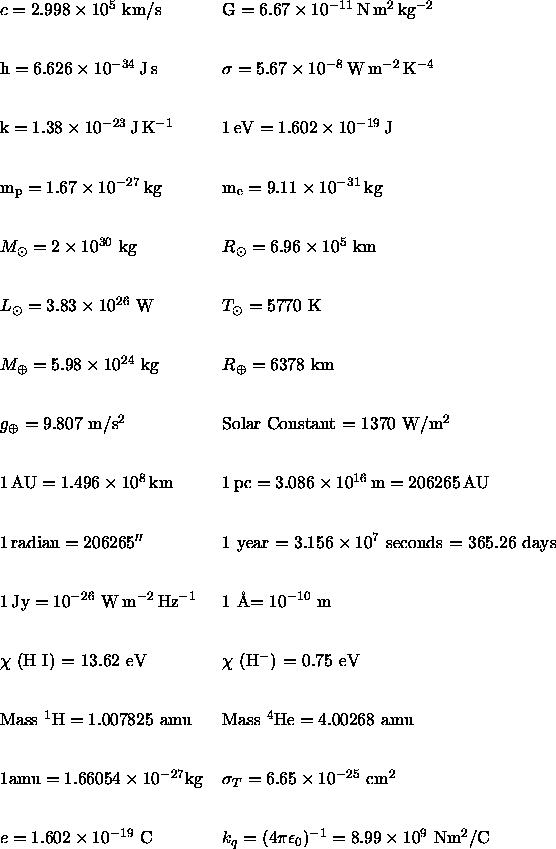
Last update: 26 April 1999
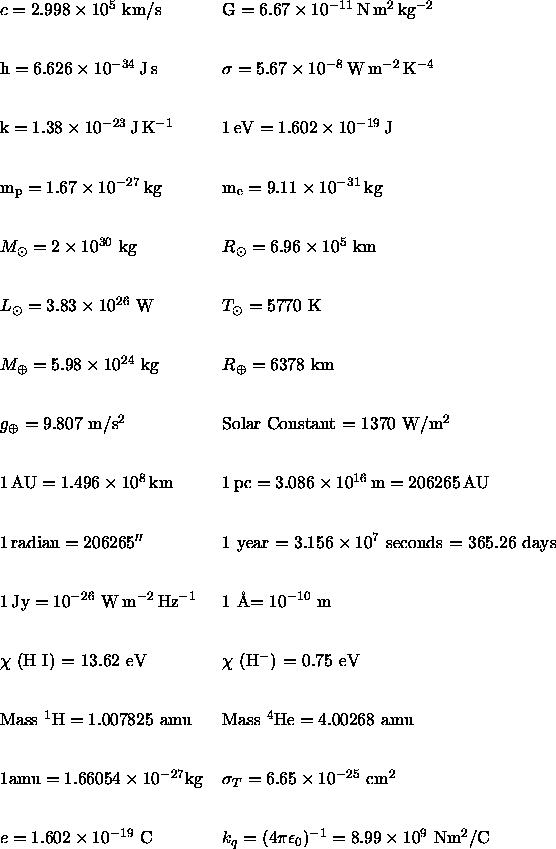
Orbital Mechanics: | |
|---|---|
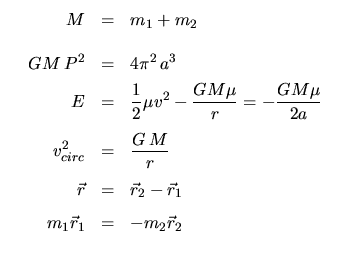 |
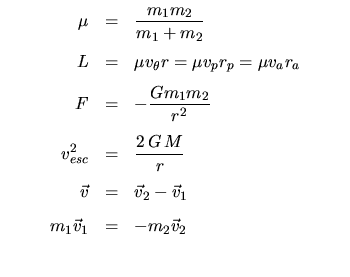 |
Electromagnetism, Light, and Atoms: | |
|---|---|
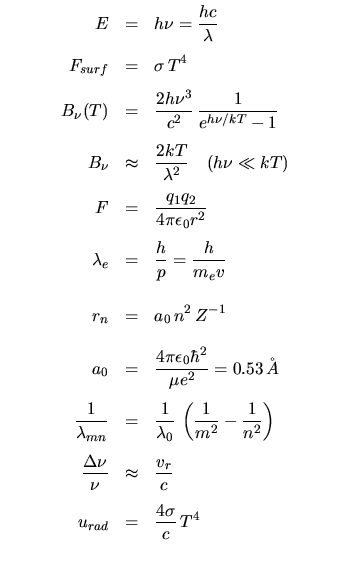 |
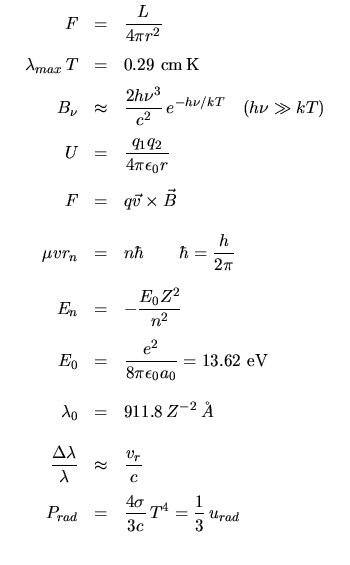 |
Intensity, Flux & Radiative Transfer: | |
|---|---|
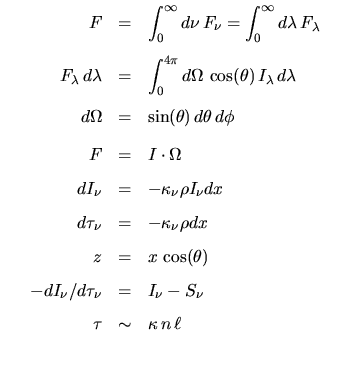 |
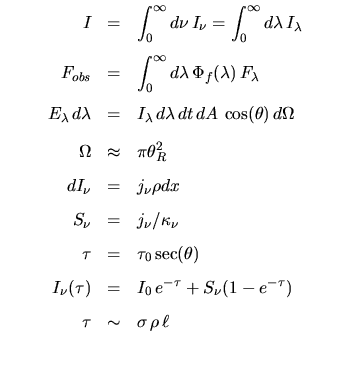 |
Stellar Distances, Magnitudes, and Properties: | |
|---|---|
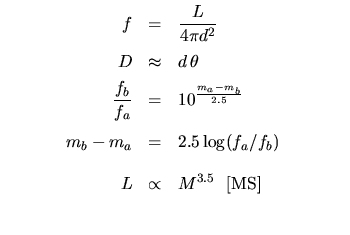 |
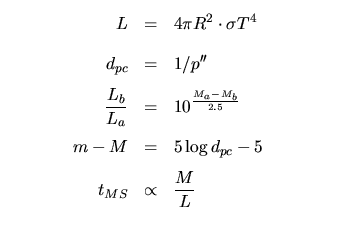 |
Binary Stars: | |
|---|---|
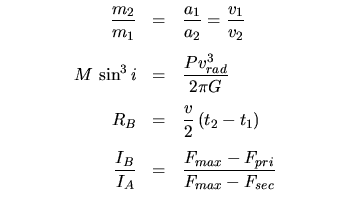 |
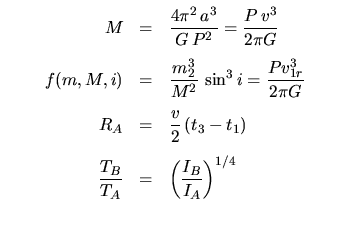 |
Note: you will need to know what an ellipse is, and what its semi-major axis and eccentricity are, and where its foci are.
Stellar Structure: | |
|---|---|
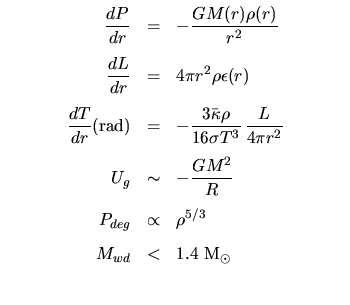 |
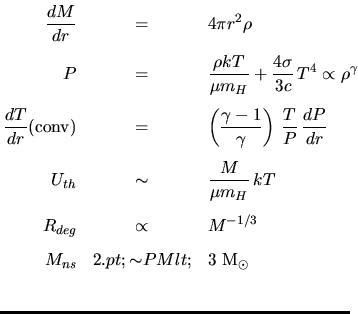 |
Atmospheres, Photospheres, & Thermodynamics: | |
|---|---|
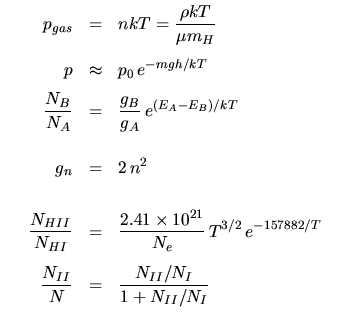 |
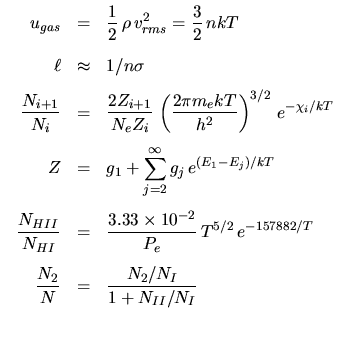 |
