both reap() and remove()! Definition at line 553 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, find_proc(), pid_t, remove_proc(), and ssize_t. Referenced by wait().
00554 {
00555 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::remove");
00556
00557 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, this->lock_, -1));
00558
00559 ssize_t const i = this->find_proc (pid);
00560
00561 if (i != -1)
00562 return this->remove_proc (i);
00563
00564 // set "process not found" error
00565 return -1;
00566 }
|
|
|
Actually removes the process at index n from the table. This method must be called with locks held. Definition at line 571 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_TRACE, current_count_, ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::exit_notify_, ACE_Process::gethandle(), ACE_Event_Handler::handle_close(), ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::process_, process_table_, ACE_Event_Handler::reactor(), ACE_Reactor::remove_handler(), and ACE_Process::unmanage(). Referenced by close(), handle_signal(), remove(), and wait().
00572 {
00573 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::remove_proc");
00574
00575 // If there's an exit_notify_ <Event_Handler> for this pid, call its
00576 // <handle_close> method.
00577
00578 if (this->process_table_[i].exit_notify_ != 0)
00579 {
00580 this->process_table_[i].exit_notify_->handle_close
00581 (this->process_table_[i].process_->gethandle(),
00582 0);
00583 this->process_table_[i].exit_notify_ = 0;
00584 }
00585
00586 #if defined (ACE_WIN32)
00587 ACE_Reactor * const r = this->reactor ();
00588 if (r != 0)
00589 r->remove_handler (this->process_table_[i].process_->gethandle (),
00590 ACE_Event_Handler::DONT_CALL);
00591 #endif /* ACE_WIN32 */
00592
00593 this->process_table_[i].process_->unmanage ();
00594
00595 this->process_table_[i].process_ = 0;
00596
00597 this->current_count_--;
00598
00599 if (this->current_count_ > 0)
00600 // Compact the table by moving the last item into the slot vacated
00601 // by the index being removed (this is a structure assignment).
00602 this->process_table_[i] =
00603 this->process_table_[this->current_count_];
00604
00605 return 0;
00606 }
|
|
|
Resize the pool of Process_Descriptors.
Definition at line 192 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_NEW_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, current_count_, max_process_table_size_, and process_table_. Referenced by append_proc(), and open().
00193 {
00194 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::resize");
00195
00196 if (size <= this->max_process_table_size_)
00197 return 0;
00198
00199 Process_Descriptor *temp = 0;
00200
00201 ACE_NEW_RETURN (temp,
00202 Process_Descriptor[size],
00203 -1);
00204
00205 for (size_t i = 0;
00206 i < this->current_count_;
00207 i++)
00208 // Structure assignment.
00209 temp[i] = this->process_table_[i];
00210
00211 this->max_process_table_size_ = size;
00212
00213 delete [] this->process_table_;
00214
00215 this->process_table_ = temp;
00216 return 0;
00217 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Sets the scheduling parameters for process identified by pid by passing params, pid to ACE_OS::sched_params().
Definition at line 646 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_INVALID_PID, ACE_TRACE, find_proc(), pid_t, ACE_OS::sched_params(), and ssize_t.
00648 {
00649 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::set_scheduler");
00650
00651 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex,
00652 ace_mon, this->lock_, -1));
00653
00654 // Check to see if the process identified by the given pid is managed by
00655 // this instance of ACE_Process_Manager.
00656 ssize_t const i = this->find_proc (pid);
00657
00658 if (i == -1)
00659 // set "no such process" error
00660 return ACE_INVALID_PID;
00661
00662 return ACE_OS::sched_params (params, pid);
00663 }
|
|
|
Sets the scheduling parameters for all the processes managed by this ACE_Process_Manager by passing params to ACE_OS::sched_params().
Definition at line 666 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, current_count_, ACE_Process::getpid(), pid_t, ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::process_, process_table_, and ACE_OS::sched_params().
00667 {
00668 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::set_scheduler_all");
00669
00670 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex,
00671 ace_mon, this->lock_, -1));
00672
00673 for (size_t i = 0; i < this->current_count_; ++i)
00674 {
00675 pid_t const pid = this->process_table_[i].process_->getpid ();
00676 if (ACE_OS::sched_params (params, pid) != 0)
00677 return -1;
00678 }
00679 return 0;
00680
00681 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Create a new process with the specified options. Register event_handler to be called back when the process exits. On success, returns the process id of the child that was created. On failure, returns ACE_INVALID_PID. Definition at line 422 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_INVALID_PID, ACE_NEW_RETURN, pid_t, and spawn().
00424 {
00425 ACE_Process *process = 0;
00426 ACE_NEW_RETURN (process,
00427 ACE_Managed_Process,
00428 ACE_INVALID_PID);
00429
00430 pid_t const pid = spawn (process, options, event_handler);
00431 if (pid == ACE_INVALID_PID || pid == 0)
00432 delete process;
00433
00434 return pid;
00435 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Create a new process with specified options. Register event_handler to be called back when the process exits. On success, returns the process id of the child that was created. On failure, returns ACE_INVALID_PID. Definition at line 440 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_INVALID_PID, ACE_TRACE, append_proc(), pid_t, and ACE_Process::spawn(). Referenced by spawn(), and spawn_n().
00443 {
00444 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::spawn");
00445
00446 pid_t const pid = process->spawn (options);
00447
00448 // Only include the pid in the parent's table.
00449 if (pid == ACE_INVALID_PID || pid == 0)
00450 return pid;
00451
00452 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex,
00453 ace_mon, this->lock_, -1));
00454
00455 if (this->append_proc (process, event_handler) == -1)
00456 // bad news: spawned, but not registered in table.
00457 return ACE_INVALID_PID;
00458
00459 return pid;
00460 }
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Create n new processes with the same options. If child_pids is non-0 it is expected to be an array of at least n pid_t, which are filled in with the process IDs of the spawned processes. Register event_handler to be called back when each process exits. Returns 0 on success and -1 on failure. Definition at line 465 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_INVALID_PID, ACE_TRACE, pid_t, and spawn().
00469 {
00470 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::spawn_n");
00471
00472 if (child_pids != 0)
00473 for (size_t i = 0;
00474 i < n;
00475 ++i)
00476 child_pids[i] = ACE_INVALID_PID;
00477
00478 for (size_t i = 0;
00479 i < n;
00480 i++)
00481 {
00482 pid_t const pid = this->spawn (options, event_handler);
00483 if (pid == ACE_INVALID_PID || pid == 0)
00484 // We're in the child or something's gone wrong.
00485 return pid;
00486 else if (child_pids != 0)
00487 child_pids[i] = pid;
00488 }
00489
00490 return 0;
00491 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Sends the specified signal to the specified process.
Definition at line 627 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, find_proc(), ACE_OS::kill(), pid_t, and ssize_t.
00628 {
00629 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::terminate");
00630
00631 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, this->lock_, -1));
00632
00633 // Check for duplicates and bail out if they're already
00634 // registered...
00635 ssize_t const i = this->find_proc (pid);
00636
00637 if (i == -1)
00638 // set "no such process" error
00639 return -1;
00640
00641 return ACE_OS::kill (pid, sig);
00642 }
|
|
|
Abruptly terminate a single process with id pid using the ACE::terminate_process() method which works on both signal-capable systems and on Windows.
Definition at line 609 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_TRACE, find_proc(), pid_t, ssize_t, and ACE::terminate_process().
00610 {
00611 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::terminate");
00612
00613 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, this->lock_, -1));
00614
00615 // Check for duplicates and bail out if they're already
00616 // registered...