Dust, Interstellar Medium & Star Formation: | |
|---|---|
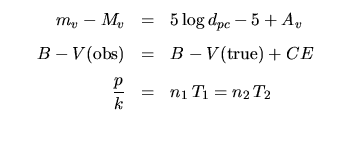 |
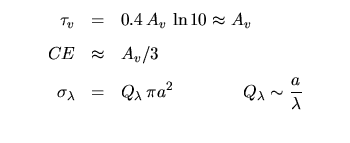 |
Sound Waves and Pulsating Stars: | |
|---|---|
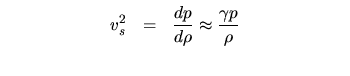 |
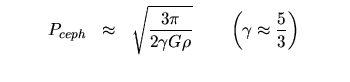 |
Relativity & Quantum Mechanics: | |
|---|---|
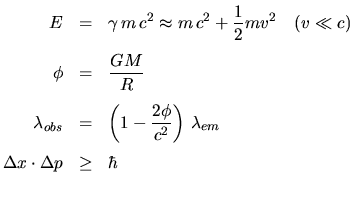 |
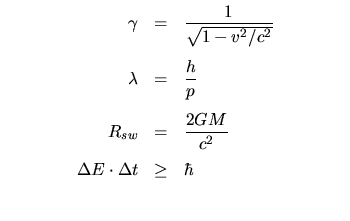 |
Galaxies, Quasars, and Clusters of Galaxies: | |
|---|---|
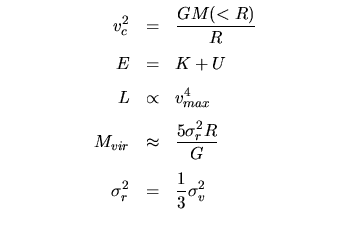 |
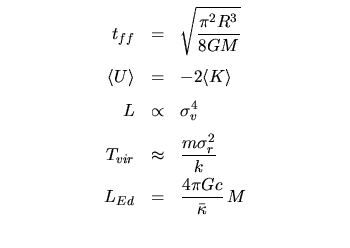 |
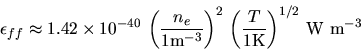
Cosmology: | |
|---|---|
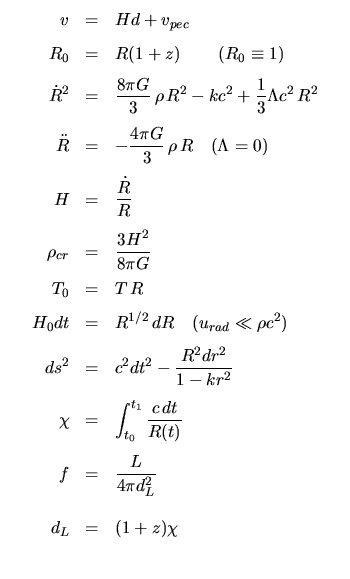 |
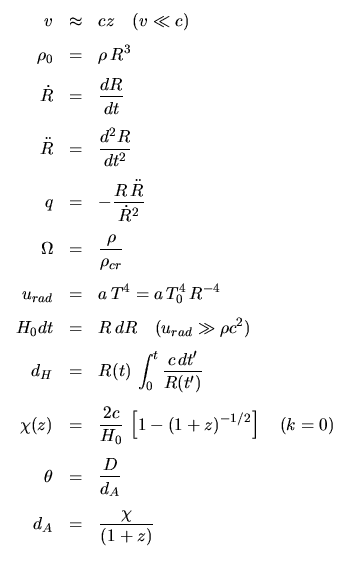 |
Important Energy Thresholds: | |
|---|---|
| Ionized Hydrogen | 13.6 eV |
| mass of electron | 511 KeV/c2 |
| mass of proton | 938 MeV/c2 |
| mass of W,Z | 90 GeV/c2 |
Solar Magnitudes: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mbol | MV | U - B | B - V | |
| Sun | +4.76 | +4.83 | +0.16 | +0.64 |
Characteristic Absolute Visual Magnitudes: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O and B stars | +0 | - | -6 | |
| Classical Cepheid | -0.5 | - | -6 | |
| Type II Cepheid | +0 | - | -3 | |
| RR Lyrae Variable | +0.5 | - | +1 | |
| Globular Cluster | -5 | - | -9 | |
| Spiral Galaxy | -15 | - | -21 | |
| Elliptical Galaxy | -9 | - | -23 | |
| Irregular Galaxy | -13 | - | -18 | |
| Type Ia Supernova | ~ | -20 | ||
| Type II Supernova | ~ | -18 | ||
Common Elements and Isotopes: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Key: massnumX) | 11H | 42He | 126C | 147N |
| 168O | 2010Ne | 3216S | 5626Fe | |
Solar Composition: | ||
|---|---|---|
X =
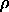 H / H /
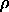
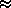 0.75 0.75
|
Y =
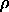 He / He /
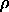
 0.23 0.23
|
Z =
 met / met /
 0.02 0.02
|
This document was generated using the LaTeX2HTML translator Version 98.1 (release) (February 19th, 1998)
Copyright © 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998 Nikos Drakos, Computer Based Learning Unit, University of Leeds.
The translation was initiated on 4/26/1999