00617 ssize_t const i = this->find_proc (pid);
00618
00619 if (i == -1)
00620 // set "no such process" error
00621 return -1;
00622
00623 return ACE::terminate_process (pid);
00624 }
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Wait indefinitely for a single, specified process to terminate. If pid is 0, waits for any of the managed processes (but see the note concerning "sloppy process cleanup on unix"). If pid != 0, this method waits for that process only.
Definition at line 759 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_exitcode, ACE_TRACE, pid_t, and wait().
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Wait up to timeout for a single specified process to terminate. If pid is 0, this method waits for any of the managed processes (but see the note concerning "sloppy process cleanup on unix"). If pid != 0, waits for that process only.
Definition at line 774 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_ASSERT, ACE_DEBUG, ACE_ERROR_RETURN, ACE_exitcode, ACE_GUARD_RETURN, ACE_INVALID_PID, ACE_NEW_RETURN, ACE_SignalHandler, ACE_TEXT, ACE_TRACE, current_count_, find_proc(), ACE_Process::gethandle(), ACE_Process::getpid(), LM_DEBUG, LM_ERROR, ACE_Time_Value::msec(), notify_proc_handler(), pid_t, ACE_Process_Manager::Process_Descriptor::process_, process_table_, ACE_Event_Handler::reactor(), ACE_Sig_Action::register_action(), remove(), remove_proc(), SIGCHLD, ACE_OS::sleep(), ssize_t, ACE_Countdown_Time::update(), ACE_Process::wait(), ACE_OS::waitpid(), and WNOHANG.
00777 {
00778 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::wait");
00779
00780 ACE_exitcode local_stat = 0;
00781 if (status == 0)
00782 status = &local_stat;
00783
00784 *status = 0;
00785
00786 ssize_t idx = -1;
00787 ACE_Process *proc = 0;
00788
00789 ACE_MT (ACE_GUARD_RETURN (ACE_Recursive_Thread_Mutex, ace_mon, this->lock_, -1));
00790
00791 if (pid != 0)
00792 {
00793 idx = this->find_proc (pid);
00794 if (idx == -1)
00795 return ACE_INVALID_PID;
00796 else
00797 proc = process_table_[idx].process_;
00798 }
00799
00800 if (proc != 0)
00801 pid = proc->wait (timeout, status);
00802 else
00803 {
00804 // Wait for any Process spawned by this Process_Manager.
00805 #if defined (ACE_WIN32)
00806 HANDLE *handles = 0;
00807
00808 ACE_NEW_RETURN (handles,
00809 HANDLE[this->current_count_],
00810 ACE_INVALID_PID);
00811
00812 for (size_t i = 0;
00813 i < this->current_count_;
00814 ++i)
00815 handles[i] =
00816 process_table_[i].process_->gethandle ();
00817
00818 DWORD handle_count = static_cast<DWORD> (this->current_count_);
00819 DWORD result = ::WaitForMultipleObjects (handle_count,
00820 handles,
00821 FALSE,
00822 timeout == ACE_Time_Value::max_time
00823 ? INFINITE
00824 : timeout.msec ());
00825 if (result == WAIT_FAILED)
00826 pid = ACE_INVALID_PID;
00827 else if (result == WAIT_TIMEOUT)
00828 pid = 0;
00829 else
00830 {
00831 // Green Hills produces a warning that result >= WAIT_OBJECT_0 is
00832 // a pointless comparison because WAIT_OBJECT_0 is zero and DWORD is
00833 // unsigned long, so this test is skipped for Green Hills.
00834 // Same for mingw.
00835 # if defined (ghs) || defined (__MINGW32__) || (defined (_MSC_VER) && _MSC_VER >= 1300)
00836 ACE_ASSERT (result < WAIT_OBJECT_0 + this->current_count_);
00837 # else
00838 ACE_ASSERT (result >= WAIT_OBJECT_0
00839 && result < WAIT_OBJECT_0 + this->current_count_);
00840 # endif
00841
00842 idx = this->find_proc (handles[result - WAIT_OBJECT_0]);
00843
00844 if (idx != -1)
00845 {
00846 pid = process_table_[idx].process_->getpid ();
00847 result = ::GetExitCodeProcess (handles[result - WAIT_OBJECT_0],
00848 status);
00849 if (result == 0)
00850 {
00851 // <GetExitCodeProcess> failed!
00852 this->remove_proc (idx);
00853 pid = ACE_INVALID_PID;
00854 }
00855 }
00856 else
00857 {
00858 // uh oh...handle removed from process_table_, even though
00859 // we're holding a lock!
00860 delete [] handles;
00861 ACE_ERROR_RETURN ((LM_ERROR,
00862 ACE_TEXT ("Process removed")
00863 ACE_TEXT (" -- somebody's ignoring the lock!\n")),
00864 -1);
00865 }
00866 }
00867
00868 delete [] handles;
00869 #else /* !defined(ACE_WIN32) */
00870 if (timeout == ACE_Time_Value::max_time)
00871 {
00872 pid = ACE_OS::waitpid (-1, status, 0);
00873 }
00874 else if (timeout == ACE_Time_Value::zero)
00875 {
00876 pid = ACE_OS::waitpid (-1, status, WNOHANG);
00877 }
00878 else
00879 {
00880 # if defined (ACE_LACKS_UNIX_SIGNALS)
00881 pid = 0;
00882 ACE_Time_Value sleeptm (1); // 1 msec
00883 if (sleeptm > timeout) // if sleeptime > waittime
00884 sleeptm = timeout;
00885 ACE_Time_Value tmo (timeout); // Need one we can change
00886 for (ACE_Countdown_Time time_left (&tmo); tmo > ACE_Time_Value::zero ; time_left.update ())
00887 {
00888 pid = ACE_OS::waitpid (-1, status, WNOHANG);
00889 if (pid > 0 || pid == ACE_INVALID_PID)
00890 break; // Got a child or an error - all done
00891
00892 // pid 0, nothing is ready yet, so wait.
00893 // Do a (very) short sleep (only this thread sleeps).
00894 ACE_OS::sleep (sleeptm);
00895 }
00896 # else
00897 // Force generation of SIGCHLD, even though we don't want to
00898 // catch it - just need it to interrupt the sleep below.
00899 // If this object has a reactor set, assume it was given at
00900 // open(), and there's already a SIGCHLD action set, so no
00901 // action is needed here.
00902 ACE_Sig_Action old_action;
00903 if (this->reactor () == 0)
00904 {
00905 ACE_Sig_Action do_sigchld ((ACE_SignalHandler)sigchld_nop);
00906 do_sigchld.register_action (SIGCHLD, &old_action);
00907 }
00908
00909 ACE_Time_Value tmo (timeout); // Need one we can change
00910 for (ACE_Countdown_Time time_left (&tmo); ; time_left.update ())
00911 {
00912 pid = ACE_OS::waitpid (-1, status, WNOHANG);
00913 # if defined (ACE_VXWORKS) && (ACE_VXWORKS >= 0x600)
00914 if (pid > 0 || (pid == ACE_INVALID_PID && errno != EINTR))
00915 # else
00916 if (pid > 0 || pid == ACE_INVALID_PID)
00917 # endif
00918 break; // Got a child or an error - all done
00919
00920 // pid 0, nothing is ready yet, so wait.
00921 // Do a sleep (only this thread sleeps) til something
00922 // happens. This relies on SIGCHLD interrupting the sleep.
00923 // If SIGCHLD isn't delivered, we'll need to do something
00924 // with sigaction to force it.
00925 if (-1 == ACE_OS::sleep (tmo) && errno == EINTR)
00926 continue;
00927 // Timed out
00928 pid = 0;
00929 break;
00930 }
00931
00932 // Restore the previous SIGCHLD action if it was changed.
00933 if (this->reactor () == 0)
00934 {
00935 old_action.register_action (SIGCHLD);
00936 }
00937 # endif /* !ACE_LACKS_UNIX_SIGNALS */
00938 }
00939 #endif /* !defined (ACE_WIN32) */
00940 }
00941
00942 if (pid != ACE_INVALID_PID && pid != 0)
00943 {
00944 if (proc == 0)
00945 {
00946 idx = this->find_proc (pid);
00947 if (idx == -1)
00948 {
00949 // oops, reaped an unmanaged process!
00950 ACE_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG,
00951 ACE_TEXT ("(%P|%t) oops, reaped unmanaged %d\n"),
00952 pid));
00953 return pid;
00954 }
00955 else
00956 proc = process_table_[idx].process_;
00957 }
00958 else
00959 ACE_ASSERT (pid == proc->getpid ());
00960
00961 this->notify_proc_handler (idx,
00962 *status);
00963 this->remove (pid);
00964 }
00965
00966 return pid;
00967 }
|
|
|
Block until there are no more child processes running that were spawned by this ACE_Process_Manager. Unlike the wait() method below, this method does not require a signal handler or use of ACE_OS::sigwait() because it simply blocks synchronously waiting for all the children managed by this ACE_Process_Manager to exit. Note that this does not return any status information about the success or failure of exiting child processes, although any registered exit handlers are called.
Definition at line 720 of file Process_Manager.cpp. References ACE_INVALID_PID, ACE_TRACE, current_count_, ACE_OS::gettimeofday(), and pid_t. Referenced by reap(), and wait().
00721 {
00722 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_Process_Manager::wait");
00723
00724 ACE_Time_Value until = timeout;
00725 ACE_Time_Value remaining = timeout;
00726
00727 if (until < ACE_Time_Value::max_time)
00728 until += ACE_OS::gettimeofday ();
00729
00730 while (this->current_count_ > 0)
00731 {
00732 pid_t const pid = this->wait (0, remaining);
00733
00734 if (pid == ACE_INVALID_PID) // wait() failed
00735 return -1;
00736 else if (pid == 0) // timeout
00737 break;
00738
00739 remaining = until < ACE_Time_Value::max_time
00740 ? until - ACE_OS::gettimeofday ()
00741 : ACE_Time_Value::max_time;
00742
00743 if (remaining <= ACE_Time_Value::zero)
00744 break;
00745
00746 // else Process terminated...wait for more...
00747 }
00748 return static_cast<int> (this->current_count_);
00749 }
|
|
|
Definition at line 101 of file Process_Manager.h. |
|
|
Declare the dynamic allocation hooks.
Definition at line 338 of file Process_Manager.h. |
|
|
Current number of processes we are managing.
Definition at line 454 of file Process_Manager.h. Referenced by append_proc(), close(), dump(), find_proc(), managed(), notify_proc_handler(), remove_proc(), resize(), set_scheduler_all(), and wait(). |
|
|
This event handler is used to notify when a process we control exits. Definition at line 458 of file Process_Manager.h. Referenced by close(), notify_proc_handler(), and register_handler(). |
|
|
Controls whether the is deleted when we shut down (we can only delete it safely if we created it!) Definition at line 62 of file Process_Manager.cpp. Referenced by close_singleton(), and instance(). |
|
|
Singleton pointer.
Definition at line 58 of file Process_Manager.cpp. Referenced by close_singleton(), and instance(). |
|
|
This lock protects access/ops on .
Definition at line 469 of file Process_Manager.h. |
|
|
Maximum number of processes we can manage (should be dynamically allocated). Definition at line 451 of file Process_Manager.h. Referenced by append_proc(), close(), open(), and resize(). |
|
|
Vector that describes process state within the Process_Manager.
Definition at line 447 of file Process_Manager.h. Referenced by append_proc(), close(), dump(), find_proc(), handle_signal(), notify_proc_handler(), register_handler(), remove_proc(), resize(), set_scheduler_all(), and wait(). |
 1.3.6
1.3.6